Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Encode N-ary tree to binary tree.
Hard
0/120
Average time to solve is 45m
Problem statement
You have been given an N-ary tree ‘N’ nodes with node ‘1’ as head of the tree. Encode the above N-ary tree into a binary tree such that if only the encoded binary tree was given to you, you could restore the N-ary tree from the encoded binary tree. You also need to write a function that could decode a given binary tree and return a N-ary tree as in input format.
Note:There is no restriction on how you encode/decode the N-ary tree.
N-ary Tree is given as follows:-
6
1 -1 2 3 4 -1 5 -1 6 -1 -1 -1 -1
The above N-ary tree and its encoded binary tree can be represented as follows:-
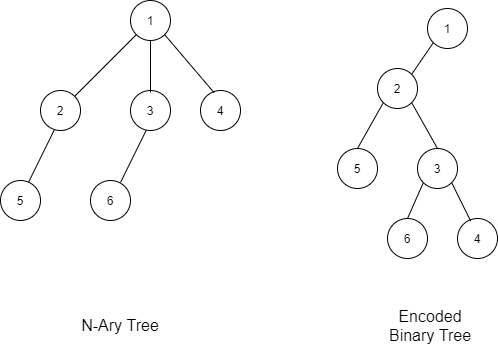
The above binary tree can be represented as follows in their level order traversal:-
1
2 -1
5 3
-1 -1 6 4
-1 -1 -1 -1
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains a single integer ‘T’ representing the number of test cases.
The first line of input contains the elements of the tree in the level order form separated by a single space.
Note:
N-ary Tree is represented in their level order traversal. Each group of children is separated by -1.
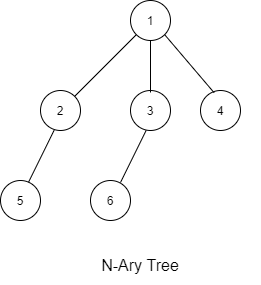
1 -1
2 3 4 -1
5 -1 6 -1 -1
-1 -1
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 -1 2 3 4 -1 5 -1 6 -1 -1 -1 -1
For each test case, for Encode function/method: return the binary tree. For Decode function/method: return the N-ary tree
1. The list/array storing binary tree must contain ‘N' + 1 element as nodes are numbered from 1 to ‘N’. The 'i'th element of the list/array must contain first the left child then the right child.
2. If a node does not have a left/right child just display that child as -1.
3. You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 1000
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
2
1 -1 2 3 4 -1 5 -1 6 -1 -1 -1 -1
1 -1 2 3 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1:
1 -1 2 3 4 -1 5 -1 6 -1 -1 -1 -1
1 -1 2 3 -1 -1 -1
Explanation for Sample Input 1:
In test case 1,
1 2 -1 5 3 -1 -1 6 4 -1 -1 -1 -1 is the binary tree user will return. Now we will pass this binary tree to be decoded. The decoded N-ary tree will be 1 -1 2 3 4 -1 5 -1 6 -1 -1 -1 -1. It is not necessary to return the same binary tree as above.
Therefore the answer is 1 -1 2 3 4 -1 5 -1 6 -1 -1 -1 -1.
In test case 2,
1 2 -1 -1 3 -1 - is the binary tree encode will return. Now we will pass this binary tree to be decoded. The decoded N-ary tree will be 1 -1 2 3 -1 -1 -1. It is not necessary to return the same binary tree as above.
Therefore the answer is 1 -1 2 3 -1 -1 -1.
Explanation for Sample Input 2:
2
1 -1 2 -1 -1
1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2:
1 -1 2 -1 -1
1 -1 -1
Hint
Hint 1
Recur by Making the right sibling as child.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Making right sibling right child.
We will convert the N-ary tree to a binary tree as follows:
- The root of the Binary Tree is the Root of the N-ary Tree.
- The leftmost child of a node in the N-ary is the Left child of that node in the Binary Tree.
- The right sibling of any node in the N-ary Tree is the Right child of that node in the Binary Tree.
We can decode from binary tree to N-ary tree. 1’s left child is the leftmost child of 1 in the N-ary tree. 3 and 4 are siblings of 2. 5’s leftmost child of 2 in the N-ary tree. 6’s leftmost child of 3 in the N-ary tree. In this way, we can decode the N-ary tree from the binary tree.
The steps are as follows:
- Declare a list/array ‘ANS’ to store left and right child initially initialized with -1.
- If 'i’th node has at least 1 child, then the 1st child is its left child.
- Then traverse children of 'i’th node. If there are still children left after this node then make the next child the right child of the current node.
- Return ‘ANS’.
Time Complexity
O(N), Where ‘N’ denotes the number of vertices in the tree.
Since we are just visiting each vertex twice. Thus the time complexity will be O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), Where ‘N’ denotes the number of vertices in the tree.
Since we created a Binary Tree and an N-ary of size ‘N’. Thus the space complexity will be O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Encode N-ary tree to binary tree.
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



