Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Minimum Fountains
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 10m
Problem statement
There is a one-dimensional garden of length 'N'. On each of the positions from 0 to 'N', there is a fountain, and this fountain’s water can reach up to a certain range as explained further. In other words, there are 'N' + 1 fountains located at positions 0, 1, 2, 3, …. 'N' which can be activated in the garden.
You are given an integer 'N' and an array/list 'ARR' of length 'N' + 1, where each index of the array denotes the coverage limit of a particular fountain.
A fountain at index 'i' can water the area ranging from the position 'i' - 'ARR'['i'] to 'i' + 'ARR'['i'].
Your task is to find the minimum number of fountains that have to be activated such that the whole garden from position 0 to 'N' has access to the water from at least some fountain.
Note:
1. 0-based indexing is used in the array.
2. We only care about the garden from 0 to 'N' only. So if i - 'ARR'['i'] < 0 or i + 'ARR'['i'] > 'N', you may ignore the exceeding area.
3. If some fountain covers the garden from position 'A' to position 'B', it means that the water from this fountain will spread to the whole line segment with endpoints 'A' and 'B'.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line of the input contains an integer 'T', denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains the integer 'N', denoting the size of the garden.
The second line of each test case contains 'N' + 1 space-separated integers denoting the array elements.
For each test case, print a single integer that corresponds to the minimum number of fountains to be activated.
Note :
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= 'T' <= 50
1 <= 'N' <= 10^4
1 <= 'ARR'[i] <= 'N'
Where 'ARR[i]' represents the elements at 'i'th index.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
2
2
1 2 1
4
2 1 2 1 1
Sample Output 1:
1
1
Explanation for Sample Input 1:
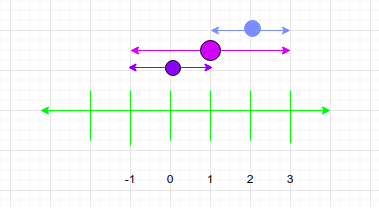
For the first test case, as shown in the figure,
Fountain at i = 0 can cover area from (-1,1).
Fountain at i = 1 can cover area from (-1, 3).
Fountain at i = 2 can cover the area from (1, 3).
So if we activate the fountain on index = 1, we will be able to cover the whole garden.
For the second test case, we can just activate the fountain on index 2 as it will cover all the positions from 0 to 4
Sample Input 2:
1
4
2 1 1 2 1
Sample Output 2:
2
Explanation for Sample Input 2:
We can activate the fountains on index 0 and 3 to cover the whole garden.
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Think of sorting and implementing dp.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Dynamic programming
- For every fountain, we can try to find the pair area = (left, right), where left and right are the leftmost and the rightmost index respectively where the current fountain can reach.For every index 'I' = 0 to 'I' = 'N' -1, 'LEFT' = max(0, 'I' - 'ARR'['I']) and 'right' = min('I' + ('ARR'['I'] + 1), 'N').
- Now we can sort the array of pairs in non-decreasing order according to 'LEFT' to find the minimum number of fountains.
- Let us create a 'DP' array of size 'N' + 1 and initialise each index to 'N' + 1 because in worst that n+1 would be the minimum number of fountains that we have to turn on and let 'DP'[0] = 0 because to cover the 0 area no fountain is required
- For each of the intervals, we can use the following transition:
- For a particular index 'I' we have 2 options, either to start a new fountain or to use the previous fountain which can cover the current index.
- So we can use the following transition, For 'I' = 'AREA'[0] +1 to 'I' = 'AREA'[1] + 1, 'DP'[i] = min('DP'[i], 'DP'['AREA'[0] + 1]), where 'AREA'[0] represents the leftmost index where the current fountain can reach and 'AREA'[1] represents the rightmost index.
- After the loop ends, 'DP'['N'] will contain the minimum number of fountains.
Time Complexity
O(N ^ 2), where ‘N’ is the size of the array.
Since we nesting two loops that go till ‘N’, Hence time complexity is O(N ^ 2).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the size of the array.
Since we are using extra space to store elements in the array.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Minimum Fountains
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console



