Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Ninja And The Malicious Software
Hard
0/120
3 upvotes
Asked in companies


Problem statement
The computer network of the company NinjaWorks has been attacked by malware, causing damage to the computer systems. Ninja is the chief security officer(CSO) of NinjaWorks and is trying to reduce the damage caused by the malware.
The computer network at NinjaWorks consists of ‘N’ computers represented as an ‘N’ x ‘N’ adjacency matrix ‘GRAPH’. GRAPH[i][j] = 1, denotes that ith computer is directly connected to the jth computer. Some computers ‘INFECTED’ are already infected by the malware. If two computers are connected, and one is infected, then both computers will be infected by the malware. The spread of malware will continue until no more computers are left to be infected.
Ninja being the CSO of NinjaWorks, can remove exactly one computer from ‘INFECTED’. But Ninja is confused about which computer to remove. Can you help Ninja find such a computer whose removal would minimize the spread of malware? If multiple such nodes exist, return the node with the smallest index.
For Example:
You are given ‘N’ = 5, ‘GRAPH’ = [[1, 1, 1, 0, 0],[1, 1, 0, 0, 0],[1, 0, 1, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 1, 1],[0, 0, 1, 0, 0]], ‘M’ = 2 and ‘INFECTED’ = [2 ,4].
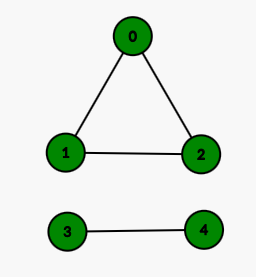
If we remove computer number 2 from infected computers, we can prevent computers numbers 0 and 1 from getting infected. Then total infected computers will be 2(3 and 4). If we remove computer number 4 from infected computers, we can prevent computer number 3 from getting infected. Then total infected computers will be 3(0, 1, and 2). Hence, it’s better to remove computer number 2 from infected computers.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line of the input contains a single integer 'T', representing the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two space-separated integers, ‘N’ and ‘M’, representing the number of the computers and the number of initially infected computers, respectively.
The next line ‘N’ lines contain ‘N’ space-separated integers representing the computer network.
The next line contains ‘M’ space-separated integers representing the infected computers.
For each test case, print the index(0-indexed) of the computer to be removed to minimize the spread of the malware.
Print the output of each test case in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
2 <= N <= 2000
1 <= M <= N
0 <= GRAPH[i][j] <= 1
GRAPH[i][j] == GRAPH[j][i]
GRAPH[i][i] = 1
0 <= INFECTED[i] < N
INFECTED contains unique elements.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
2
5 2
1 1 1 0 0
1 1 0 0 0
1 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1
0 0 1 0 0
2 4
4 1
1 1 1 0
1 1 0 0
1 0 1 1
0 0 1 1
1
Sample Output 1:
2
1
Explanation of Sample Input 1:
For the first test case, the graph will look like this:

If we remove computer number 2 from infected computers, we can prevent computers numbers 0 and 1 from getting infected. Then total infected computers will be 2(3 and 4). If we remove computer number 4 from infected computers, we can prevent computer number 3 from getting infected. Then total infected computers will be 3(0, 1, and 2). Hence, it’s better to remove computer number 2 from infected computers.
For the second test case, the graph will look like this:
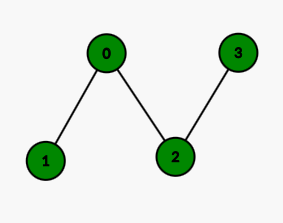
We can only remove computer number 1.
Sample Input 2:
2
2 2
1 1
1 1
0 1
3 1
1 0 1
0 1 0
1 0 1
2
Sample Output 2:
0 2
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Find connected components.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Depth-First Search
In this approach, we will color each component with color using a depth-first search. Each connected component will have a different color. Now, we can observe that if two computers in ‘INFECTED’ have the same color, removing any one of them won’t decrease the spread because the other can still infect the whole component. So, we will remove a computer that satisfies the following properties:
- Have unique color among the infected computers.
- Belong to the largest component.
If there exists more than one such computer, we will remove the one with the lowest index.
Algorithm :
- Initialize a list ‘COLORS’ to store the color of each computer.
- Initialize a variable ‘CLR’ to store the current color.
- Iterate ‘V’ in 0 to ‘N’
- If ‘COLORS’[‘V’] is equal to -1.
- Call DFS on ‘V’ and increment ‘CLR’ by 1.
- If ‘COLORS’[‘V’] is equal to -1.
- Initialize a list ‘COLORSIZE’ to store the size of each color.
- Iterate ‘COLOR’ in ‘COLORS’:
- Increment ‘COLORSIZE’[‘COLOR’] by 1.
- Iterate ‘V’ in ‘INFECTED’:
- Increment ‘COLORCOUNT’[‘COLORS’[‘V’]] by 1.
- Initialize a variable ‘ANS’ with the maximum integer value.
- Iterate ‘V’ in ‘INFECTED’:
- Initialize a variable ‘C’ with the value ‘COLORS’[‘V’].
- If ‘COLORCOUNT’[‘C’] is equal to 1:
- If ‘ANS’ is equal to the maximum integer value:
- Set ‘ANS’ as ‘V’.
- Otherwise, if ‘COLORSIZE’[‘C’] is greater than ‘COLORSIZE’[‘COLORs’[‘ANS’]]:
- Set ‘ANS’ as ‘V’.
- Otherwise, if ‘COLORSIZE’[‘C’] is equal to‘COLORSIZE’[‘COLORs’[‘ANS’]] and ‘V’ is less than ‘ANS’:
- Set ‘ANS’ as ‘V’.
- If ‘ANS’ is equal to the maximum integer value:
- If ‘ANS’ is equal to a maximum integer value:
- Iterate ‘V’ in ‘INFECTED’:
- Set ‘ANS’ as the minimum of ‘ANS’ and ‘V’.
- Iterate ‘V’ in ‘INFECTED’:
- Return ‘ANS’.
Maintain a function DFS(int[][] ‘GRAPH’, int[] ‘COLORS’, int ‘V’, int ‘COLOR’)
- Set ‘COLORS’[‘V’] as ‘COLOR’.
- Iterate ‘NEIGHBOR’ in 0 to ‘GRAPH.LENGTH’:
- If ‘GRAPH’[‘V’][‘NEIGHBOR’] is equal to 1 and ‘COLORS’[‘NEIGHBOR’] is equal to -1:
- Call DFS on ‘NEIGHBOR’.
- If ‘GRAPH’[‘V’][‘NEIGHBOR’] is equal to 1 and ‘COLORS’[‘NEIGHBOR’] is equal to -1:
Time Complexity
O(N ^ 2), where ‘N’ is the total computers.
We have to traverse the ‘N’ x ‘N’ matrix, which will take O(N ^ 2) time. Hence, the total time complexity is O(N ^ 2).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the total computers.
The maximum size auxiliary arrays ‘COLORS’, ‘COLORSIZE’ and ‘COLORCOUNT’ is ‘N’. Hence, the total space complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Ninja And The Malicious Software
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
