Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Depth of BST
Moderate
0/80
1 upvote
Asked in company

Problem statement
You are given an array ‘ARR’ having ‘N’ elements ranging from 1 to ‘N’.Each number appears in the array only once. Your task is to find the maximum depth of the Binary Search Tree formed if these values are inserted into the tree in the given order.
For ExampleIf 'ARR' is [2,1,4,3] ,the formed tree will be:
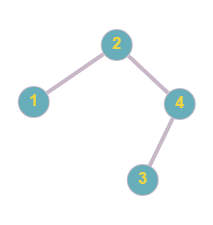
The maximum depth of the tree is 3. Hence the answer is 3.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line of the input contains an integer, 'T,’ denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer, 'N,’ denoting the number of elements in ‘ARR’.
The next line of each test case has ‘N’ integers corresponding to the elements of 'ARR’.
For each test case, return a single integer corresponding to the maximum depth of the BST.
You do not need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 10^5
1 <= 'ARR'[i] <= N
Time limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
2
4
2 1 4 3
5
4 3 2 5 1
Sample Output 1:
3
4
Explanation of sample input 1:
For the first test case, the possible subsets are:
The BST formed by the given array is:

So the maximum depth of the BST is 3. Hence the answer is 3.
For the second test case, the possible subsets are:
The BST formed by the given array is:
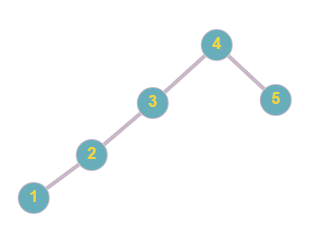
So the maximum depth of the BST is 3. Hence the answer is 4.
Sample Input 2:
2
3
2 1 3
4
1 2 3 4
Sample Output 2:
2
4
Hint
Hint 1
Can you find the depth of each value in the formed BST?
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Using Ordered Set
In this approach, we will prepare an array 'DEPTH' to store the depth of all values in the BST.
We will store the values in sorted order in an ordered Set as insertion, deletion, and searching takes O(logN) time. We will iterate through all values and search for the value 'VAL' in the set whose value is just greater than the current value and set the depth of the current value as the depth of 'VAL' + 1, and we will also store the maximum depth in a variable.
Algorithm:
- Declare an integer 'ANS' to store the maximum depth and initialize it with 0.
- Declare an array 'DEPTH' of size 'N'+1 to store the depth of all values.
- Declare an ordered set 'VALUES' to store the values in sorted order.
- Set 'DEPTH' of 'ARR'[0] as 1.(Root Node of BST)
- Insert 'ARR'[0] into 'VALUES'.
- For each index IDX in range 1 to 'N'-1, do the following:
- Set 'VAL' as the value in an ordered set whose value is just greater than V[i].
- If no such value exists , set 'VAL' as the maximum value present in the ordered set.
- Set 'DEPTH'[ 'ARR'[IDX] ] as depth of 'VAL' +1.
- Set 'ANS' as the maximum of 'ANS' and 'DEPTH'[ 'ARR'[IDX] ].
- Insert 'ARR'[IDX] into 'VALUES'.
- Return 'ANS'.
Time Complexity
O(N*log(N)), where ‘N’ is the number of elements in 'ARR'.
In this approach, we are iterating over all array elements and inserting the values in an ordered set that takes log(N) time. So the total time taken is N*log(N). Hence the overall time complexity is O(N*log(N)).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of elements in 'ARR'.
In this approach, we are using an array of size N to store depths and an ordered set of size N. Hence the overall space complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Depth of BST
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
