Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Network Delay Time
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 20m
21 upvotes
Asked in companies



Problem statement
You have been given a network of ‘N’ nodes from 1 to ‘N’ and ‘M’ edges. For each edge, you are given three values (ui, vi, wi) where “ui” and “vi” denote the nodes and “wi” denotes an integer value which represents the time taken by a signal to travel from “ui” to “vi”. Now, you are supposed to find the time which a signal takes to travel from a given node ‘K’ to all nodes. If it is impossible for all nodes to receive the signal then print -1.
Note:The signal which starts from the source node travels to all nodes simultaneously.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains a single integer ‘T’ representing the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case will contain three space-separated integers ‘N’, ‘M’ and ‘K’ where ‘N’ is the number of the nodes in the network, and ‘M’ is the number of edges and ‘K’ is the source node.
The next ‘M’ lines contain three space-separated integers (u, v, w) which denote a directed edge in the network from node ‘u’ to node ‘v’ with weight ‘w’.
For each test case, print a single line containing a single integer denoting the time it takes for all the ‘N’ nodes to receive the signal. Print -1 if it is impossible for all nodes to receive the signal from the source node.
The output for every test case will be printed in a separate line.
You don’t need to print anything; It has already been taken care of. Just implement the function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 50
1 <= N <= 3000
0 <= M <= 10000
1 <= u, v, K <= N
0 <= w <= 10000
Where ‘T’ is the number of test cases, ‘N’ is the number of the nodes in the network, and ‘M’ is the number of edges and ‘K’ is the source node and ‘u’, ‘v’, ‘k’ are the nodes of the network and ‘w’ is the weight of the edges.
Time limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
2
4 3 1
1 2 2
1 3 1
3 4 2
3 2 1
1 2 1
3 2 3
Sample Output 1:
3
-1
Explanation of sample input 1:
In the first test case,
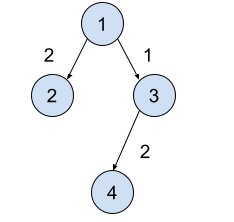
The signal will reach every node in 3 units of time.
In the second test case,
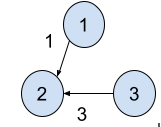
The signal will never reach node 3. So, print -1.
Sample Input 2:
2
4 5 3
3 1 2
3 4 3
1 4 1
1 2 1
2 4 2
2 1 1
1 2 5
Sample Output 2:
3
5
Explanation for sample input 2:
In the first test case, the signal will reach each node in 3 units of time.
In the second test case, the signal will reach each node in 5 units of time.
Hint
Hint 1
Can you find the shortest path from the source node (‘K’) to each node in the network?
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Dijkstra's Algorithm based approach.
The basic idea of this approach is to find the shortest path from the source node (‘K’) to each node in the network. We will use Dijkstra’s Algorithm to achieve this task. We will use priority_queue based implementation for this problem.
You can refer here for a more detailed explanation of Dijkstra’s Algorithm -
Now, consider the following steps:
- Create an adjacency list “adj” of the graph from the given list of edges.
- Create an array/list “dist” and initialize it to a very large number (say “INF”). It stores the shortest path length for each node from the source node (‘K’).
- Create a min priority_queue of pair<int, int> which stores the pair of path distance and the node itself.
- Push {0, ‘K’} in the priority_queue as K is the source node and the initial distance is 0.
- Now, iterate while there is an element in the priority_queue.
- Extract the top element and pop it from the priority_queue. Let’s say the current node is ‘v’ and distance is ‘w’.
- If the current shortest path length for ‘v’ is less than ‘w’ then go to step 5 (a).
- Otherwise, iterate through edges that start from node ‘v’ and ends at ‘u’ (let’s say). If the shortest path length is greater than ‘w’ + weight of the current edge then update the path length for node ‘u’ and set dist[u]=w + weight of current edge and push the updated shortest path length in the priority_queue.
Now, we will iterate through the “dist” array/list and find the maximum value. If the maximum value is equal to “INF” then return -1 else return the maximum value.
Time Complexity
O(M * log(N)), where ‘N’ and ‘M’ are the number of nodes and the number of edges, respectively.
Since we are using a priority_queue to store the intermediate shortest path length for each node and then for each node we are iterating through the adjacent edges, and pop and push operations in a priority queue take log(N) time, so the overall time complexity will be O(M * log(N)).
Space Complexity
O(N + M), where ‘N’ and ‘M’ are the number of nodes and the number of edges, respectively.
Since we are storing the shortest path length of each node in an array/list which takes O(N) space and the adjacency list takes O(M) space. So, the overall space complexity will be O(N + M).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Network Delay Time
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
