Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 25m
Problem statement
You are given arrays 'inOrder' and 'postOrder', which represent 'inorder' traversal and 'postorder' traversal of a 'Binary Tree' respectively.
Construct a 'Binary Tree' represented by the given arrays and return it's head.
Assume that the Binary Tree contains only unique elements.
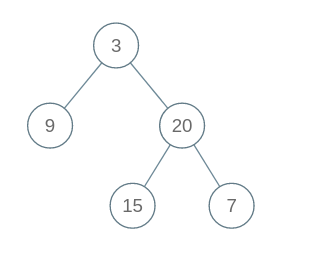
Input: 'inOrder' = [9, 3, 15, 20, 7], 'postOrder' = [9, 15, 7, 20, 3]
Output:
We get the following binary tree from Inorder and Postorder traversal:
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format
The first line of each test case contains an integer 'n' which represents the number of nodes in the Binary Tree.
The next line of each test case contains 'n' single space-separated integers, representing the Postorder traversal of the Binary Tree.
The next line of each test case contains 'n' single space-separated integers, representing the Inorder traversal of the Binary Tree.
Return the head of the binary tree constructed.
The level order traversal of the Binary Tree is printed.
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Sample Input 1:
7
4 5 2 6 7 3 1
4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Output on console:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
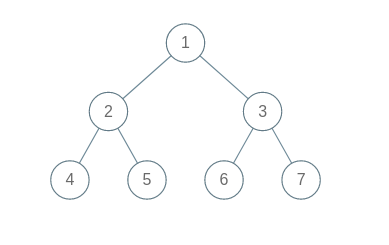
Explanation for Sample Output 1:
We get the following Binary Tree from the given Inorder and Postorder traversal:
Sample Input 2:
6
2 9 3 6 10 5
2 6 3 9 5 10
Sample Output 2:
5 6 10 2 3 9
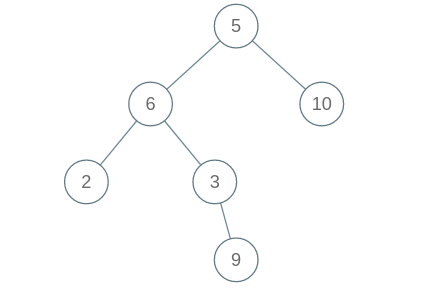
Explanation for Sample Output 2:
We get the following Binary Tree from the given Inorder and Postorder traversal:
Expected Time Complexity:
Try to solve this in O(n).
Constraints :
1 <= 'n' <= 10000
1 <= 'inOrder[i]' , ‘postOrder[i]’ <= 100000
Time Limit: 1 second
Hint
Hint 1
Think of the Depth First Search approach.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Depth First Search
To solve this problem, first, we take the last element in the ‘POST_ORDER’ array/list as the root because we know post-order traversal is like the first traverse of the left subtree nodes and then the right subtree node at the end traverse root. Hence the root is present as the last element of post-order traversal. Then we find the position of the root data in the ‘IN_ORDER’ array/list. Let’s assume at the ‘Kth’ index we find the root data in the ‘IN_ORDER’ array/list. Then we locate the range for the left subtree and right subtree and recursively call the function for finding the left subtree and the right subtree.
For example:
First, we select the last element of the ‘POST_ORDER’ array/list as a root. Then we find the 3 in the ‘IN_ORDER’ array/list. All the elements to the left of 3 in the ‘IN_ORDER’ array/list will be part of the left subtree and all the elements to the right of 3 in ‘IN_ORDER’ will be part of the right subtree as highlighted above.
The number of elements on the left side of the ‘IN_ORDER’ array/list is 1 in our example. So, 1 element in the ‘POST_ORDER’ array/list from starting will be part of the left subtree and the next elements less than the root index will be part of the right subtree.
Here is the algorithm:
- We declare four variables ‘POST_START’, ‘POST_END’, ‘IN_START’, and ‘IN_END’ representing the starting and ending position of ‘POST_ORDER’ and ‘IN_ORDER’ respectively.
- Base case: If ‘POST_START’ is greater than ‘POST_END’ or ‘IN_START’ is greater than ‘IN_END’:
- Return ‘NULL’.
- We declare a variable ‘ROOT_VAL’ which is equal to ‘POST_ORDER[‘POST_END’]’.
- We make a Binary Tree node using ‘ROOT_VAL’ as data of the node.
- We declare a variable ‘ROOT_INDEX’ in which we store the index of root value that is present in the ‘IN_ORDER’ array/list.
- We run a loop for ‘i’ = ‘IN_START’ to ‘IN_END’:
- If ‘ROOT_VAL’ is equal to ‘IN_ORDER[i]’:
- ‘ROOT_INDEX’ is equal to ‘i’.
- Break.
- If ‘ROOT_VAL’ is equal to ‘IN_ORDER[i]’:
- Now, the left subtree ‘IN_END’ is ‘ROOT_INDEX’ - 1 and ‘POST_END’ is ‘POST_START’ + ROOT_INDEX’ - 1 - ‘IN_START’.
- The right subtree ‘IN_START’ is ‘ROOT_INDEX’ + 1 and ‘POST_START’ is ‘POST_START’ + ‘ROOT_INDEX’ - ‘IN_START’ and ‘POST_END’ is ‘POST_START’ - 1.
- Now, we use recursion for finding the left subtree and the right subtree.
- Finally, we return the ‘ROOT’ of the Binary Tree.
Time Complexity
O(N) where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the Binary Tree.
Because we are traversing the ‘POST_ORDER’ array/list and ‘IN_ORDER’ array/list only once. Hence the time complexity is O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N) where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the Binary Tree.
O(N) different function calls are stored in the stack space. So the space complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console




