Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Deepest Left
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 15m
11 upvotes
Asked in companies


Problem statement
You are given a binary tree having ‘N’ number of nodes. Your task is to find the deepest leaf node in the given input tree.
Note:
The deepest leaf node is the leaf node which will be the left child of some node and will be at the maximum level in the tree.
If there are multiple deepest left leaf nodes, return the node with maximum value.
Note :
1. A binary tree is a tree in which each node can have at most two children.
2. The given tree will be non-empty i.e. the number of non-NULL nodes will always be greater than or equal to 1.
3. Multiple nodes in the tree can have the same values, all values in the tree will be positive.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’, which denotes the number of test cases. Then each test case follows.
The first line of every test case contains elements of the Binary Tree in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For Example :
Consider the binary tree:
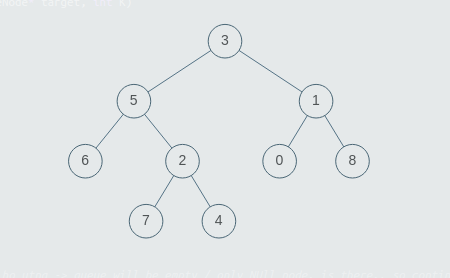
The input for the tree depicted in the above image would be :
3
5 1
6 2 0 8
-1 -1 7 4 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1 -1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 3
Level 2 :
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 1
Level 3 :
Left child of 5 = 6
Right child of 5 = 2
Left child of 1 = 0
Right child of 1 = 8
Level 4 :
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null(-1)
Left child of 2 = 7
Right child of 2 = 4
Left child of 0 = null (-1)
Right child of 0 = null (-1)
Left child of 8 = null (-1)
Right child of 8 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Output format :
For each test case, print the deepest leaf node’s data which is the left child of some node.
The output of each test case should be printed in a separate line.
Note:
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 5
1 <= N <= 3 * (10 ^ 3)
1 <= nodeVal <= 10 ^ 9
Time Limit: 1 sec.
Sample Input 1 :
2
3 5 1 6 2 0 8 -1 -1 7 4 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
1 2 3 4 5 -1 -1 6 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1 :
7
6
Explanation for Sample Input 1 :

Test Case 1 :
The deepest left leaf node is 7 as the level at which node with value 7 is present is 4 and is a left child of the node with value 2.
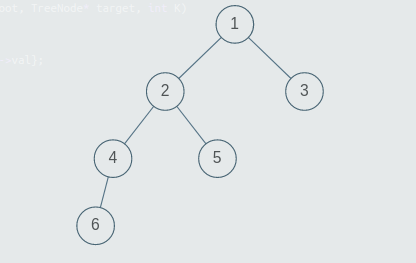
Test Case 2 :
The deepest left leaf node is 6 as the level at which node with value 6 is present is 4 and is a left child of the node with value 4.
Sample Input 2 :
2
5 2 3 8 1 -1 -1 7 9 -1 -1 5 6 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
1 5 7 -1 -1 6 3 9 8 -1 -1 -1 -1 13 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2 :
5
13
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Think of using Breadth First Search.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Breadth First
The idea is to traverse the tree iteratively and whenever a left tree node is pushed into the queue, check if it is a leaf node, if it’s a leaf node, then update the result. Since we go level by level, the last stored leaf node is the deepest one.
Approach:
- First, check if the root is null or not.
- Make a queue for breadth-first search.
- Initialize a variable of int type say ‘result’ to 0, ‘maxLevel’ to 0, ‘level’ to 1.
- Push the root inside the queue.
- Make an iteration till the queue does not become empty.
- Store the size of the queue in a variable, say ‘si’.
- Iterate till size does not become 0.
- Store the queue’s front element in a variable, say ‘temp’, and pop the element from the queue.
- Check if there existed the left element of ‘temp’ in the tree or not.
- If a left element of ‘temp’ exists:
- Push temp’s left into the queue.
- If temp’s left node is the leaf node then:
- Check if temp’s left level is greater than the ‘maxLevel’ then store the temp’s left’s data in the variable ‘result’ and update ‘maxLevel with the level of temp’s left’s level.
- Else, if temp’s left’s level is already reached level then store the maximum element in ‘result’
- If a right element of ‘temp’ exists:
- Push temp’s right into the queue.
- If a left element of ‘temp’ exists:
- Increment ‘level’.
- Update ‘maxLevel’.
- Return ‘result’ to the function.
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the given tree.
As we are traversing each node only once. Therefore, the overall time complexity will be O(N).
Space Complexity
O(X), where ‘X’ is the maximum number of nodes at a level in the given tree.
As we are using a queue for depth first search and storing the nodes into the queue. Therefore, space complexity will be O(X).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Deepest Left
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
