int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
// Write your code here.
if(root == NULL)return 0;
int leftHeight = heightOfBinaryTree(root->left);
int rightHeight = heightOfBinaryTree(root->right);
return 1 + max(leftHeight,rightHeight);
}
Problem of the day
The height of a tree is equal to the number of nodes on the longest path from the root to a leaf.
You are given an arbitrary binary tree consisting of 'n' nodes where each node is associated with a certain value.
Find out the height of the tree.
Input: Let the binary tree be:

Output: 2
Explanation: The root node is 3, and the leaf nodes are 1 and 2.
There are two nodes visited when traversing from 3 to 1.
There are two nodes visited when traversing from 3 to 2.
Therefore the height of the binary tree is 2.
The first and only line contains the values of the tree’s nodes in the level order form ( -1 for NULL node). Refer to the example for further clarification.
Consider the binary tree:
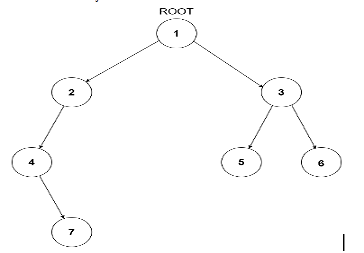
The input of the tree depicted in the image above will be like:
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level, the second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level, and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Print a single integer denoting the height of the given binary tree.
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
3 1 2 -1 -1 -1 -1
2
The given tree is:

The root node is 3, and the leaf nodes are 1 and 2.
There are two nodes visited when traversing from 3 to 1.
There are two nodes visited when traversing from 3 to 2.
Therefore the height of the binary tree is 2.
3 -1 1 2 -1 -1 -1
3
The given tree is:

The root node is 3, and there is only one leaf node, which is 2.
All three nodes are visited while traversing from 3 to 2.
Therefore the height of the binary tree is 3.
2 -1 -1
1
The expected time complexity is O(n).
1 <= 'n' <= 10000
Time Limit: 1 second
Tree/ Traversal Techniques( DFS )
To find the depth of the tree, We will do the DFS on the tree starting from the root node.
In DFS, we visit all the nodes (child and grandchild nodes) of one child node before going to the second child node, which will help us determine the tree's height. We will take the maximum of both the child’s height.
We will go to the left node and increase one if it is not NULL and do DFS on the left node, the similar thing we will do on the correct node and return the max of the left and right node.
The steps are as follows:
heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode 'root'):
O(n), Where 'n' is the number of nodes in the tree.
We are traversing the whole tree, and the number of nodes in the tree is 'n'.
Hence time complexity is O(n).
O(n), Where 'n' is the number of nodes in the tree.
The recursion stack space might consume O(n) space in the worst case.
Hence, the overall Space Complexity is O(n).
Interview problems
recursion || IBH || very easy and clean cpp
int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
// Write your code here.
if(root == NULL)return 0;
int leftHeight = heightOfBinaryTree(root->left);
int rightHeight = heightOfBinaryTree(root->right);
return 1 + max(leftHeight,rightHeight);
}
Interview problems
Effortless Method to Calculate the Height of Any Binary Tree – Step-by-Step C++ Solution with Comments
int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
// Base case: If the root is null, the height is 0
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
// Recursively find the height of the left subtree
int leftHeight = heightOfBinaryTree(root->left);
// Recursively find the height of the right subtree
int rightHeight = heightOfBinaryTree(root->right);
// Return the larger of the two heights, plus 1 for the current root node
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}Interview problems
Height of Binary Tree Easy CPP Solution 100%
int level(TreeNode<int> *root){
if(root == NULL) return 0 ;
int ans = 1 + max(level(root->left) , level(root->right));
return ans;
}
int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
// Write your code here.
return level(root) ;
}
Interview problems
C++ EASY CODE
int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
// If the root is NULL
// (empty tree), depth is 0
if(root == NULL){
return 0;
}
// Recursive call to find the
// maximum depth of the left subtree
int lh = maxDepth(root->left);
// Recursive call to find the
// maximum depth of the right subtree
int rh = maxDepth(root->right);
// Return the maximum depth of the
// tree, adding 1 for the current node
return 1 + max(lh, rh);
}
}
Interview problems
Height throught Level order Traves...
/************************************************************
Following is the TreeNode class structure
template <typename T>
class TreeNode
{
public:
T val;
TreeNode<T> *left;
TreeNode<T> *right;
TreeNode(T val)
{
this->val = val;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
************************************************************/
int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
// height of binary tree throught level order traversal
if(root==NULL){
return 0;
}
queue<TreeNode<int>*>q;
int cnt= 0;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode<int>* temp;
temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if(temp==NULL){
cnt++;
if(!q.empty()){
q.push(NULL);
}
}
else{
if(temp->left){
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(temp->right){
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
Interview problems
Height of Binary Tree || Easy Understanding
int hCheck(TreeNode<int> *root){
if(root==NULL){
return 1;
}
return max(hCheck(root->left)+1,hCheck(root->right)+1);
}
int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
// Write your code here.
int l=hCheck(root->left);
int r=hCheck(root->right);
return max(r,l);
}
Interview problems
Easy 2 line C++ Code
using recursion to find height of given binary tree.
int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
if(!root)return 0;
return 1+ max(heightOfBinaryTree(root->left), heightOfBinaryTree(root->right));
}Interview problems
C++ four line easy solution (100%)||(best way)
int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
// Write your code here.
if( root == NULL) return 0;
int lh = heightOfBinaryTree(root->left);
int rh = heightOfBinaryTree(root->right);
return 1+max(lh,rh);
}
Interview problems
Most Simple Recusrsive Solution
void solve(TreeNode<int> *root, int level, int &ans){
if(root==NULL){
return;
}
if(level>=ans){
ans = level;
}
solve(root->left, level+1, ans);
solve(root->right, level+1, ans);
}
int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode<int> *root)
{
int ans = 0;
solve(root, 0, ans);
return ans;
} Interview problems
Java recursive approach
public class Solution {
public static int heightOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
// Write your code here.
if(root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(heightOfBinaryTree (root.left), heightOfBinaryTree(root.right)) +1;
}
}