Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Critical Connection
Hard
0/120
Average time to solve is 60m
Problem statement
You are given a network with ‘N’ system nodes [0 to N - 1] and ‘M’ connection. Your task is to find out all critical connections in a given network.
Note: A connection between node ‘u’ and ‘v’ is said to be a critical connection, if after removal of a connection ‘u’ - ‘v’, there is no connection between node ‘u’ and ‘v’ and the network goes down.
For example:
For given N = 4, M = 4,
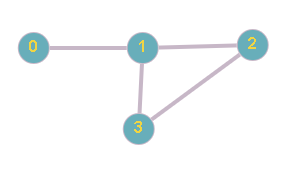
The connection between system node 0 and 1 is a critical connection.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains one positive integer ‘T’, denoting the number of test cases, then ‘T’ test case follow
The first line of each test case contains two integers ‘N’ and ‘M’, denoting the number of system nodes and the number of connections.
The next ‘M’ line contains two space-separated integers ’u’ and ‘v’, denoting the connection between ‘u’ and ‘v’.
The first line of each test case contains one integer ‘X’, denoting the number of critical connections.
The next ‘X’ lines contain two space-separated integers ’u’ and ‘v’, denoting critical connection between ‘u’ and ‘v’and ‘u’ is smaller than ‘v’.
The output of each test case will be printed on a separate line.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 5
1 <= N, M <= 10 ^ 6
0 <= u, v <= N - 1
There are no repeated connections.
Time Limit: 1 sec.
Sample Input 1:
2
4 4
0 1
1 2
1 3
2 3
6 6
0 1
1 2
1 3
3 4
4 5
0 4
Sample Output 1:
1
0 1
2
1 2
4 5
Explanation of Sample Output1:
In the first test case, the given network looks like this:

The only connection between nodes 0 and 1 is critical. So, the number of critical connections is 1.
In the second test case, the given network looks like this:
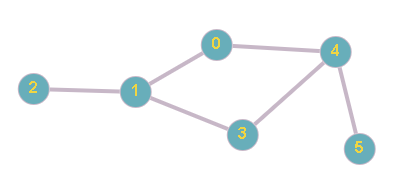
The connection between nodes 1, 2, and 4, 5 is a critical connection. So, there are 2 critical connections. If anyone's failure makes the network go down
Sample Input 2:
2
5 6
0 1
1 3
2 1
2 2
2 4
3 3
5 3
0 1
2 0
4 3
Sample Output 2:
4
0 1
1 2
1 3
2 4
3
0 1
0 2
3 4
Hint
Hint 1
Can you take the help of dfs tree?
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Bridge in a graph
If we observe carefully the critical connection is a similar bridge in a graph(edge whose removal increases the number of components in a graph).
The idea is to do Depth first search(DFS) traversal of the given graph. In DFS tree an edge (‘u’, ‘ v’) (‘u’ is parent of ‘v’ in DFS tree) is bridge if there does not exist any other alternative to reach ‘u’ or an ancestor of ‘u’ from subtree rooted with ‘v’.
In order to implement the above thought, we will maintain two arrays :
- low[] : the value low[v] indicates earliest visited vertex reachable from subtree rooted with v.
- Disc[]: the value of disc[u] indicates the discovery time of node ‘u’.
- The condition for an edge (u, v) to be a bridge is, “low[v] > disc[u]”.
The steps are as follows :
We will use following variables :
- timer, to keep track of discovery time.
- ‘disc’ array, the value of disc[u] indicates the discovery time of node ‘u’.
- ‘low’ array, the value low[v] indicates earliest visited vertex reachable from subtree rooted with v.
- visited array, mark whether node ’i’ is visited or not.
- Array of list, to construct graph.
Let ‘criticalConnection(n, ‘connections’)’ be the function that returns all the critical connections in a network, where ‘n’ is the number of nodes in a given network and ‘connections’ contain all connections.
- Take a variable ‘timer’, Initialize ‘timer’ to 0.
- Take an array ‘disc’ of length ‘n’.
- Take an array ‘visited’ of length.
- Take an array ‘low’ of length.
- Take a variable ‘m’ and initialize it with the size of connections array.
- Run a loop from 0 to ‘m’:
- Take a variable ‘u’ and store the first element of connections[i].
- Take a variable ‘v’ and store the second element of connections[i].
- Push ‘u’ in graph[v].
- Push ‘v’ in graph[u].
- Take an array ‘ans’ to store the critical connections.
- Run a loop from 0 to ‘n’:
- Initialize disc[i] with 0.
- Initialize low[i] with large value.
- Initialize visited[i] with 0.
- Make a function dfs(start, ‘ans’, parent, ‘disc’, ‘low’, ‘visited’, ‘graph’, ‘timer’) , to find all the critical connection:
- Run a loop from 0 to ‘n’ - 1
- If visited[i] is equal to 0
- Call dfs(start, ‘ans’, parent, ‘disc’, ‘low’, ‘visited’, ‘graph’, ‘timer’) function
- Return ‘ans’ array.
- Run a loop from 0 to ‘n’ - 1
Description of ‘dfs(‘start(s)’, ‘ans’, parent(p),‘disc’, ‘low’, ‘visited’, ‘graph’, ‘timer’)’ function
This utility function finds all the critical connections in a network.
- Mark ‘visited[s]’ equal to 1.
- Increment the ‘timer’ by 1.
- Store the ‘timer’ in ‘disc[s]’ and ‘low[s]’.
- Run a loop from 0 to size of graph[s] array ( number of nodes adjacent to the node ‘s’)
- Take a variable ‘adj’ and initialize it with graph[s][i].
- Check if this adjacent node ‘adj’ is visited or not, if visited:
- Recursively call dfs(‘adj’, ans, ‘s’).
- Update ‘low[s]’ equal to min of ( low[adj]’ and ‘low[s]’).
- If ‘low[adj]’ is greater than ‘disc’ of ‘s’, this is a critical connection store in ‘ans’ array.
- Take a temporary array ‘temp’.
- Push min of ‘s’ and ‘adj’ in temp.
- Push max of ‘s’ and ‘adj’ in temp.
- Else if ‘adj’ is not the parent of ‘s’ i.e ‘p’:
- Update ‘low[s]’ as minimum of ‘low[adj]’ and ‘low[s]’.
Time Complexity
O(M + N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes and ‘M’ is the number of connections.
We are using the standard ‘dfs’ function that takes O(N + M). Hence, the overall time complexity is O(N + M).
Space Complexity
O(M + N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes and ‘M’ is the number of connections.
Mainly, We are using space in creating a graph, which takes O(N + M) space, visited array, which takes O(N) space, ‘low’ array which takes O(N) space, ‘disc’ array which takes O(N) space. Hence, the overall space complexity is O(N + M) + 3 * O(N) = O(N + M).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Critical Connection
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console




