Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 20m
Problem statement
You are given a binary tree with ‘N’ nodes.
Your task is to find the “Maximum Path Sum” for any path.
Note :
1. A ‘path’ is a sequence of adjacent pair nodes with an edge between them in the binary tree.
2. The ‘path’ doesn’t need to pass through the root.
3. The ‘path sum’ is the sum of the node’s data in that path.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases to be run.
The first line of each test case contains elements of the tree in the level order form. The line consists of values of nodes separated by a single space. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree is depicted in the below image.
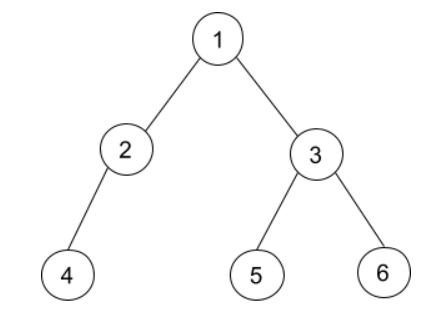
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the above image would be :
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = null (-1)
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Output Format :
For each test case, print an integer denoting the maximum path sum.
The output of each test case will be printed in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 2000
-5000 <= data <= 5000 and data != ‘-1’ (because -1 is used to mark the null nodes).
Where ‘N’ is the total number of nodes in the given binary tree, and ‘data’ is the value of the node of the binary tree.
Time Limit : 1sec
Sample Input 1 :
1
-4 -2 3 -1 -1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1 :
5
Explanation For Sample Input 1 :
The tree will be

The path marked in yellow is the maximum sum path.
Sample Input 2 :
1
-2 2 1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2 :
2
Explanation For Sample Input 2 :
The tree will be:

The maximum sum path will only contain one node and marked in yellow.
Hint
Hint 1
Try to form the recursive solution.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Recursive Approach
The idea here is to use the recursion. For each node, We can calculate the maximum path sum by keeping track of the following paths:
- Max path sum starting from Left child + Max Path sum starting from Right child + Node’s value.
- Max path sum starting from Left child + Node’s value
- Max path sum starting from Right child + Node’s value
- Node’s value
We then pick the maximum one among them. The root of every subtree will be going to return the maximum sum path having 0 or 1 child of the same.
Steps:
- Declare a variable named ans to store the final answer.
- Initialize it with INT_MIN.
- Call the function find and pass root, a sum that is initially 0, and ans.
- Return ans.
int find(root, sum, ans):
- If the root is NULL, then return 0.
- Call find again with the left of the root, and store its result into the variable leftSum.
- Again call the find function, but this time, pass the root’s right, ans store its result into the variable rightSum.
- Then try all four possible combinations:
- Update ans with max(ans, (leftSum + rightSum + root.data)).
- Update ans with max(ans, (leftSum + root.data)).
- Update ans with max(ans, (rightSum + root.data)).
- Update ans with max(ans, root.data).
- Return the max(root.data, max(leftSum, rightSum) + root.data).
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the Binary Tree.
We are using the recursive function and visiting each node exactly once. Hence, the overall time complexity will be O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the Binary Tree.
In the worst case, the recursive stack can increase up to a size of N. Hence, the space complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console




