Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Check if two trees are Mirror
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 15m
9 upvotes
Asked in companies



Problem statement
You are given two arbitrary binary trees consisting of N and M number of nodes respectively, your task is to check whether the two trees are mirror of each other or not.
Two trees are said to be mirror of each other, if
1. Roots of both the given trees are same.
2. Left subtree of the root of the first tree is the mirror of the right subtree of the root of the second tree.
3. Right subtree of the root of the first tree is the mirror of the left subtree of the root of the second tree.
For example,both the given trees are mirror image of each other:
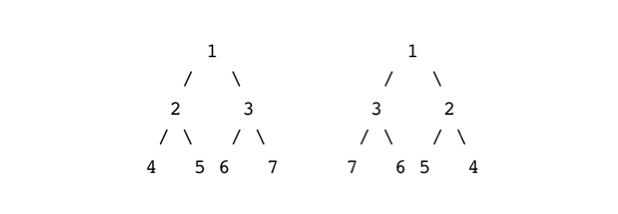
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ representing the number of test cases. Then the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains elements of the first tree in the level order form. The line consists of values of nodes separated by a single space. In case a node is null, we take -1 on its place.
The second line of each test case contains elements of the second tree in the level order form. The line consists of values of nodes separated by a single space. In case a node is null, we take -1 on its place.
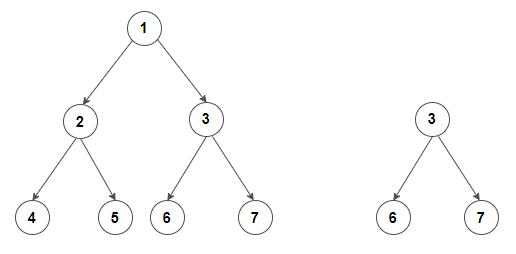
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be:

1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation:
Level 1:
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2:
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3:
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4:
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5:
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node(of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null(-1).
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
For each test case, the only line of output prints “true” if two trees are mirror of each other else prints “false”.
The output for each test case is in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 80
1 <= N, M <= 3000
-10^6 <= data <= 10^6 and data != -1
Where ‘T’ is the number of test cases, ‘N’ and ‘M’ are the number of nodes in the given binary trees’, and “data” is the value of the binary tree node.
Time Limit: 1sec
Sample Input 1:
2
9 8 -1 6 1 -1 -1 -1 -1
9 -1 8 1 6 -1 -1 -1 -1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
3 6 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1:
true
false
Explanation of Sample Input 1:

For the first test case, true gets printed as the second tree is the mirror image of the first tree.
For the second test case, false gets printed as both trees are not the mirror image of each other.
Sample Input 2:
2
9 8 -1 6 1 -1 -1 -1 -1
9 -1 8 1 6 -1 -1 -1 -1
26 10 3 4 6 -1 3 -1 30 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
10 4 6 -1 30 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2:
true
false
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Recursively check if the left subtree of the first tree is the mirror of the right subtree of the second subtree and vice versa.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Recursive Approach
Traverse the tree T in preorder fashion and treat every node of the given tree T as the root, treat it as a subtree and compare the corresponding subtree with the given subtree S for equality. For checking the equality, we can compare all the nodes of the two subtrees.
For two trees ‘S’ and ‘T’ to be mirror images, the following three conditions must be true:
- Their root node’s data must be the same.
- Left subtree of ‘S’ and the right subtree of ‘T’ are mirror.
- Right subtree of ‘S’ and the left subtree of ‘T’ are mirror.
Below is the algorithm:
- Check for base cases,
- If both trees are empty, return true.
- If only one tree is empty, return false.
- Check if the root of the first tree is equal to the root of the second tree or not. If not, return false.
- Recursively call left subtree of the first tree and right subtree of the second tree, and vice-versa.
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the given binary trees.
Since in the worst case (Skewed Trees), we might be visiting all the nodes of the binary tree. So, the time complexity will be O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the given binary trees.
We are using O(H) extra space for the call stack where ‘H’ is the height of the recursion tree, and height of a skewed binary tree could be ‘N’ in the worst case.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Check if two trees are Mirror
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console
