Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Partition
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 10m
Problem statement
You are given a linked list and a number ‘x’, You have to partition the linked list in such a way that all nodes with a value less than 'x' comes before the nodes with values greater than or equal to 'x'. The original relative order should be preserved.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format
The first line of input contains an integer 'T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The next ‘2*T’ lines represent the ‘T’ test cases.
The first line of each test case contains integers denoting the nodes of the linked list. Each line is guaranteed to have -1 at the end to signify the end of the linked list.
The second line contains an integer ‘x’.
For each test case, print space-separated integers terminated by -1 denote the elements of the given linked lists which are sorted in non-decreasing order.
The output of each test case should be printed in a new line.
Constraints
1 <= ’T’ <= 50
-1000 <= ’x’ <= 1000
0 <= Length of linked list <= 10000
-1000 <= "data" <= 1000
"data" != -1, 'x' != -1
Where 'T' is the number of test cases. 'x' denotes the given integer and "data" denotes the linked list node value.
Sample Input 1
2
5 4 7 1 2 3 -1
4
1 2 3 4 0 5 6 -1
3
Sample Output 1:
1 2 3 5 4 7
1 2 0 3 4 5 6
Explanation:-
Here is the linked list for the first test case:-
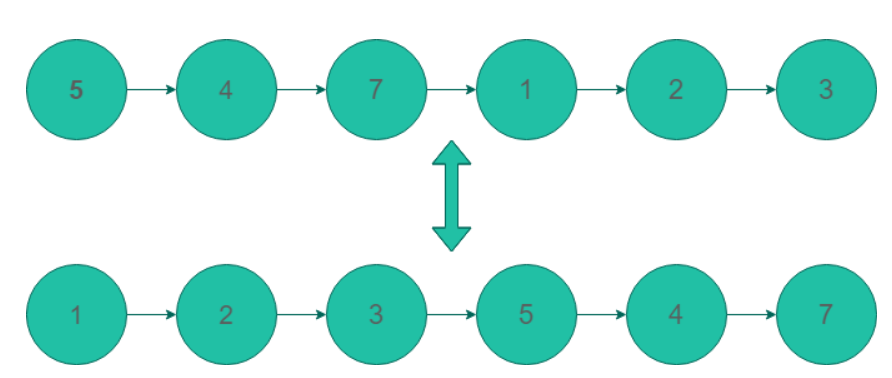
The nodes with value 1,2,3 are less than x that is
4.They should appear before 5,4,7
Sample Input 2:
2
-3 5 -2 6 4 7 -1
5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 -1
1
Sample Output 2:
-3 -2 4 5 6 7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Hint-Create an array and copy the values of linked lists into an array.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Partition
Explanation:-
The key idea will be to create two vectors ‘small’ and ‘big’ and store all the values less than ‘x’ in the small vector and values greater than ‘x’ in the big vector. In this way, the relative order will be preserved.
The algorithm is as follows:
- Create two vectors ‘small’ and ‘big’
- Iterate the linked list. If the value of a current node is less than ‘x’ insert the value of a current node in a small vector else insert the value of a current node in a big vector.
- Insert all the values of ‘big’ vector at the end of ‘small’ vector.
- After inserting update the value of ith node of a given linked list with the ith value of ‘small’ vector.
- Return the head of the given linked list
Time Complexity
O(n), Where ‘n’ is the length of the linked list.
We are iterating over the linked and traversing every node, Hence it would take O(n)
time.
Space Complexity
O(n), Where ‘n’ is the length of the linked list.
We are creating the vector to store the values of the linked list.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Partition
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console




