Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Detect Cycle in an Undirected Graph
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 32m
115 upvotes
Asked in companies


Problem statement
Given an undirected graph of 'V' vertices and 'E' edges. Return true if the graph contains a cycle or not, else return false.
Note:
There are no self-loops(an edge connecting the vertex to itself) in the given graph.
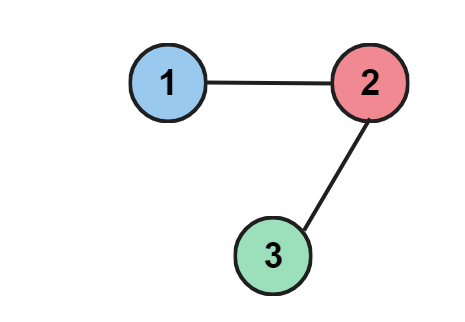
Given N=3, M =2, and edges are (1, 2) and (2, 3), with nodes 1, 2, and 3.
We return false because the given graph does not have any cycle.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first input line will contain two integers, 'V', and 'E', separated by a single space.
From the second line onwards, the following 'E' lines will denote the edges of the graphs.
Every edge is defined by two single space-separated integers 'a' and 'b', which signifies an edge between vertice 'a' and 'b'.
The single line contains a string, "True" if a cycle exists, else "False".
4 4
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 0
True
From node 0, we can reach 0 again by following this sequence of nodes in the path: 0,1,2,3,0.
Similarly, from any of the nodes, we can reach again to that node by following a path. The graph in itself is a cycle.
5 3
0 1
1 2
3 4
False
Constraints:
1 <= V <= 10^5
0 <= E <= 2 * 10^5
0 <= u,v < V
Time Limit: 1sec
Hint
Hint 1
Does BFS help?
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
BFS
Using Breadth First Search
1. We will take the input number of vertices and edges in variables in V and E resp.
2. Create a adjacency list by taking input of E number of edges.
3. Call function detectCycle() which will return true or false if detectCycle() returns true print "True" else "False".
4. Create a visited array to track visited nodes of a graph.
5. To handle disconnected graph run a loop over V number of vertices.
6. If a node is not visited call function checkForCycle() where we create a parent vector to track parent of each node.
7. Mark the node as visited. push node inside queue with -1 as parent because its starting node.
8. Visit each neighboring node of source node if it is not visited push it in the queue.
9. If a neighboring node is visited and not a parent of node return true.
10. Once the queue becomes empty return false because we haven't been able to find a cycle.
Time Complexity
O(V + E), where ‘V’ is the number of vertices in the input graph, and ‘E’ is the number of edges in the input graph.
Space Complexity
O(V), where ‘V’ is the number of vertices in the input graph.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Detect Cycle in an Undirected Graph
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
