Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Board Cutting
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 10m
Problem statement
You have been given a flat board of size M * N and you have to cut this board into M * N pieces each of size 1 * 1. To cut the board, you can make only horizontal and vertical cuts.
The cost of cutting horizontal cuts is given by array HORIZONTAL and that of cutting vertical cuts is given by array VERTICAL. The cost is multiplied by the number of segments cut to get the total cost.
Your task is to minimize the overall cost which is the sum of costs of all successive cuts.
For example :
For the board of size 3 * 2 given below, with horizontal = [2] and vertical = [1, 3], the minimum cost of cutting it is explained below:
1st cut: Horizontal cut with cost 3 cutting 1 segment. Cost = 3 * 1.
2nd cut: Vertical cut with cost 2 cutting 2 segments. Cost = 2 * 2.
3rd cut: Horizontal cut with cost 1 cutting 2 segments. Cost = 1 * 2.
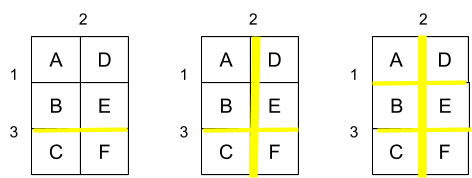
Above is the pictorial representation.
Cost = 3 + 4 + 2 = 9.
Note :
As the answer can be large, return your answer modulo 10^9 + 7.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases or queries to be run. Then, the T test cases follow.
The first line of each test case or query contains two space-separated integers 'M' and ‘N’ denoting the number of rows and columns in the board.
The second line contains ‘M-1’ single space-separated integers, representing the costs of cutting Horizontal edges.
The second line contains 'N-1' single space-separated integers, representing the costs of cutting Vertical edges.
For each test case, print an integer denoting the minimum possible cost modulo 10^9+7 in a separate line.
Note :
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 5
2 <= M <= 10^3
2 <= N <= 10^3
1 <= horizontal[i] <= 10^9
1 <= vertical[i] <= 10^9
Time limit: 1 sec
Sample input 1 :
1
2 2
5
2
Sample output 1 :
9
Explanation for sample input 1 :
The board of size 2 * 2 can be cut by cutting 1 segment Horizontally with cost 5, i.e. 5*1 and making the second cut vertically with cost 2 cutting 2 segments i.e. 2*2.
The final cost becomes 5 + 4 = 9.
Sample input 2 :
2
2 2
1
3
6 4
2 1 3 1 4
4 1 2
Sample output 2 :
5
42
Hint
Hint 1
Observe that in order to minimize the cost we need to cut minimum segments with the edge that costs the most.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Sorting
The idea is to solve the problem with a greedy approach. The total cost will be the sum of C1.S1 + C2.S2 + … C(M + N).S(M + N) where Ci is the cost of cutting a distinct edge and Si is the number of segments present when cutting that particular edge.
Declare two variables, one to store the count of horizontal segments, say ‘hori’ and second to store the count of vertical segments, say ‘verti’. Initialize both with 1.
Now, to achieve the minimum cost, we need to cut the edge with maximum cutting cost first to reduce the total cost, i.e. edge cost * the number of segments.
Here is the algorithm:
- Sort the two arrays ‘horizontal’ and ‘vertical’ in decreasing order.
- Initialize ‘cost’ to 0 which stores the final cost up to a point.
- Take all the edge costs one by one and keep on updating the cost:
- If the current maximum edge cost is horizontal, then, cost = cost + (maxEdgeCost * verti) as ‘verti’ is the number of vertical segments which will get cut.
- Increment ‘hori’ by one as the horizontal segment increases.
- Otherwise, if the maximum edge cost is vertical, then, cost = cost + (maxEdgeCost * hori) as ‘hori’ is the number of horizontal segments which will get cut.
- Increment ‘verti' by one as the vertical segment increases.
- If the current maximum edge cost is horizontal, then, cost = cost + (maxEdgeCost * verti) as ‘verti’ is the number of vertical segments which will get cut.
- Return the calculated ‘cost’.
Time Complexity
O(K*logK), where K is max(M, N) and M and N are the number of rows and columns of the given board.
We are sorting both the given arrays which takes O(NlogN + MlogM) complexity.
Space Complexity
O(1).
In the worst case, only constant extra space is used.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Board Cutting
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console


