Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Maximum Sum No Larger Than K
Hard
0/120
Average time to solve is 25m
Problem statement
You are given an ‘N’ x ‘M’ matrix ‘MAT’ and an integer ‘K’. Your task is to find the maximum sum of a rectangle in the matrix which is less than or equal to ‘K’.
For Example:
You are given ‘MAT’= [[1, 2],[3, 4]] and ‘K’ = 8.
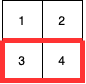
Then the answer will be 7 (the sum of the red rectangle).
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line of the input contains a single integer 'T', representing the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains three space-separated integers, ‘N’ and ‘M’ representing the number of rows and columns in ‘MAT’, respectively, and ‘K’.
The next ‘N’ lines contain ‘M’ space-separated integers representing the elements of ‘MAT’.
For each test case, print the maximum sum of a rectangle in the matrix which is less than or equal to ‘K’
Print the output of each test case in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 100
1 <= M <= 100
-10^6 <= K <= 10^6
-10^6 <= MAT[i][j] <= 10^6
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
2
2 2 8
1 2
3 4
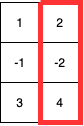
3 2 5
1 2
-1 -2
3 4
Sample Output 1:
7
4
Explanation of Sample Input 1:
For the first test case, the answer will be 7 (the sum of the red rectangle).

For the second test case, the answer will be 4 (the sum of the red rectangle).
Sample Input 2:
2
2 2 2
1 1
1 1
3 2 4
1 2
-1 2
-4 -7
Sample Output 2:
2
4
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Try to use the concept of the prefix sum.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Prefix Sum
Prerequisite: Subarray sum equals K
In this approach, we will first calculate the prefix sum of each row. We will use the input matrix itself to store the prefix sum of each row. We will get the range sum for every two columns using the subtraction of the prefix sum. Then for every index ‘X’, we will store the prefix sums in a sorted container. Now, to find the maximum possible sum which is less than or equal to ‘K’, we will find if there is a possible sub-array with sum ‘K’ that ends at ‘X’ and if not, will try to find the sum with possible sum k -1 and so on.
Algorithm :
- Initialize a variable ‘ANS’ with the minimum integer value.
- Iterate ‘I’ in 0 to ‘N’:
- Iterate ‘J’ in 1 to ‘M’:
- Set ‘MAT’[‘I’][‘J’] as ‘MAT’[‘X’][‘J’] + ‘MAT’[‘X’][‘I’ - 1].
- Iterate ‘J’ in 1 to ‘M’:
- Iterate ‘I’ in 0 to ‘M’:
- Iterate ‘J’ in ‘I’ to ‘M’:
- Initialize a sorted container ‘SET’.(set in c++, TreeSet in java, SortedSet in python).
- Add 0 to ‘SET’.
- Set ‘SUM’ as 0.
- Iterate ‘X’ in 0 to ‘N’:
- If ‘I’ is greater than 0, add (‘MAT’[‘X’][‘J’] - ‘MAT’[‘X’][‘I’ - 1] to ‘SUM’, otherwise, add ‘MAT’[‘X’][‘J’] to ‘SUM’.
- Set ‘VAL’ as CEIL(’SET’[‘SUM’ - ‘K’]).
- If ‘VAL’ is not null.
- Set ‘ANS’ as the maximum value of ‘ANS’ and ‘SUM’ - ‘VAL’.
- Add ‘SUM’ to ‘SET’.
- Iterate ‘J’ in ‘I’ to ‘M’:
- Return ‘ANS’.
Time Complexity
O( (M ^ 2) * N * LOG(N)), where 'N' and 'M' are the number of rows and columns of the matrix, respectively.
We iterate over each ‘I’ and ‘J’ where 0 < ’I’ < ’J’ < M, within this nested loop, we iterate ‘X’ from 0 to ‘N’, and within this loop, we perform add and get operation on the sorted container which takes LOG(N) time. Hence, the total time complexity is O((M ^ 2) * N * LOG(N)).
Space Complexity
O(N).
The sorted container contains at most ‘N’ elements. Hence, the total space complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Maximum Sum No Larger Than K
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



