Zeta interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 2
Zeta
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 5 months
Topics: Data Structure(Array, String, Linked list, Stack, Queue, Tree, Heap), Algorithm (Searching, Sliding Window, Greedy, Dynamic), OOPS(Inheritance, Polymorphism, Encapsulation, Abstraction ), High Level System Design - (AWS Solution Architect Associate Certification), Low Level System Design( Design patterns - Singleton, Factory, Strategy, Class Diagram, Activity Diagram ).
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice at least 10 problem on each topic of DS and Algo from easy to hard.
Tip 2 : Cover all the topics with basic operation and with their time complexity.
Tip 3 : Read about System Design approach - it is equally important when you have 2+ year of experience.
Application process
Where: Linkedin
Eligibility: No Criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some certification in the resume.
Tip 2 : Mention the proper keyword as per the role you are applying.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date6 May 2022
Coding problem2
HR called for the interview availability. This round was set up during day time. This round was elimination round and based on DS and Algorithm problem.Overall the interview experience was really great. I was able to provide optimised solution for both DS Algo problem.
1. Minimum Sum Subarray
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies


You have been given an array/list 'ARR' consisting of 'N' integers.
Your task is to find the minimum possible sum of a non-empty subarray of this array.
Note:
An array 'C' is a subarray of array 'D' if it can be obtained by deletion of several elements(possibly zero) from the beginning and the end of array 'D'. For example, all the non-empty subarrays of array [1,2,3] are [1], [2], [3], [1,2], [2,3], [1,2,3].
For Example :
Input: 'N' = 3 , 'ARR' = [-5, 10 , 0]
Output: -5
Explanation : The non empty subarrays possible for 'ARR' are [-5], [10], [0], [-5, 10], [-5, 0], [10, 0], [-5, 10, 0]. The sum of the elements of these subarrays are -5, 10, 0, 5, -5, 10, 5. The minimum of them is -5.
Problem approach
Step: This problem was based on sliding window concepts:
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
int i =0;
int j = 0;
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while(j= target){
ans = Math.min(ans, j-i+1);
sum -= nums[i];
i++;
}
j++;
}
return ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : ans;
}
2. Count Ways To Reach The N-th Stairs
Moderate
30m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a number of stairs. Initially, you are at the 0th stair, and you need to reach the Nth stair.
Each time, you can climb either one step or two steps.
You are supposed to return the number of distinct ways you can climb from the 0th step to the Nth step.
Note:
Note: Since the number of ways can be very large, return the answer modulo 1000000007.
Example :
N=3
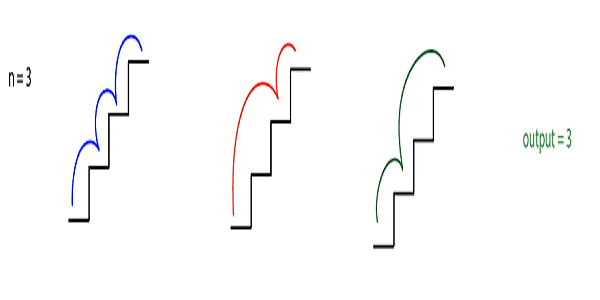
We can climb one step at a time i.e. {(0, 1) ,(1, 2),(2,3)} or we can climb the first two-step and then one step i.e. {(0,2),(1, 3)} or we can climb first one step and then two step i.e. {(0,1), (1,3)}.
Problem approach
Solution:
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int second = 0;
int first = 1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
int temp = first+second;
second = first;
first = temp;
}
return first;
}
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date13 May 2022
Coding problem2
This round was set up during day time. This round was elimination round and based on DS and Algorithm problem.Overall the interview experience was really great. I was able to provide optimised solution for both DS Algo problem.
1. Zigzag Binary Tree Traversal
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a ‘Binary Tree’.
Return the level-order traversal of the Binary Tree.
Example:
Input: Consider the following Binary Tree:

Output:
Following is the level-order traversal of the given Binary Tree: [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 4]
Problem approach
Step: I used queue to use this problem. Over all time complexity for this problem was linear.
public List> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List> ans = new ArrayList();
if(root == null ) return ans;
Deque queue = new ArrayDeque();
int count = -1;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List list = new ArrayList();
int n = queue.size();
if(count == -1 ){
for(int i=0; i TreeNode node = queue.removeFirst();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null ) queue.addLast(node.left);
if(node.right != null ) queue.addLast(node.right);
}
}else{
for(int i=0; i TreeNode node = queue.removeLast();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.right != null ) queue.addFirst(node.right);
if(node.left != null ) queue.addFirst(node.left);
}
}
ans.add(list);
count = -count;
}
return ans;
}
2. Rotate array
Easy
25m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given an array 'arr' with 'n' elements, the task is to rotate the array to the left by 'k' steps, where 'k' is non-negative.
Example:
'arr '= [1,2,3,4,5]
'k' = 1 rotated array = [2,3,4,5,1]
'k' = 2 rotated array = [3,4,5,1,2]
'k' = 3 rotated array = [4,5,1,2,3] and so on.
Problem approach
Steps to solve the problem:
public void rotate(int[] arr, int k) {
int n = arr.length;
k = k%n;
reverse(arr, 0, n-1);
reverse(arr, 0, k-1);
reverse(arr, k, n-1);
}
public void reverse(int arr[], int start, int end){
while(start < end){
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date19 May 2022
Coding problem1
This round a system design round. Overall the interview experience was great. Interviewer was satisfied with the approach that I have given.
1. LRU Cache Implementation
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache to support the following operations:
1. get(key) - Return the value of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.
2. put(key, value), Insert the value in the cache if the key is not already present or update the value of the given key if the key is already present. When the cache reaches its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting the new item.
You will be given ‘Q’ queries. Each query will belong to one of these two types:
Type 0: for get(key) operation.
Type 1: for put(key, value) operation.
Note :
1. The cache is initialized with a capacity (the maximum number of unique keys it can hold at a time).
2. Access to an item or key is defined as a get or a put operation on the key. The least recently used key is the one with the oldest access time.
Problem approach
Steps to solve this problem:
class LRUCache {
Map nodeMap;
DoublyLinkedList doublyLinkedList;
int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
nodeMap = new HashMap();
doublyLinkedList = new DoublyLinkedList();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(nodeMap.containsKey(key)){
Node node = nodeMap.get(key);
doublyLinkedList.removeGiven(node);
doublyLinkedList.addFirst(node);
return node.val;
}
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(nodeMap.containsKey(key)){
Node node = nodeMap.get(key);
node.val = value;
doublyLinkedList.removeGiven(node);
doublyLinkedList.addFirst(node);
}else{
if(nodeMap.size() == capacity){
Node node = doublyLinkedList.getTail();
doublyLinkedList.removeLast();
nodeMap.remove(node.key);
}
Node node = new Node(key, value);
doublyLinkedList.addFirst(node);
nodeMap.put(key, node);
}
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList{
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public DoublyLinkedList(){
head = null;
tail = null;
}
public Node getHead(){
return head;
}
public Node getTail(){
return tail;
}
public void addFirst(Node node){
node.prev = null;
node.next = null;
if(head == null ){
head = node;
tail = node;
}else{
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
}
public void removeLast(){
if(tail == null ) return;
if(tail.prev == null ) {
tail = null;
head = null;
return;
}
tail.prev.next = null;
tail = tail.prev;
}
public void removeGiven(Node node){
if(node.prev == null ){
head = node.next;
if(node.next == null) tail = null;
else node.next.prev = null;
}else{
node.prev.next = node.next;
if(node.next == null) tail = node.prev;
else node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
}
}
class Node{
int val;
int key;
Node prev;
Node next;
public Node(int key, int val){
this.key = key;
this.val =val;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 2
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Zeta
5172 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Zeta
2307 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Zeta
3381 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
2 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Zeta
159 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 2
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Walmart
29739 views
8 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
6728 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
6 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
5225 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





