Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Minimum Falling Path Sum
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 25m
Problem statement
You have been given a square array 'VEC' of integers of size 'N' rows and 'N' columns. Your task is to find the minimum sum of a falling path through the square array. The number of rows and columns in the given array will be the same.
A falling path starts at any element in the first row and chooses one element from each row. The next row's choice must be in a column that is different from the previous row's column by at most one.
Example:
VEC[][]= {{5, 10}, {25, 15}}
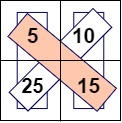
All the rectangles denote the possible falling paths. The rectangle with red filler is the minimum falling path with the minimum falling path sum of 20 (5+15).
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each test contains an integer ‘N’ denoting the number of rows and columns.
The next ‘N’ lines of each test case contain ‘N’ space-separated integers denoting the elements of the square array.
For each test case, print a single integer the minimum sum of a falling path through the square array.
The output of each test case will be printed in a separate line.
You don’t need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just return the minimum sum calculated.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 50
1 <= N <= 100
-10^7 <= VEC[i][j] <=10^7
Where ‘T’ is the total number of test cases, ‘N’ denotes the number of rows and columns in the array, and ‘VEC[i][j]’ denotes the range of elements in the 2 Dimensional array.
Time limit: 1 second
Sample input 1:
2
3
11 12 13
14 15 16
17 18 19
2
5 10
25 15
Sample output 1:
42
20
Explanation For Sample Input 1:
Test Case 1:
The possible falling paths are
[11,14,17], [11,14,18], [11,15,17], [11,15,18], [11,15,19]
[12,14,17], [12,14,18], [12,15,17], [12,15,18],
[12,15,19], [12,16,18], [12,16,19]
[13,15,17], [13,15,18], [13,15,19], [13,16,18], [13,16,19]
Paths [11, 14, 19], [13, 16, 17] are not the falling paths. In [11, 14, 19], 14 lies in column 0 and 19 lies in column 2. So, the difference in their columns is greater than 1. The same is the case for path [13, 16, 17]
The falling path with the smallest sum is [11, 14, 17], so the answer is 42.
Test case 2:
The possible falling paths are
[5, 25], [5, 15]
[10, 25], [10, 15]
The falling path with the smallest sum is [5, 15], so the answer is 20.
Sample input 2:
2
3
4 3 5
2 5 7
3 6 8
2
12 14
17 18
Sample output 2:
8
29
Hint
Hint 1
Figure out all the possible falling paths.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Dynamic Programming
Since the difference between the previous ‘ROW’ ‘COLUMN’ number and the current ‘ROW’ ’COLUMN’ number should be at most one, the possible next step from point A[‘ROW’ ][‘COLUMN’] will be A[‘ROW’ +1][‘COLUMN’-1], A[‘ROW’+1][‘COLUMN’] and A[‘ROW’+1][‘COLUMN’+1]. So, the idea is to traverse these possible paths and keep storing the minimum result for each ‘COLUMN’. Finally, return the minimum of all the values of each ‘COLUMN’.
- Run a loop where ‘‘ROW’’ ranges from ‘N-2’ to 0 and another nested loop where ‘COLUMN’’ ranges from 0 to ‘N-1’.
- We maintain a variable ‘MINFALL’ which is initialized to ‘VEC[‘ROW’+1][‘COLUMN’].
- If ‘COLUMN’’ is greater than or equal to 0, compare the value of variable ‘MINFALL’ with ‘VEC[‘ROW’+1][‘COLUMN’-1]’ and store the minimum of the two in variable ‘MINFALL’.
- If ‘COLUMN’+1’ is less than ‘N’, compare the value of variable ‘MINFALL’ with ‘VEC[‘ROW’+1][‘COLUMN’+1]’ and store the minimum of the two in variable ‘MINFALL’.
- Through steps 2, 3 & 4, we will get the minimum path from the end ‘ROW’ to the point ‘VEC[‘ROW’][‘COLUMN’]’ and will add this minimum value to ‘VEC[‘ROW’][‘COLUMN’]’.
- We will use these values for finding the minimum falling path for upper ‘ROW’s.
- Finally, we will compare and find the minimum values among ‘VEC[0][I]’ where ‘I’ ranges from 0 to ‘N-1’ and return the smallest value.
Time Complexity
O(N^2), where ‘N’ is the number of rows/columns.
The matrix of size ‘N’ rows and ‘N’ columns is traversed once, hence the overall complexity will be N*N i.e O(N^2).
Space Complexity
O(1).
As it uses constant space.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Minimum Falling Path Sum
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console



