Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Merge Two Binary Max Heaps
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 10m
Problem statement
You are given two integer arrays ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ of size ‘N’ and ‘M’ respectively, Both ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ represent a Max-Heap. Your task is to merge the two arrays firstly keep all the elements of the ‘ARR1’ (without changing order) than elements of array ‘ARR2’ (without changing order), and then find the Max-Heap obtained by merging arrays. Print an array of sizes ‘N + M’, representing the Max-Heap obtained after merging.
A binary Max-Heap is a complete binary tree in which the value in each internal node is greater than or equal to the values in the children of that node.
Max-Heaps are usually represented by an array, as follows :
1. Each element in the array represents a node of the heap.
2. Element at index 0 represent the root of the heap.
3. If a node is represented by elements at index ‘i’ then its left and right child is represented by elements at indices ‘2*i + 1’ and ‘ 2*i + 2’ respectively.
Consider ‘ARR1’ = [10, 5, 6, 2] and ‘ARR2’ = [12, 7, 9].
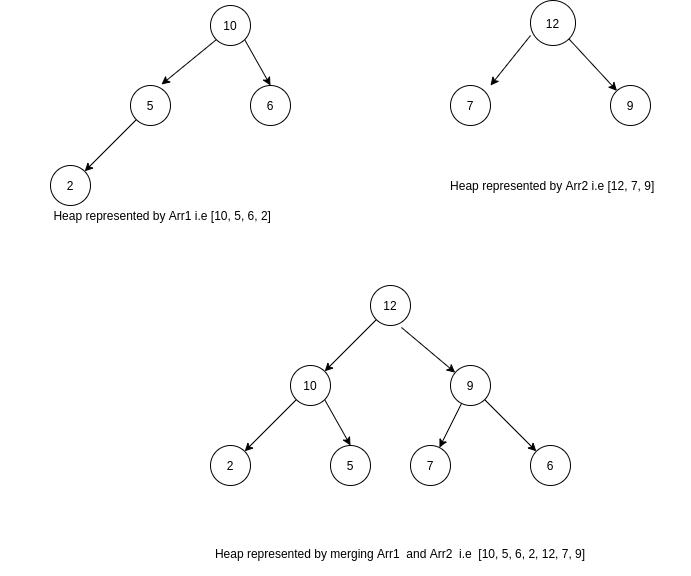
The max-heap obtained by merging can be represented by array [12, 10, 9, 2, 5, 7, 6]
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The next ‘3*T’ lines represent the ‘T’ test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two space-separated integers ‘N’, and ‘M’ representing the size of the array ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ respectively.
The second line of each test case contains ‘N’ space-separated integers representing the array ‘ARR1’.
The third line of each test case contains ‘M’ space-separated integers representing the array ‘ARR2’.
For each test case, print a separate one line consisting of ‘N + M’ space-separated integers representing the Max-Heap obtained after merging.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
If the returned Heap is max-Heap of the given heaps then "Correct answer" will be printed else "Wrong answer" will be printed.
Constraints :
1 <= ‘T’ <= 50
1 <= ‘N’ <= 10^4
1 <= ‘M’ <= 10^4
1 <= ‘ARR1[i]’, ‘ARR2[i]’ <= 10^9
Time limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1 :
2
1 1
2
2
4 3
10 5 6 2
12 7 9
Sample Output 1 :
2 2
12 10 9 2 5 7 6
Explanation For Sample Input 1:
Test case 1:
In this case, Both heaps have only one element i.e 2, thus after merging, the new array obtained will be [2, 2] which also represents a max-heap of size 2.
Test case 2:
See the problem statement for an explanation.
Sample Input 2:
2
6 7
10 5 6 4 5 6
9 7 9 4 3 8 3
2 3
3 1
10 6 8
Sample Output 2:
10 9 9 7 5 8 6 5 4 4 3 6 3
10 8 3 6 1
Hint
Hint 1
Merge both arrays and then use the Max-Heapify algorithm to build the max-heap.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Heapify
In this approach first, we simply merged both arrays ‘ARR1’and ‘ARR2’ by first keeping all the elements of the ‘ARR1’ (without changing order) followed by the elements of array ‘ARR2’ (without changing order). Let ‘merged’ be the array obtained by merging ‘ARR1’and ‘ARR2’. We consider that ‘merged’ represents a complete binary tree, where the element at index ‘0’ is the root and for any index ‘i’ its left and right child nodes are at index ‘2*i + 1’ and ‘2*i + 2’ respectively. In order to convert it into Max-Heap, we need to use the Max-Heapify algorithm. We use the Max-Heapify algorithm to correct a max-heap if one of its nodes is misplaced.
The following is Max-Heapify Algorithm:-
Create a recursive function maxHeapify(Arr, i), where an array ‘ARR’ represents the heap (consider 0-based indexing) and ’i’ is the index to start at when heapifying down. In this function do the following.
- Initialize an integer variable ‘LARGEST’:= ‘i’.
- If index ‘2*i + 1’ exist and element at the index 'LARGEST’ is smaller than element at index ‘2*i + 1’ then assign ‘LARGEST’ := ‘2*i + 1’.
- If index ‘2*i + 2’ exist and element at the index 'LARGEST’ is smaller than element at index ‘2*i + 2’ then assign ‘LARGEST’ := ‘2*i + 2’.
- Swap ‘ARR[LARGEST]’ with ‘ARR[i]’.
- If ‘LARGEST != i’, then recursively call ‘maxHeapify(ARR, LARGEST)’.
Time taken by the Max-Heapify algorithm is O(H),. where ‘H’ is the height of node ‘i’.
We need to convert the array ‘merged’ of size ‘N+M’ in max-heap. It can be clearly seen that the complete binary tree represented by the array ‘merged’ does not follow the Max-Heap property. So, the idea is to heapify the complete binary tree formed from the array in reverse level order following a top-down approach. That is first max-heapify, the last node in level order traversal of the tree, then max-heapify the second last node, and so on.
We can observe that in the complete binary tree half of the nodes are leaf nodes and a single leaf node is a valid Max-Heap, Thus it is enough if we start applying max-heapify from the index ‘(N + M)/2’ to ‘0’, instead of ‘N + M’ in array ‘merged’.
Algorithm:
Int[] mergeHeap(N, M, ARR1, ARR2)
- Create an array ‘MERGED’ of length ‘N + M’.
- Copy the elements of ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ into ‘MERGED’.
- Run a loop where ‘i’ ranges from ‘0’ to ‘N+M-1’.
- If ‘i’ is less than ‘N’
- Assign, ‘MERGED[i]’ := ‘ARR1[i]’
- Else
- Assign ‘MERGED[i]’ := ‘ARR2[i-N]’.
- If ‘i’ is less than ‘N’
- Run a for loop in reverse order from ‘(N + M)/2 - 1’ to ‘0’
- Call ‘maxHeapify(merged, i)’.
- Return ‘MERGED’.
Time Complexity
O(N + M), where ‘N’ and ‘M’ represents the size of the array ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ respectively.
The time required to merge two arrays of sizes ‘N’ and ‘M’ is O(N + M). Building a heap using the max-heapify algorithm takes linear time.
Thus overall time complexity will be O(N + M)
Space Complexity
O(N + M), where ‘N’ and ‘M’ represents the size of array ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ respectively.
In the above algorithm, We are making an array ‘merged’ of size ‘N + M’.
Thus, the space complexity will be O(N + M).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Merge Two Binary Max Heaps
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console


