Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Evaluate Expression Tree
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 10m
Problem statement
You are given an expression tree, your task is to evaluate the expression.
An expression tree is a binary tree where leaf nodes are integer values and internal nodes are mathematical operations.
A binary tree is a tree where every node has at most two child nodes.
Note:There can be 4 operators: +,-,*,/. For division, you need to return the floor(a/b).
Consider the following expression tree:
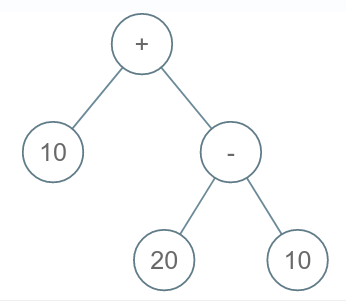
While evaluating the expression tree we replace the value at a node with any operation OP by evaluating LEFTCHILD (OP) RIGHTCHILD
Here, the expression will be evaluated as 20 - 10 = 10 (FOR ‘-’), then ‘-’ will be replaced by 10 (symbolic), then we evaluate for node’+’, 10 + 10 = 20.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ representing the number of test cases. Then the test cases follow.
The only line of each test case contains elements in the level order form. The line consists of values of nodes separated by a single space. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be:
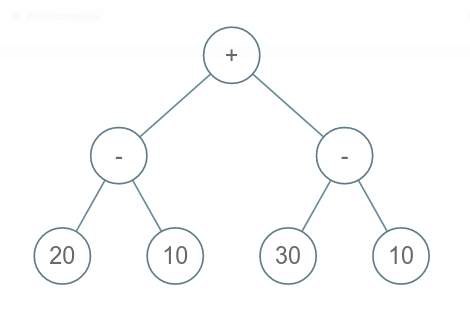
+
- -
20 10 30 10
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Explanation:
Level 1:
The root node of the tree is ‘+’.
Level 2:
Left child of ‘+’ = ‘-’
Right child of ‘+’ = ‘-’
Level 3:
Left child of ‘-’ = 20
Right child of ‘-’ = 10
Left child of ‘-’ = 30
Right child of ‘-’ = 10
Level 4:
Left child of 20 = null (-1)
Right child of 20 = null(-1)
Left child of 10 = null (-1)
Right child of 10 = null (-1)
Left child of 30 = null (-1)
Right child of 30 = null (-1)
Left child of 10 = null (-1)
Right child of 10 = null (-1)
The first not-null node(of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null(-1).
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
+ - - 20 10 30 10 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
For each test case, the output will be the evaluated value for the expression tree.
The output for each test case will be in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 100
1 <= N <= 2047
1 <= data <= 1000
Time Limit: 1 second
Sample Input 1:
3
+ 10 - -1 -1 20 10 -1 -1 -1 -1
+ - - 20 10 30 10 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
/ * 1 20 10 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1:
20
30
200
Explanation of Sample Input 1:

For the first test case, the equation is (10 + (20 - 10)) which will be evaluated to 20.
For the second test case, the equation is ((20 - 10) + (30 - 10)) which will be evaluated to 30.
For the third test case, the equation is ((20 * 10) / 1) which will be evaluated to 200.
Sample Input 2:
4
+ 5 2 -1 -1 -1 -1
- 5 2 -1 -1 -1 -1
* 5 2 -1 -1 -1 -1
/ 5 2 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2:
7
3
10
2
Hint
Hint 1
Try to reach out to each node and evaluate the expression at that node.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Recursive
Consider function EVALUATEEXPRESSION that accepts as a parameter, a BinaryTreeNode of Strings, ROOT and do:
- If ROOT is NULL return 0.
- If both LEFT and RIGHT child of ROOT are NULL return value of ROOT as an integer.
- Define LEFTVAL. Call function EVALUATEEXPRESSION for a LEFT child of ROOT and assign its value to LEFTVAL.
- Define RIGHTVAL. Call function EVALUATEEXPRESSION for a RIGHT child of ROOT and assign its value to RIGHTVAL.
- If ROOT’s value is +, return LEFTVAL + RIGHTVAL
- If ROOT’s value is -, return LEFTVAL - RIGHTVAL
- If ROOT’s value is *, return LEFTVAL * RIGHTVAL
- If ROOT’s value is /, return LEFTVAL / RIGHTVAL
Time Complexity
O(N), where N is the number of nodes in the tree.
Because we will be traversing all the nodes of the tree at least once.
Space Complexity
O(N), where N is the number of nodes in the tree
Because of the stack of functions implemented in memory
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Evaluate Expression Tree
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console



