Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Car Pooling
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 30m
Problem statement
You are working as a cab driver. Your car moves in a straight line and moves toward the forward direction only. Initially, you have ‘C’ empty seats for the passengers.
Now, you are given ‘N’ number of trips that you have to make. In each trip, you are given three integers ‘Num’, ‘pickPoint’, and ‘dropPoint’ denoting that there are ‘Num’ numbers of passengers standing at 'pickpoint’ and you have to drop them at 'droppoint’.
Your task is to find if it is possible to pick up and drop off all the passengers of all the given trips or not.
Note :You have a special type of car containing any number of seats.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line contains a single integer ‘T’, denoting the number of test cases.
Each test case’s first line contains ‘C’ and ‘N’, denoting the car’s capacity and the number of trips you have to make.
The next ‘N’ lines contain 3 integers, each denoting the number of passengers, pick up point, and drop point of the trip respectively.
For each test case, print “True” if possible to make the trip and “False” otherwise.
Print the output of each test case in a separated line.
You don’t need to print anything; It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 50
1 <= C <= 10^5
1 <= N <= 10^3
0 <= passengers <= 100
0 <= pickPoint, dropPoint <= 1000
Where ‘T’ is the number of test cases, ‘C’ is the car’s capacity, and “N’ is the number of trips you have to make.
Time limit: 1 sec.
Sample Input 1 :
2
3 2
2 1 5
3 5 7
4 2
2 1 5
3 3 7
Sample Output 1 :
True
False
Explanation Of Sample Input 1 :
Test Case 1 :
At point 1 :
We have 2 passengers. So, two seats will be filled.
Now Empty seats: 1
At point 5:
Two passengers descend from the car. So Empty seats = 3.
At the same time, 3 passengers ascend on the car. So Empty seats = 0.
At point 7:
All three passengers descend from the car. Now empty seats = 3.
So, it is possible to complete the trips, hence print True.
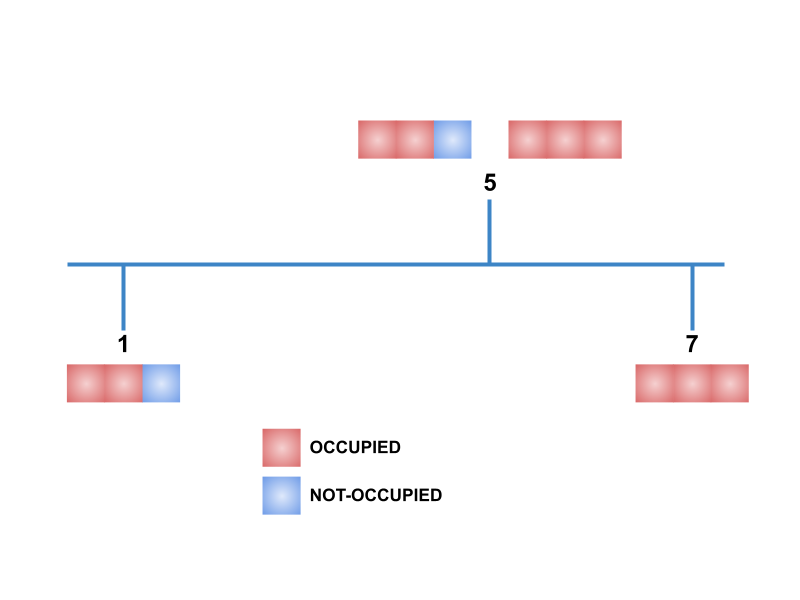
Test Case 2 :
The capacity of car: 4. At position 3, we have one seat empty but 3 passengers to pick, so this trip is not possible hence print False.
Sample Input 2 :
2
5 2
2 1 5
3 3 7
11 3
3 2 7
3 7 9
8 3 9
Sample Output 2 :
True
True
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Think of the number of passengers changed at any time.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Hash Map Implementation
The simple idea is that we will keep a record of the number of passengers changed at every time in a hash map ‘passengers’ where the key represents the time at which the number of passengers changed and the value at that key represents the count of passengers changed.
For Example- If we have trips = [ 2, 1,4 ], [ 2, 2,5 ] then at time = 1, no of passengers changed and increased by 2. So passengers[ 1 ] = 2. At time = 4, these passengers reach their destination so at time = 4, no of passengers get reduced by 2. So passengers[ 4 ] = -2.
Similarly passengers[ 2 ] = 2 and passengers[ 5 ] = -2.
In the hash map, we will increment the value at the pickup point of the ‘i-th’ trip and decrement the value at the drop point of the ‘i-th’ trip by the number of passengers in the ‘i-th’ trip.
As in the hash map, keys are stored in sorted order. So adding the values of this hash map will give the number of passengers at every key time. If no of the passengers exceeds the capacity of the car at any time, we will return false.
Algorithm
- Initialize a hash map ‘passengers’ that maps from integer to integer.
- Run a loop i: 0 to N - 1 to check every trip detail.
- Increment passengers[ trip[ i ][ 1 ] ] by trip[ i ][ 0 ].
- Decrement Passengers[ trip[ i ][ 2 ] ] by trip[ i ][ 0 ].
- Traverse through the hash map.
- Store the sum of values of the hash map in a variable ‘count’.
- If count > C( capacity ), return false.
- Return true.
Time Complexity
O( N*log(N) ), where ‘N’ is the number of trips.
We are storing every trip value in a hash map that will take O(N*log(N)) time and then iterating through the hash map that will cost O(N) time. So the overall time complexity is O(N) + O(N*log(N)) = O(N*log(N)).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of trips.
We are using a hash map to store every trip’s details, making space complexity O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Car Pooling
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



