Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Minimum steps to reach target by a Knight
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 25m
Problem statement
You have been given a square chessboard of size ‘N x N’. The position coordinates of the Knight and the position coordinates of the target are also given.
Your task is to find out the minimum steps a Knight will take to reach the target position.
knightPosition: {3,4}
targetPosition: {2,1}
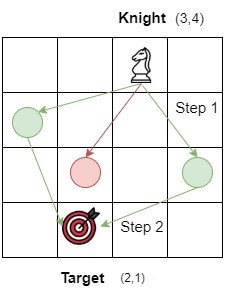
The knight can move from position (3,4) to positions (1,3), (2,2) and (4,2). Position (4,2) is selected and the ‘stepCount’ becomes 1. From position (4,2), the knight can directly jump to the position (2,1) which is the target point and ‘stepCount’ becomes 2 which is the final answer.
Note:
1. The coordinates are 1 indexed. So, the bottom left square is (1,1) and the top right square is (N, N).
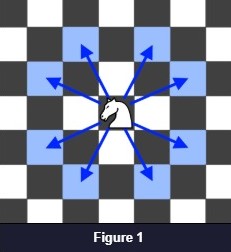
2. The knight can make 8 possible moves as given in figure 1.
3. A Knight moves 2 squares in one direction and 1 square in the perpendicular direction (or vice-versa).
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The next ‘3*T’ lines represent the ‘T’ test cases.
The first line of each test case contains a pair of integers denoting the initial position of the knight.
The second line of each input contains a pair of integers denoting the target position.
The third line of each test case contains an integer ‘N’ denoting the rows/columns of the chessboard.
Output format:
For each test case, print an integer representing the minimum steps a Knight will take to reach the target position.
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 1000
1 <= KNIGHTPOSITION(X, Y), TARGETPOSITION(X, Y) <= N
Time limit: 1 second
Sample input 1
2
8
2 1
8 5
6
4 5
1 1
Sample output 1
4
3
Explanation of sample input 1:
Test case 1:
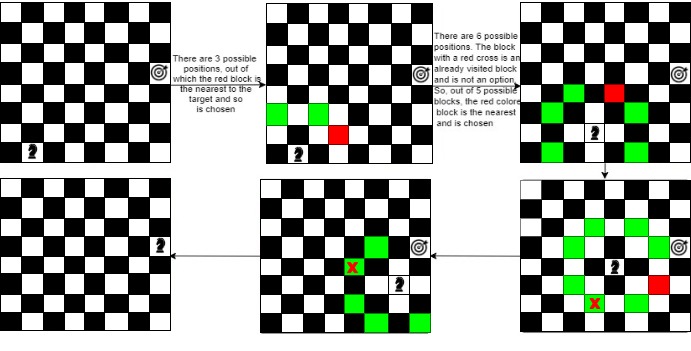
The knight is initially at position [2,1]. It has 3 possible blocks to move to, [4,2], [3,3], and [1,3]. The knight chooses [4,2]. Now, there are 6 more possible blocks to move to. The knight chooses [5,4]. Further, the knight chooses position [7,3]. Finally, the knight moves to the target position which is [8,5] which calculates to 4 steps.
Test case 2:
The knight moves from position [4,5] to [5,3] to [3,2] and finally to the target position [1,1] which gives us the minimum steps by the knight, that is, 3.
(4, 5) -> (5, 3) -> (3, 2) -> (1, 1).
Sample input 2:
2
6
2 4
6 4
6
1 1
4 5
Sample output 2:
2
3
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Consider all possible positions of the knight and select the most favourable one with the minimum steps.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Using BFS
The idea is to perform BFS traversal. Start from the initial position of the Knight and proceed to further cells. Traversal is performed using a queue. The queue stores the different paths travelled by the knight and also keeps storing the count of steps. When the target is popped from the queue, the corresponding count of the steps is the answer.
- Define a class with the following data members
a. ‘X_COORDINATE’ denoting the x-coordinate
b. ‘Y_COORDINNATE’ denoting the y-coordinate
c. ‘STEP_COUNT’ denoting the number of steps. - Take two arrays ‘DIRECTION_X’ and ‘DIRECTION_Y’ storing the direction in which the knight can move.
- Create a queue to store the class objects.
- Take a visited array to mark the cells already visited and initialize it to false.
- Push the initial position of the knight to the queue and mark it as visited.
- Loop till the queue is not empty.
- Pop the front element.
a. If the current cell is equal to the target cell, return the 'STEP_COUNT’ which is the minimum step a Knight will take to reach the target position.
b. Else, loop for all the reachable coordinates. If the coordinate is not yet visited and is reachable, push it to the queue along with the incremented value of ‘STEP_COUNT’.
Time Complexity
O(N^2), where ‘N’ is the number of rows/columns.
In the worst case, all the cells will be visited.
Space Complexity
O(N^2), where ‘N’ is the number of rows/columns.
In the worst case, all nodes will be stored in the queue.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Minimum steps to reach target by a Knight
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console




