Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
LCA - Lowest Common Ancestor
Hard
0/120
Average time to solve is 40m
4 upvotes
Asked in companies



Problem statement
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) is a concept in graph theory and computer science.
Let ‘T’ be a rooted tree with ‘N’ nodes. The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes, ‘u’ and ‘v’, as the lowest node in ‘T’ that has both ‘u’ and ‘v’ as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself). - Wikipedia
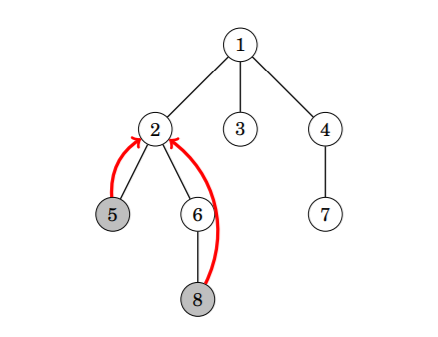
For the given tree, The LCA of nodes 5 and 8 will be node 2, as node 2 is the first node that lies in the path from node 5 to root node 1 and from node 8 to root node 1.
Path from node 5 to root node looks like 5 → 2 → 1.
Path from node 8 to root node looks like 8 → 6 → 2 → 1.
Since 2 is the first node that lies in both paths. Hence LCA will be 2.
Given any two nodes ‘u’ and ‘v’, find the LCA for the two nodes in the given Tree ‘T’.
Note: For each test case, the tree is rooted at node 1.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format-
The first line contains an integer ‘T’ which denotes the number of test cases.
For each test case:
The first line contains a single integer ‘N’, denoting the number of nodes.
Each of the following ‘N’ - 1 line contains two space-separated integers, ‘ui’ and ‘vi’, which means an edge connects these two nodes.
The following line will contain a single integer ‘Q’, denoting the number of queries you have to answer for the given tree.
In the following ‘Q’ lines, each one will have two numbers, ‘u’ and ‘v’, for which you have to find the LCA of ‘u’ and ‘v’.
Your task is to print ‘Q’ lines for each test case.
The ‘Q’ lines should be the LCA of the given ‘u’ and ‘v’, respectively.
Constraints -
1<= ‘T' <= 5
1 <= ‘N’ <= 10^5
1 <= ‘Q’ <= 10^5.
1 <= ‘u’, ‘v’ <= ‘N’.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input-1
2
5
1 2
2 3
1 4
2 5
2
3 5
4 5
3
1 2
3 2
2
1 3
2 2
Sample Output-1
2 1
1 2
Explanation for Sample Input 1:
For test case 1:
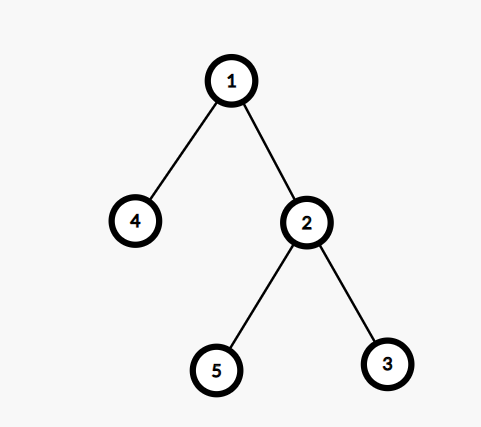
From the above graph,
we can see that for nodes ‘5’ and ‘3’, ‘2’ is the direct parent of both the nodes. Hence the LCA will be 2.
For nodes ‘4’ and ‘5’, the first node that has both node 4 and node 5 in its subtree is 1. Hence, ‘1’ is the LCA.
Sample Input-2
2
4
1 2
2 3
4 1
2
3 4
4 1
5
1 4
2 4
3 5
5 1
2
2 3
3 4
Sample Output-2
1 1
1 1
Hint
Hint 1
How can you find the kth ancestor of a node?
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Brute Force
Prerequisite - DFS
Approach:
We will store the depth and the direct parent of each node using a dfs.
Now, if we have to find the LCA to two nodes, first we would move upward the node which has a higher depth until both the nodes reach the same depth, then we will move both the node upward until they become the same, the node that we reach will be the LCA.
Algorithm:
- Initialize two arrays of length ‘N + 1’ to store depth and the direct parent of each node.
- Func dfs(cur, parent):
- Update depth[cur] to depth[parent] + 1.
- Update par[cur] to parent
- Iterate in all the children of node ‘cur’ and call dfs as dfs(child, cur)
- Func get_lca(u, v):
- While depth[u] > depth[v]:
- Update u to par[u]
- While depth[v] > depth[u]:
- Update v to par[v]
- While u != v:
- Update u to par[u]
- Update v to par[v]
- Return u
- While depth[u] > depth[v]:
- Func Main():
- dfs(1, 0)
- For u,v in query:
- print(get_lca(u, v))
Time Complexity
O(N * Q). Where ‘N’ is the number of nodes, and ‘Q’ is the number of queries.
We might use the while loop for each query for a total of ‘N’ time in the worst case. Hence overall complexity is O(N * Q).
Space Complexity
O(N), Where ‘N’ is the number of nodes of the tree.
We are creating two arrays of length ‘N + 1’. Hence overall complexity will be O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
LCA - Lowest Common Ancestor
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
