Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Averages Of Levels In Binary Tree
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 15m
3 upvotes
Asked in companies


Problem statement
You are given an arbitrary binary tree consisting of 'N' nodes numbered from 1 to 'N', and each node is associated with some positive integer value. Your task is to find the average of all the levels in the given tree, i.e you have to find the average of all the node values present on the level, for each level.
Two nodes of a tree are said to be at the same level ‘K’ if both of them are at equal distance( 'K' ) from the 'ROOT' node. The 'ROOT' node is said to be at level 0.
Note :
1. Two nodes may have the same value associated with it.
2. Average of any level is computed as the sum of the values of all the nodes at that level divided by the number of nodes at that level.
3. You will be given the 'ROOT' node of the binary tree.
4. You need to print the floor value for each average. For example, if the average of node values at some level is 3.5 then you have to print 3.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line of the input contains a single integer 'T', representing the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer 'N' denoting the number of nodes in the tree.
The second line contains the values of the nodes of the tree in the level order form ( -1 for NULL node)
Consider the binary tree
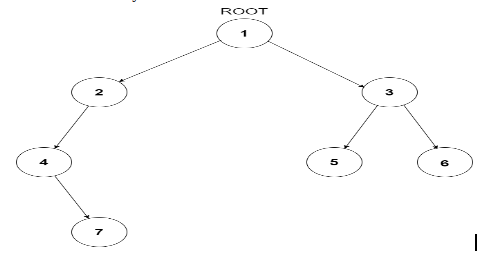
The input of the tree depicted in the image above will be like :
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first non-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second non-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
For each test case, print 'X' space-separated values where 'X' is the number of levels in the given binary tree, where the 'i'th integer will denote the average of node values at the 'ith level.
You don't need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 10^2
1 <= N <= 10^4
1 <= data <= 10^9
Time Limit : 1 sec
Sample Input 1 :
1
3
1 2 3 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1 :
1 2
Explanation For Sample Input 1 :
This is the tree as described in the input here l0 denotes level-0 and l1 denotes level-1. Now the average of nodes at level 0 is (1/1), which is 1. And the average at level 1 is ((2+3)/2) which is 2.50
Sample Input 2 :
1
4
5 6 7 8 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2 :
5 6 8
Explanation For Sample Input 2 :
This is the tree as described in the input here l0 denotes level-0 and l1 denotes level-1 and l2 denotes level-2. Now the average of nodes at level 0 is (5/1), which is 5. And the average at level 1 is ((6+7)/2) which is 6.50, and the average at level-2 is (8/1) which is 8.
Hint
Hint 1
Do the level - order traversal.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Level-Order Traversal
The fact that we need to find the average at each level clearly indicates the need to do a level order traversal of the given tree. So we will run a BFS using a FIFO queue and compute the average at each level.
Here is the algorithm :
- Create a queue (say, ‘Q’) to maintain a queue and an array (say, ‘ANS’) to store the result.
- Now run a loop till the queue is not empty:
- Before starting with the nested loop, store the size (say, ‘X’) of the queue, so as to maintain a count of the number of nodes in the level being traversed.
- Run a nested loop to pop ‘X’ nodes from the queue and while popping a node keep a track of the ‘SUM’ of all the node values popped. And after popping a node from the queue insert all its child nodes into the queue.
- After coming out from the nested loop calculate ‘SUM’/(no. Of nodes = ‘X’) and add it into the 'ANS' array and then reinitialize the ‘SUM’ variable to 0.
- Finally, return the ‘ANS’ array which contains the average of each level.
Example :
- Let us consider an example to understand the working of the algorithm. Consider the tree {1,2,3}:
- At the start insert root node(1). So, the queue contains (1).
- Now we calculate the value of variable ‘X’ which will be 1 in our case.
- Now pop ‘X’( X = 1) nodes from the queue and maintain the sum. So in our case sum will be 1. And then nodes 2 and 3(child of 1) will be pushed into the queue. So now the queue will contain {2,3}, and ('SUM'/'COUNT' i.e. 1/1 will be inserted into the ‘ANS’ array) and then reinitialize the ‘SUM’ and ‘COUNT’ variable to 0.
- Again when we repeat step 1, nodes 2 and 3 will be popped and the ‘COUNT’ will become 2 and ‘SUM’ becomes 5, then we will insert ‘SUM’/'COUNT' (i.e. 5/2) in the ‘ANS' array and will then come out of the loop.
- Now the ‘ANS’ array contains (1,2), so it will be returned as the answer.
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the tree.
We traverse all the nodes of the binary tree to find the average. Hence, the overall time complexity will be O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the tree.
We use a queue to store nodes present at a level which in the worst case can be equal to ‘N’ / 2. In the case of a complete binary tree number of nodes present at each level is 2^'L' (where ‘L’ is the current level). If the tree has 2 levels then the last level will have 2^2 = 4 nodes and the total nodes will be 7 i.e. nodes at the last level is equal to ‘N’/2. Therefore, the overall space complexity will be O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Averages Of Levels In Binary Tree
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console
