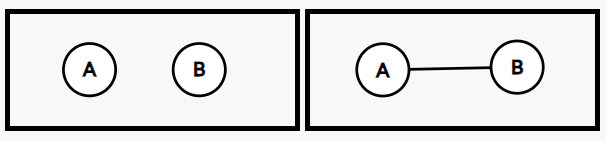
To determine the total number of edges possible in a graph with 'N' vertices, we can use the combination formula. Each edge requires two vertices so we can choose any two vertices from the 'N' vertices. Therefore, the total number of edges possible, denoted as 'E', is given by the formula E = (N * (N-1)) / 2.
Now, when counting the total number of graphs, we can consider that each edge in the graph may either exist or not exist. This gives us two options for each edge. Since there are 'E' edges, the total number of possible combinations of edge choices is 2^E. This represents all the different possible graphs that can be formed.