Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Construct BST from Level Order
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 15m
28 upvotes
Asked in companies



Problem statement
You have been given an array ‘levelOrder’ consisting of ‘N’ elements. The array represents the level order traversal of a Binary Search Tree(BST). You need to construct the BST from this level order traversal.
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure that has the following properties -
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
For Example:
For the given level order traversal: 5 3 6 2 4 7
The BST will be:
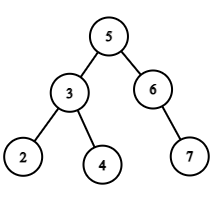
The Inorder Traversal of this BST is 2 3 4 5 6 7.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases. Then each test case follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer ‘N’ denoting the length of the array.
The second line of each test case contains ‘N’ single space-separated integers denoting the elements of the array.
For each test case, print the inorder traversal of the BST.
The inorder traversal of a binary tree is the traversal method in which for any node its left subtree is visited first, then the node itself, and then the right subtree.
Print the output of each test case in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 10^5
0 <= levelOrder[i] <= 10^5
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
2
7
15 10 20 8 12 16 25
3
2 1 3
Sample Output 1:
8 10 12 15 16 20 25
1 2 3
Explanation of Sample Input 1:
Test Case 1: For the given level order traversal the BST can be represented as follows
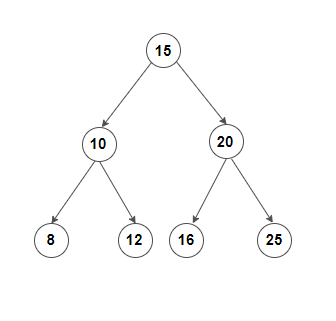
The inorder traversal of this BST is 8 10 12 15 16 20 25.
Test Case 2: For the given level order traversal the BST can be represented as follows
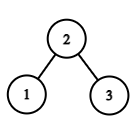
The inorder traversal of this BST is 1 2 3
Sample Input 2:
2
2
10 5
1
20
Sample Output 2:
5 10
20
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Think of finding the position for every number by recursively traversing the tree.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Using Recursion
The basic idea is that for every number we will find its position in BST using recursion.
Algorithm
- Let “insertNode” be the recursive function that takes ‘root’ of tree(initially NULL) and the element to be added in BST as input parameters and insert the given element to the BST.
- Traverse the given array using a variable ‘i’ and insert each element into BST using “insertNode” function.
- Now, the “insertNode” function will work as follows:
- If the root is NULL, then insert the element at the root position.
- Else if the data of the root is greater than the element.
- Insert element to the left subtree by recursively calling “insertNode” for the left child of the root.
- Else if the data of the root is smaller than the element.
- Insert element to the right subtree by recursively calling “insertNode” for the right child of the root.
- Return ‘root’
Time Complexity
O(N^2), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the Binary Search Tree.
In the worst case(skewed trees), we are traversing the whole BST while inserting each element. Hence, the time complexity is O(N^2).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the Binary Search Tree.
In the worst case (skewed trees), all the nodes of the BST will be in the recursion stack. Therefore the space complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Construct BST from Level Order
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
