Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Negative Cycle in a Directed Graph
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 25m
Problem statement
You have been given a directed weighted graph of ‘N’ vertices labeled from 1 to 'N' and ‘M’ edges. Each edge connecting two nodes 'u' and 'v' has a weight 'w' denoting the distance between them.
Your task is to detect whether the graph contains a negative cycle or not. A negative cycle is a cycle whose edges are such that the sum of their weights is a negative value.
Example:
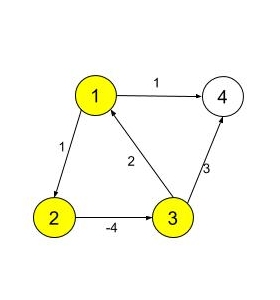
The above graph contains a cycle ( 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 1 ) and the sum of weights of edges is -1 (1 - 4 + 2 = -1) which is negative. Hence the graph contains a negative cycle.
Note:
It's guaranteed that the graph doesn't contain self-loops and multiple edges.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two single space-separated integers ‘N’ and ‘M’ denoting the number of vertices and the number of edges in the directed graph, respectively.
The next ‘M’ lines each contain three single space-separated integers ‘u’, ‘v’, and ‘w’, denoting an edge from vertex ‘u’ to vertex ‘v’, having weight ‘w’.
Output format:
For each test case, return “True” if there is a negative cycle, else “False”.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 50
1 <= M <= 300
1 <= u,v <= N
-10^5 <= w <= 10^5
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample input 1
1
5 6
1 5 2
2 1 1
2 3 -4
3 4 2
4 5 -3
5 2 1
Sample output 1
True
Explanation of sample input 1
In the 1st test case, there are two cycles ( 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 2) and ( 1 -> 5 -> 2 -> 1), but only the first one is the negative cycle.

Sample input 2
2
3 2
1 3 2
2 1 1
2 2
1 2 -1
2 1 -1
Sample output 2
False
True
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
We can use Bellman–Ford algorithm to detect a negative cycle in a graph.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Bellman-Ford Algorithm
Bellman-Ford Algorithm:
In this algorithm, we have a source vertex and we find the shortest path from source to all the vertices.
For this, we will create an array of distances ‘D[1...N]’, where ‘D[i]’ stores the distance of vertex ‘i’ from the source vertex. Initially all the array values contain an infinite value, except ‘D[source]’, ‘D[source]’ = 0.
The algorithm consists of several iterations and in each iteration, we try to produce relaxation in the edges. Relaxation means reducing the value of ‘D[i]’.
For this, we will iterate on the edges of the graph, let’s consider an edge (‘u’, ’v’, ’w’) :
- If ‘D[v]’ is greater than ‘D[u]’ + ‘w’, then ‘D[v]’ = ‘D[u]’ + ‘w’.
The algorithm claims that ‘N-1’ iterations are enough to find the distances of the vertices from the source vertex.
How to use this algorithm to detect a negative cycle in a graph?
Using this algorithm, we can find the distances of the vertices from the source vertex. But instead of ‘N-1’ iteration, we will do ‘N’ iterations and in the last iteration, if there is any change in the values of array ‘D’, then the given graph contains a negative cycle.
Algorithm:
- Iterate on the source (vertex 1 to vertex ‘N’).
- Make an array ‘D’ and initialize the array with an infinite value, except ‘D[source]’, ‘D[source]’ = 0.
- Do ‘N’ iterations and in each iteration follow the below steps:
- Iterate on the edges on the graph and for each edge (‘u’,’v’,’w’) update the value to ‘D[v]’, i.e., ‘D[v]’ = min(‘D[v]’, ‘D[u]+w’).
- In the Nth iteration, if there is an edge (‘u’,’v’,’w’) such that, ‘D[v]’ is less than ‘D[u]+w’, then the given graph contains a negative cycle.
Time Complexity
O(N^2 * M), where ‘N’ is the number of vertices in a graph and ‘M’ is the number of edges in the graph.
We are iterating on the source vertex and there are ‘N’ vertices so it will take O(N) time. For every source vertex, we are doing ‘N’ iterations and in each iteration, we are iterating on the edges of the graph, so it will take O(N * M) time. Thus, the final time complexity will be O(N * N * M) = O(N^2 * M).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of vertices in a graph.
We are making an array ‘D’ which will take O(N) extra space.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Negative Cycle in a Directed Graph
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console


