Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Pair Sum in BST.
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 15m
Problem statement
You are given a Binary Search Tree (BST) and a target value ‘K’. Your task is to return true if there exist two nodes in the given BST such that the sum of their values is equal to the given target ‘K’, else return false.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
1. All the elements of the Binary Search Tree are unique.
2. You can’t use the same node value/element of BST twice.
tree: 8 5 10 2 6 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 7 -1 -1
'K' = 13,

The nodes with values 8 and 5 as shown in the above figure gives sum equal to the given target 13.
Therefore, the output will be “true” i.e it is possible to find a pair in the given BST having sum equal to ‘K’.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains elements of the Binary Search Tree in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case, a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
The second line contains a single integer ‘K’ which denotes the target value.
The input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
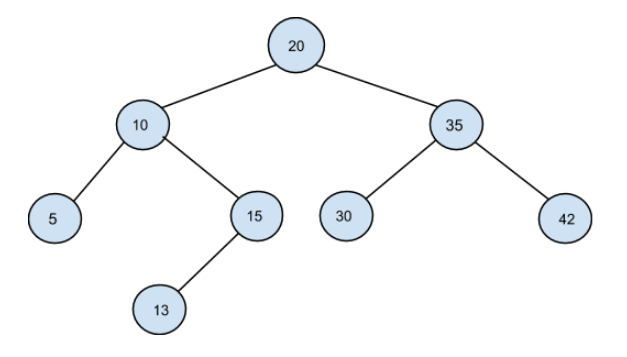
20 10 35 5 15 30 42 -1 -1 13 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
The only line contains "true" if there exist two nodes in the given BST such that the sum of their values is equal to the given target ‘K’, otherwise "false".
Note:
You don’t need to print the output, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Sample Input 1:
8 5 10 2 6 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 7 -1 -1
19
Sample Output 1:
false
Explanation for sample input 1:
There are no two elements in the given BST such that their sum equals the given target ‘K’ = 19.
Sample Input 2 :
20 16 -1 12 -1 8 -1 4 -1 -1 -1
12
Sample Output 2:
true
Constraints:
1 <= 'N' <= 10^5
1 <= DATA <= 10^6
1 <= 'K' <= 10^6
Where ‘DATA’ denotes the value of each node in the given tree and ‘N’ denotes the number of nodes in BST.
Time limit: 1 sec
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Hint 3
Hint 4
Think of a solution where you will look for the difference of the given value, ‘K’ and the current node’s value in the given BST.
Approaches (4)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Approach 3
Approach 4
Brute Force Approach
The idea is that if the sum of any two elements say, ‘A’ and ‘B’ is equal to the given value ‘K’, and we already know that ‘A’ is present in the given tree then we only need to check whether element ‘B’ = ‘K’ - ‘A’ exists in the tree or not. We can check this by using the property of the binary search tree.
Approach :
- Using depth-first search (DFS), we traverse the given BST.
- For each node, we calculate the value ‘Q’ i.e ‘K’ - current node’s value.
- Now, using the property of BST, we search this value in the given tree.
- If the value of the current node is less than ‘Q’, we will search in the right subtree recursively.
- If the value of the current node is more than ‘Q’, we will search in the left subtree recursively.
- If the value of the current node equals ‘Q’, we will return “true” to the function.
- If the value is not found for any node, we will return “false” to the function.
Time Complexity
O(N ^ 2), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the given BST (Binary Search Tree).
Since, we will be traversing each node of BST with O(N), and for each node, we will be searching in a given BST which takes O(H) time. For skewed trees, H will become N.Hence, the overall time complexity will be O(N ^ 2).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the given BST (Binary Search Tree).
O(H) recursion stack space is used by the algorithm where H is the height of BST. In the worst case (for skewed trees), H will become N. Hence, the overall space complexity will be O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Pair Sum in BST.
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



