Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Largest Component
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 45m
Problem statement
You are given an array 'ARR' of size 'N' containing positive integers. Consider an undirected graph using the given array with the following conditions:
-> The graph consists of 'N' vertices.
-> The ith vertex has a value 'ARR[i]'.
-> There is an edge between two vertices 'i' and 'j' (where 'i' < 'j'), if and only if GCD('ARR[i]', 'ARR[j]') is greater than 1.
GCD(a, b) is the maximum number x such that both a and b are divisible by x.
Your task is to find the size of the largest component in the graph.
A component of an undirected graph is a subgraph in which any two vertices are connected to each other by paths, and which is connected to no additional vertices in the rest of the graph. The size of a component is the number of vertices in it.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
The first line of input contains a single integer 'T', representing the number of test cases or queries to be run.
Then the 'T' test cases are as follows.
The first line of each test case contains a positive integer 'N', which represents the size of the array 'ARR'.
The next line contains 'N' single space-separated positive integers representing the elements of the array.
For each test case, print an integer denoting the size of the largest component in the graph.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 10^3
1 <= ARR[i] <= 10^5
Where 'ARR[i]' is the ith element in the array.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
1
6
10 4 2 5 3 9
Sample Output 1:
4
Explanation for Sample Input 1:
In the first test case, there are two components of size 4 and 2.
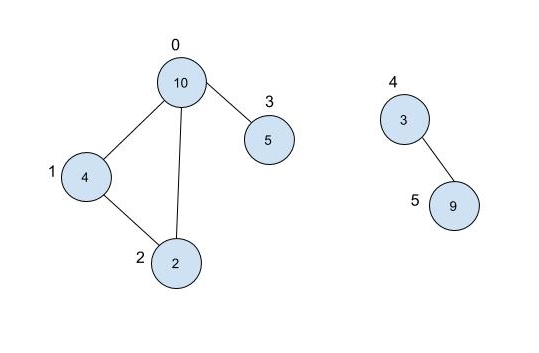
Sample Input 2:
2
3
1 2 3
4
2 2 2 2
Sample Output 2:
1
4
Explanation for Sample Input 2:
In the first test case, there are three components and each is of size 1.
In the second test case, there is only one components and it is of size 4.
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Can you make the graph and find the size of every component?
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
DFS
In this approach, we will make the graph, for this, we will make an adjacency list to store the edges of the graph. Iterate on the vertices using two loops and add an edge between vertex i and j, if GCD('ARR[i]', ‘ARR[j]’) is greater than 1.
Now, find the size of every component in the graph. We can do this using DFS.
- Make an array to store the visited vertices.
- Iterate on the vertex of the graph
- If a vertex ‘v’ is unvisited, run a DFS from the vertex 'v'.
- In the DFS, we will visit all the vertices which are reachable from the vertex ‘v’.
- This will form one component with its size being the number of vertices we visit in the DFS.
- Else, continue.
Time Complexity
O(N^2 * log(K)), Where N is the size of the given array and K is the maximum element in the given array.
For finding the edges of the graph, we are considering every pair of vertices and it takes O(N^2) time to consider every pair and O(K) is the time complexity to calculate GCD of a pair using the Euclidean algorithm.
There can be at most N*(N-1)/2 edges in the graph, so in the worst case, DFS will take O(N + N*(N-1)/2) time.
Thus, the final time complexity is O(N^2 * log(K) + N + N*(N-1)/2) = O(N^2 * log(K)).
Space Complexity
O(N^2), Where N is the size of the given array.
We are storing the edges in an adjacency list which will take O(N^2) space ( there can be at most N*(N-1)/2 edges ). We are doing DFS which will take O(N) recursion stack space. Thus, the final space complexity is O(N^2 + N) = O(N^2).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Largest Component
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



