Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Gray Code
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 25m
Problem statement
Given a number ‘grayNumber’. Find the gray code sequence.
Conditions for a gray code sequence :
1. Gray code sequence contains numbers from 0 to 2^'grayNumber'-1 in bit/binary form.
2. Two consecutive gray code sequence numbers only differ by 1 bit.
3. Gray code sequence must start with 0.
Example :
Given 'grayNumber' : 2.
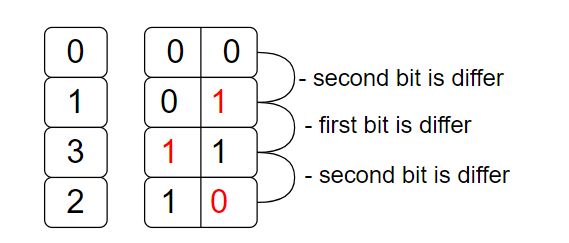
As depicted from above image, the gray code sequence is 0,1,3,2.
Note :
1. The output sequence must contain the decimal representation of numbers instead of the binary form.
2. There can be multiple answers print anyone.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of every test case contains an integer ‘grayNumber’.
For each test case, return the ‘list/vector’ of the Gray code sequence.
The output is ‘Valid’ if returned gray code sequence is correct. Else ‘Invalid’.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 2
0 <= grayNumber <= 15
Time Limit : 1 sec
Sample Input 1 :
2
2
3
Sample Output 1 :
Valid
Valid
Explanation For Sample Input 1 :
For first test case,
Given 'grayNumber' : 2
Bits representation of a number from 0 to 2^2-1 = 3 is “ 00, 01, 10, 11’’.
But we have arranged these bits in such a way that two consecutive bits only differ by 1.
Only one possible way is “00, 01, 11, 10 ”.
Hence return value of every number “ 00 - 0 , 01 - 1, 11 - 3, 10 - 2”.
Sequence : {0, 1, 3, 2}.
For second test case,
Given 'grayNumber' : 3
Bits representation of a number from 0 to 2^3-1 =7 is “000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111’’.
But we have arranged these bits in such a way that two consecutive bits only differ by 1.
One of the possible ways is “000, 001, 011, 111, 101, 100, 110, 010”.
Hence return value of every number “000 - 0, 001 - 1, 011 - 3, 111 - 7, 101 - 5, 100 - 4, 110 - 6, 010 - 2 ”.
Sequence : {0, 1, 3, 7, 5, 4, 6, 2}.
One another possible sequence can be : {0, 1, 3, 2, 6, 7, 5, 4}.
Sample Input 2 :
2
4
1
Sample Output 2 :
Valid
Valid
Explanation For Sample Input 2 :
For first test case,
Given 'grayNumber' : 4
Sequence : {0, 1, 3, 2, 6, 7, 5, 4, 12, 13, 15, 14, 10, 11, 9, 8}.
For second test case,
Given 'grayNumber' : 1
Sequence : {0, 1}.
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Hint 3
Hint 4
Observe the pattern of the Gray code sequence.
Approaches (4)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Approach 3
Approach 4
Iterative
Suppose are finding an answer for ‘N’ size but we have already the solution for ‘N-1’. then use the previous answer for a new answer. (where ‘N’ is ‘grayNumber’)
- Let’s consider ‘N' : 3 and we have solution of ‘N-1' : 2 : { ‘00’, ‘01’, ‘10’, ‘11’} and called it ‘PRE’.
- Create a new list/vector of ‘PRE’ in reverse order { ‘11’, ‘10’, ‘01’, ‘00’ } called it ‘NEW’.
- Add ‘0’ as a prefix, in all the elements of ‘PRE’ : { ‘000’, ‘001’, ‘010’, ‘011’ } /
- Add ‘1’ as a prefix, in all the elements of ‘NEW’ : { ‘111’, ‘110’, ‘101’, ‘100’} .
- Concatenate the ‘PRE’ + ‘NEW’ and it will be answered for ‘N' : 3.
- Return a number conversion of new concatenated ‘list/vector’.
Time Complexity
O(2^N*Log(N)), where ‘N’ is the given number ‘grayNumber’.
We are iterating the loop of size ‘2^N and Log(n) represents the number of bits in number ‘N’ in binary bits representation. Therefore, the overall time complexity will be O(2^N*Log(N)).
Space Complexity
O(2^N), where 'N' is the given number 'grayNumber'.
We are using a list/vector ('grayCode') of size 2^'N' to store the numbers. Therefore, the overall space complexity will be O(2^N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Gray Code
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console


