Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
k-th node from the end of the linked list
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 15m
Problem statement
Given the head node of the singly linked list and an integer ‘k’, , find the value at the kth node from the end of the linked list.
For example: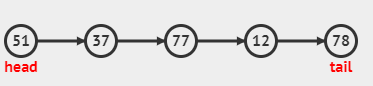
For the above-linked list, if k=2, then the value at the kth i.e second node from the end is ‘12’.
1.You don’t need to take any input. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function and return a pointer pointing to the k-th element from the last of the linked list.
2.It is guaranteed that k<=size of the linked list.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The next ‘2*T’ lines represent the ‘T’ test cases.
The first line of each test case contains integers denoting the nodes of the linked list. Each line is guaranteed to have -1 at the end to signify the end of the linked list.The second line of each test case contains an integer ‘k’
For each test case, return a pointer pointing to the node
which is at the k-th position from the last of the linked list.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 50
0 <= N <= 10^5
-10^9 <= data <= 10^9
1 <=k <=N
node->data ≠ -1.
Where ‘T’ is the total number of test cases, ‘N’ denotes the number of elements in each Linked List, and ‘data‘ is the value of any node of the linked list and ‘k’ is the position of the element from the end to be returned.
Time Limit : 1 sec
Sample Input 1 :
2
43 6 9 1 5 -1
4
3 7 -32 8 11 -1
5
Sample Output 1 :
6
3
Explanation Of Sample Input 1 :
First Test Case :
The given linked list is: 43->6->9->1->5
We can clearly see that the 4th element from the last is 6 therefore we return a pointer pointing to the element ‘6’.
Second Test Case :
The linked list in this case is 3->7->-32->8->11
The 5th element from last is the first node of the list therefore we return a pointer pointing to the first node i.e. ‘3’
Sample Input 2 :
1
2 26 35 5 -1
1
Sample Output 2 :
5
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Find the total number of nodes in the linked list.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Naive Approach
- We can find the kth node from end very easily if we know the total number of nodes in the list.
- We take a pointer ‘cur’ (initially pointing to head) and a variable ‘cnt’ to count total number of nodes.
- We move the ‘cur’ pointer forward by one step until we reach NULL and increment the count variable by one in each move.
- We will use the following property to find the kth node from the end.
- Kth node from end = (cnt-k+1)th node from the beginning.
- Let us store the value of cnt-k+1 in a variable ‘n’.
- Now traverse the linked list again and return the pointer to the ‘nth’ node.
Time Complexity
O(n), where n is the total number of nodes in the list.
We have to traverse the linked list twice. Firstly to calculate the total number of nodes and then to find the kth node from the end.So the complexity is of order ‘n’
Space Complexity
O(1)
Constant Space is used.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
k-th node from the end of the linked list
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



