Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Path visiting all nodes
Hard
0/120
Average time to solve is 45m
Problem statement
You are given a connected undirected unweighted graph of ‘N’ nodes and ‘M’ edges, such that there is only one undirected edge between any two nodes and no self-loop. Your task is to find the length of the shortest path that visits all ‘N’ nodes at least once.
Note :
1) Here length of the path refers to the number of edges in that path.
2) You can start and stop at any node.
3) You can visit any node 0 or more times.
4) You can use any given edge 0 or more times.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line of input contains an integer 'T' representing the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two space-separated integers, ‘N’ and ‘M’, where ‘N’ denotes the total number of nodes and ‘M’ denotes the total number of edges in the graph.
The next ‘M’ lines contain two space-separated integers, ‘U’ and ‘V’, where ‘U’ and ‘V’ represent the nodes that share a common undirected edge between them.
Output Format :
For each test case, print the length of the shortest path that visits all ‘N’ nodes in the given graph.
The output of each test case will be printed in a separate line.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 5
1 <= N <= 10
N - 1 <= M <= N * (N - 1) / 2
0 <= U, V <= N - 1
Where ‘T’ is the number of test cases, ‘N’ denotes the total number of nodes and ‘M’ denotes the total number of edges in the graph, and ‘U’ and ‘V’ denotes the nodes that share a common undirected edge between them.
Note :
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Sample Input 1 :
2
3
3
0 1
0 2
1 2
4
3
0 1
1 2
2 3
Sample Output 1 :
2
3
Explanation of Sample Input 1 :
Test Case 1 :
The given graph is shown below.
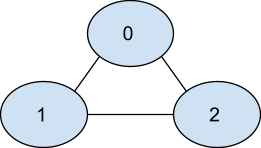
One possible shortest path that starts from node 0 ends at node 2 and visits all nodes is [0 - 1 - 2]
The number of edges in this path is 2.
So the length of the shortest path that visits all nodes in the given graph will be 2.
Test Case 2 :
The given graph is shown below.
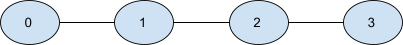
One possible shortest path that starts from node 0 ends at node 3 and visits all nodes is [0 - 1 - 2 - 3]
The number of edges in this path is 3.
So the length of the shortest path that visits all nodes in the given graph will be 3.
Sample Input 2 :
1
5
8
0 1
0 2
0 3
0 4
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 3
Sample Output 2 :
4
Explanation of Sample Input 2 :
Test Case 1 :
The given graph is shown below.
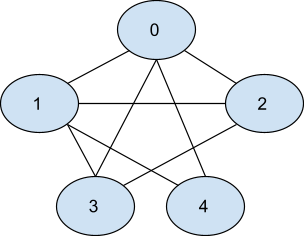
One possible shortest path that starts from node 3 ends at node 4 and visits all nodes is shown below. The edges marked in red-colored are the edges that are traversed in the path.
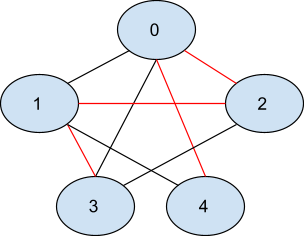
The number of edges in the path [3 - 1 - 2 - 0 - 4] is 4.
So the length of the shortest path that visits all nodes in the given graph will be 4.
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Hint 3
Do a depth-first search on the given graph and try all possible paths that visit all the ‘N’ nodes.
Approaches (3)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Approach 3
Depth-First Search
The idea here is to do a depth-first search from all ‘N’ nodes and try all possible paths that visit all the nodes in the given graph. Out of all possible paths that start from any node ‘i’ and end at any node ‘j’, where ‘i’ and ‘j’ are from 0 to ‘N’ - 1 inclusive, we will take the path that has the shortest length, i.e., the path with the minimum number of edges and visits all the ‘N’ nodes in the given graph.
Algorithm:
- Declare a 2 - Dimensional array of integers, say ‘adjList’, to store the adjacency list of the given graph.
- Build the adjacency list using the ‘edges’ array given in the problem.
- Declare an integer, say ‘minLength’, to store the length of the shortest path that visits all the ‘N’ nodes in the given graph and initialize it with 2 * ‘N’
- Declare an ‘N’ bit integer, say ‘visited’, where the i-th bit denotes whether the i-th node is visited or not, and initialize it with 0.
- Declare a 2 - Dimensional array of booleans, say ‘inProcess’, of size N * 2 ^ N, to avoid cycles during the depth-first search and initialize it with false.
- Run a loop for ‘i’ from 0 to ‘N’ - 1
- Declare an integer, say ‘currVisited’, and initialize it with ‘visited’.
- Mark the i-th bit of ‘currVisited’ as 1.
- Call the ‘depthFirstSearch’ function with ‘i’, ‘currVisited’, ‘inProcess’ and ‘adjList’ as arguments, and store its returned value in ‘currLength’
- Update ‘minLength’ as the minimum of ‘minLength’ and ‘currLength’.
- Return the maximum of ‘minLength’ - 1 and 0.
Description of ‘depthFirstSearch’ function
This function is used to traverse the given graph and find the length of the shortest path that visits all the ‘N’ nodes.
This function will take four parameters :
- node: An integer denoting the node in the given graph.
- visited: An ‘N’ bit integer denoting the visited nodes.
- inProcess: A 2 - Dimensional array of booleans to avoid cycles.
- adjList: A 2 - Dimensional array of integers denoting the adjacency list of the given graph.
int depthFirstSearch(node, visited, inProcess, adjList)
- If all the bits of ‘visited’ is 1, then return 0.
- Declare an integer, say ‘minLength’, to store the length of the shortest path that visits all the ‘N’ nodes in the given graph and initialize it with 2 * ‘N’
- If ‘inProcess[node][visited]’ is false:
- Mark ‘inProcess[node][visited]’ as true.
- Run a loop for ‘i’ from 0 to the size of adjList[node] - 1
- Declare an integer, say ‘currVisited’, and initialize it with ‘visited’.
- Mark the ‘node’ bit of ‘currVisited’ as 1.
- Call the ‘depthFirstSearch’ function with ‘adjList[node][i]’, ‘currVisited’, ‘inProcess’ and ‘adjList’ as arguments, and store its returned value in ‘currLength’.
- Update ‘minLength’ as the minimum of ‘minLength’ and ‘currLength’ + 1.
- Mark ‘inProcess[node][visited]’ as false.
- Return ‘minLength’
Time Complexity
O(N ^ N + M), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes and ‘M’ is the number of edges in the given graph.
Here, building the adjacency list will take O(M) time since we have ‘M’ edges to insert in the adjacency list.
In the worst case, we can have 2 * N - 1 nodes in the shortest path, this case occurs when the given graph is a star graph, and for every node, we have ‘N’ choices. Therefore there will be approximately N ^ N different possible paths.
Hence, the overall time complexity will be O(M) + O(N ^ N), which is O(N ^ N + M).
Space Complexity
O(M + N + (N * 2 ^ N)), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes and ‘M’ is the number of edges in the given graph.
We are using an adjacency list that takes O(M) space to insert ‘M’ edges into the list. Moreover, we need O(N) extra space in the form of recursive calls for depth-first search when the given graph is a path graph. Also, O(N * (2 ^ N)) space is taken by the ‘inProcess’ array.
Hence, the overall space complexity will be O(M) + O(N) + O(N * (2 ^ N)), which is O(M + N + N * (2 ^ N)).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Path visiting all nodes
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



