Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Leftmost & Rightmost Nodes of Binary Tree
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 20m
9 upvotes
Asked in companies



Problem statement
Given a Binary Tree of 'N' number of total nodes, return the sequence of values of the leftmost and rightmost node at each level.
For example:For the given binary tree:
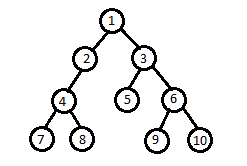
Output: 1 2 3 4 6 7 10
Explanation: The leftmost and rightmost node respectively of each level are
Level 0: 1(only one node is present at 0th level)
Level 1: 2 3
Level 2: 4 6
Level 3: 7 10
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The only line of input contains tree elements in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
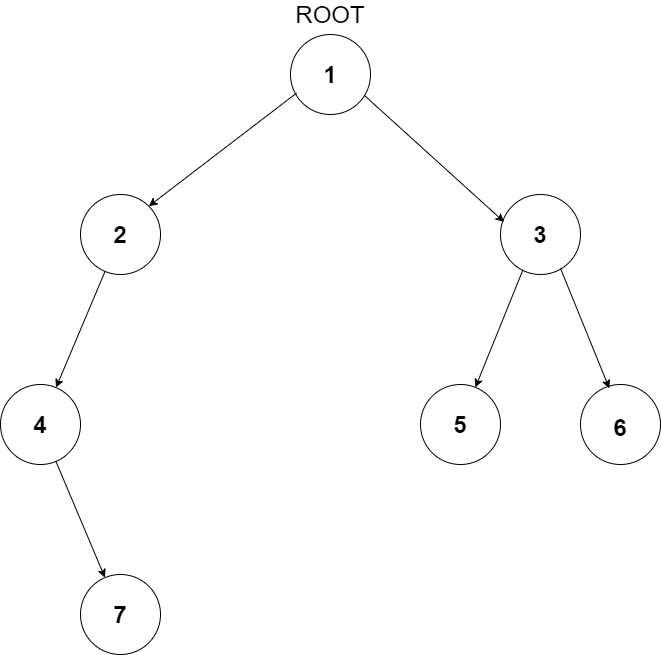
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
For each test case, print a single line containing space-separated integers denoting a sequence of integers written progressively from top to bottom of the tree such that for each level, left most data is followed by the rightmost one.
The output of each test case will be printed in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
0 <= N <= 10 ^ 5
Time Limit: 1 sec.
Sample Input 1:
1 2 3 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1:
1 2 3
Sample Input 2:
1 2 3 -1 4 4 -1 -1 5 6 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2:
1 2 3 4 4 5 6
Explanation to Sample Input 2:
The input binary tree will be represented as
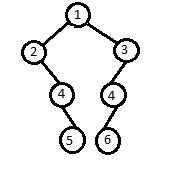
From the above representation, the leftmost and rightmost node respectively of each level are:
Level 0: 1 (only one node is present at 0th level)
Level 1: 2 3
Level 2: 4 4
Level 3: 5 6
Note: Do not consider the vertical distance of nodes from the root node to find the leftmost and rightmost nodes. As in this example, at level 3(0 based indexing) the node with value 5 will have a vertical distance of +1 from the root node and the node with value 6 will have a vertical distance of -1 from the root node.
Hint
Hint 1
Use level-wise order traversal.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Level Order Traversal Approach
Using level-wise order traversal, we will be maintaining the queue to store the pending nodes. Starting from the 0th level i.e the root node we will add root node into the queue. Now for each level stored into the queue(initially we have 0th level). We will poll nodes one by one from the queue and add corresponding children into the queue. While popping nodes we will also print the first(leftmost node) and last(rightmost node) nodes of that level. This way we will be having another level pending in our queue to traverse. This process goes on until the last level is traversed(see below algorithm for the approach).
Algorithm:
- Initialize an empty list to store the leftmost and rightmost nodes.
- If the root is null, return the list.
- Initialize the queue storing the pending nodes and add the root in this. (marking 0th level pending).
- For each of the pending nodes in the queue(denoting the current level) i.e i=1 to size.
- Initialize current node with the queue’s front node i.e current node = queue.poll().
- If i == 1 or i == size, add the current node to the list. This will be denoting the leftmost or rightmost node respectively for the current level.
- Add the left child(if not null) of the current node to the queue.
- Add the right child(if not null) of the current node to the queue.
- Repeat step 4
- Return list.
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the total number of nodes in the given binary tree.
In the worst case, the tree is a skew tree. Hence, all the ‘N’ nodes are distributed as the left most path and the right most path. So, the required path will have all ‘N’ nodes. Thus, the overall complexity becomes O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the total number of nodes in the given binary tree.
In the worst case, the tree is a skew tree. Hence, all the ‘N’ nodes are distributed as the left most path and the right most path. So, the required path will have all ‘N’ nodes. Hence, a list/ array of size at most ‘N’ is needed. Thus, the overall complexity becomes O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Leftmost & Rightmost Nodes of Binary Tree
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console
