Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Minimum HP
Hard
0/120
Average time to solve is 25m
Problem statement
You are playing a board game where you die when your hp (health points) becomes 0 or negative. Now you start with some initial hp, and start moving in the board starting from the top-left corner. You have to reach the bottom right corner of the board by only moving right and down. Whenever you arrive on a cell in the board your hp may increase or decrease by the amount written on the cell. If the cell has a positive value it means your hp increases, if it has a negative value it means your hp decreases. You need to return the minimum initial health required so that you can reach the rightmost corner.
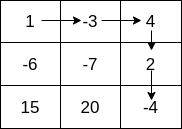
For Example:In the example below, if we follow the path shown in the figure, then the minimum initial hp required will be 3.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line of the input contains ‘T,’ denoting the number of test cases. The 'T' test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains two integers, ‘N’ and ‘M’, denoting the number of rows and columns of the board.
Next ‘N’ lines contain 'M' space-separated integers denoting the elements of the array 'board'.
For each test case, print an integer denoting the minimum initial hp required to reach the bottom-right corner of the board.
The output of each test case is printed in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 5
1 <= N, M <= 1000
-3000 <= board[i][j] <= 3000
Where 'board[i][j]' represent the value of board at 'jth' column of 'ith' row.
Time Limit: 1 second
Sample Input 1 :
2
3 3
1 -3 4
-6 -7 2
15 20 -4
1 1
-4
Sample Output 1 :
3
5
Explanation For Sample Input 1 :
In test case 1:

If we follow the path shown in the figure then the minimum initial hp required will be 3.
In test case 2:
There is only 1 element in the board, if where minimum 5 initial hp is required. Because 5 + (-4) = 1, if we have anything lower than 5, we will have 0 or negative hp at the end.
Sample Input 2 :
2
3 4
-1 -7 3 -10
10 -13 3 -14
-13 6 -6 9
5 5
3 -1 2 14 19
-8 -5 5 -15 -19
-9 -10 -5 -18 -8
6 20 13 1 -9
0 13 5 6 -1
Sample Output 2 :
5
1
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Hint 3
Try all possible paths from the top left to the bottom right and minimize the health required.
Approaches (3)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Approach 3
Recursion
The main idea is to use recursion to reduce the big problem into several smaller subproblems.
Algorithm :
- We will call a minimumHealth function that returns us the minimum health required from the current point to destination ('N' - 1, ‘M’ - 1).
- From each point ('i', ‘j’), we have 2 choices:
- We can move right to ('i' , ‘j’ + 1). Then we will do a recursive call with ('i', ‘j’ + 1) as our starting point, say the minimum health required from this call comes out to be ‘op1’.
- Or we can move down to ('i' + 1, ‘j’). Then we will do a recursive call with ('i' + 1, ‘j’) as our starting point, say the minimum health required from this call comes out to be ‘op2’.
- our minimum health required from ('i' , ‘j’) to ('N' - 1, 'M' - 1) will be ‘board[i][j]' + min('op1', 'op2').
- The algorithm for minimumHealth will be as follows:
- Int minimumHealth(‘board’, ‘i’, ‘j’, ‘N’, 'M)
- If ‘i’ >= ‘N’ or ‘j’ >= ‘M’ : if the point is out of grid.
- return large integer value
- If ‘i’ == ‘N’ - 1 and j == ‘M’ - 1:
- if board[i][j]' ≤ 0:
- return abs(board[i][j])+ 1
- else:
- return 1
- if board[i][j]' ≤ 0:
- int ‘op1’ = minimumHealth (board, 'i', 'j' + 1, ‘N’, ‘M’)
- int 'op2' = minimumHealth (‘board, ‘i’ + 1, ‘j’, ‘N’, ‘M’)
- int minHealthRequired = min(op1, op2) - board[i][j];
- if minHealthRequired ≤ 0:
- return 1
- else
- return minHealthRequired.
- if minHealthRequired ≤ 0:
- If ‘i’ >= ‘N’ or ‘j’ >= ‘M’ : if the point is out of grid.
- Int minimumHealth(‘board’, ‘i’, ‘j’, ‘N’, 'M)
Time Complexity
O(2 ^ (N + M)), Where 'N' and 'M' are the dimensions of the board.
Since we are making 2 recursive calls for each cell visited. The maximum length covered will be (N + M). Hence, the overall time complexity will be O(2 ^ (N + M)).
Space Complexity
O(N + M), Where 'N' and 'M' are the dimensions of the board.
Since extra space is used by the recursion stack, which goes to a maximum depth of N + M. Hence, the overall space complexity will be O(N + M).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Minimum HP
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



