Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Prim's MST
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 15m
99 upvotes
Asked in company

Problem statement
You are given an undirected connected weighted graph having ‘N’ nodes numbered from 1 to 'N'. A matrix ‘E’ of size M x 2 is given which represents the ‘M’ edges such that there is an edge directed from node E[i][0] to node E[i][1]. You are supposed to return the minimum spanning tree where you need to return weight for each edge in the MST.
For example :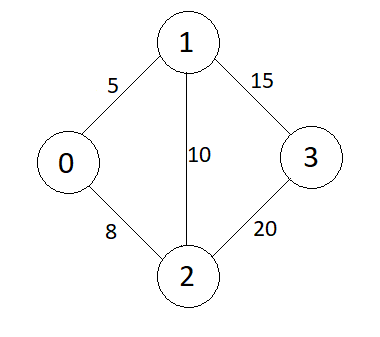
The MST (Minimum Spanning Tree) for the above graph is:
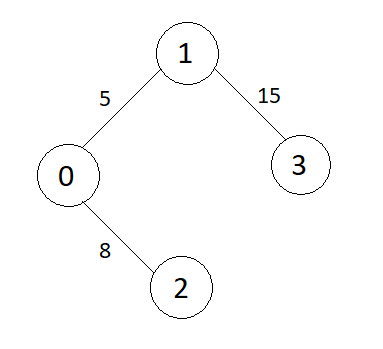
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line of input contains an integer 'T' representing the number of the test case. Then the test cases are as follows.
The first line of each test case argument given is an integer ‘N’ representing the number of nodes in the graph.
The second line of each test case contains a given integer ‘M’ representing the number of edges.
The next ‘M’ lines in each test case contain a matrix ‘E’ of size M x 2 which represents the ‘M’ edges such that there is an edge directed from node E[i][0] to node E[i][1].
For each test case, print the minimum spanning tree in the form of edges and their weights which are included in the MST.
You do not need to print anything; It has already been taken care of.
Constraints :
1 ≤ T ≤ 5
2 <= N <= 100
1 <= M <= min(1000, N(N - 1) / 2)
1 <= E[i][0], E[i][1] <= N
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1 :
1
5 14
1 2 2
1 4 6
2 1 2
2 3 3
2 4 8
2 5 5
3 2 3
3 5 7
4 1 6
4 2 8
4 5 9
5 2 5
5 3 7
5 4 9
Sample Output 1 :
1 2 2
1 4 6
2 3 3
2 5 5
Explanation of Input 1 :
The Minimum spanning tree for the given graph will contain the edges: (1,2) with weight 2, (1,4) with weight 6, (2,3) with weight 3 and (2,5) with weight 5.
Sample Input 2 :
1
5 15
1 2 21
1 4 16
2 1 12
2 3 13
2 4 18
2 5 15
3 2 13
3 5 17
4 1 16
4 2 18
4 5 19
5 1 18
5 2 15
5 3 17
5 4 19
Sample Output 2 :
1 2 12
1 4 16
2 3 13
2 5 15
Explanation of Input 2 :
The Minimum spanning tree for the given graph will contain the edges: (1,2) with weight 12, (1,4) with weight 16, (2,3) with weight 13 and (2,5) with weight 15.
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Think of implementing Prim’s algorithm to create Minimum Spanning Tree(MST).
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Prim's Algorithm
Here, we will use Prim’s algorithm to calculate MST(Minimum Spanning Tree). The idea behind Prim’s algorithm is simple, a spanning tree means all vertices must be connected. So the two disjoint subsets of vertices must be connected to make a Spanning Tree. And they must be connected with the minimum weight edge to make it a Minimum Spanning Tree.
Prim’s algorithm is a greedy algorithm that maintains two sets, one represents the vertices included (in MST), and the other represents the vertices not included (in MST). At every step, it finds the minimum weight edge that connects vertices of set 1 to vertices of set 2 and includes the vertex on the other side of edge to set 1(or MST).
Prim’s algorithm finds the minimum weight edge in the cut and includes the vertex on this edge in MST and repeats this process till all the vertices are included in the MST.
- Create an array ‘INCLUDED_MST’, that represents whether or not the current vertex is included (in MST).
- Create another array ‘MIN_EDGE_CUT’, that represents the minimum weight edge in the cut from the current vertex.
- Initialize ‘MIN_EDGE_CUT' as INFINITE for all the vertices and 0 for the first vertex.
- Pick a vertex(say ‘U’) with ‘MIN_EDGE_CUT’ value that is not included (in MST) and include it in MST.
- Update the values of ‘MIN_EDGE_CUT’ for all the adjacent vertices that are not included(in MST) for the picked vertex.
- To update values, for every adjacent vertex ‘V’, if the weight of edge ‘U’ - ‘V’ is less than the current ‘MIN_EDGE_CUT’ value of ‘V’, update the ‘MIN_EDGE_CUT’ value as the weight of the ‘U’ - ‘V’.
- Repeat steps 4, 5, and 6 till all the vertices are not included.
Time Complexity
O(N ^ 2), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes and ‘M’ is the number of edges.
The Time Complexity of Prim’s method uses a matrix, so the overall time complexity will be O(N ^ 2).
Space Complexity
O(N ^ 2), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes.
Since we create an edges matrix for ‘N’ nodes, so the overall space complexity will be O(N ^ 2).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Prim's MST
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
