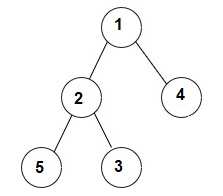
public static List < Integer > getPreOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> treelist = new ArrayList<>();
preOrderTraversal(root, treelist);
return treelist;
}
public static void preOrderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> treelist){
if(root == null){
return;
}
treelist.add(root.data);
preOrderTraversal(root.left, treelist);
preOrderTraversal(root.right, treelist);
}