Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Rotate DLL
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 10m
Problem statement
You are given a doubly-linked list with 'N' nodes, rotate the linked list counter-clockwise by 'K' nodes. 'K' is a positive integer and is smaller than the number of nodes in the linked list, that is 'N'.
For exampleThe given linked list is -
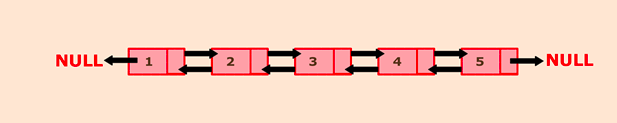
If K = 3, then the list after rotating it by K nodes is:
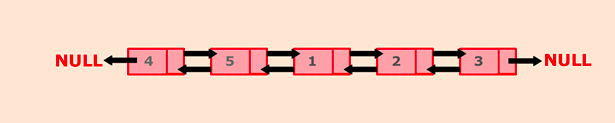
1. The value of any node in the linked list will not be equal to -1.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains 'N' space-separated integers representing the value of each node. -1 at the end denotes NULL pointer.
The second line of each test case contains a single positive integer 'K'.
For each test case, in a separate line, print the final rotated linked list.
You don’t have to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 5
1 <= N <= 3000
1 <= K < N
-10 ^ 7 <= data <= 10 ^ 7
where ‘T’ is the total number of test cases, 'N' is the total number of nodes in the linked list and ‘data’ is the value of any node of the linked list.
Sample Input 1 :
2
4 3 9 1 7 8 -1
4
1 2 3 4 5 -1
2
Sample Output 1 :
7 8 4 3 9 1
3 4 5 1 2
Explanation of The Sample Input 1:
For the first test case:
The given linked list is :
4 <-> 3 <-> 9 <-> 1 <-> 7 <-> 8 <-> NULL
And K = 4 therefore we have to rotate the linked list by 4 nodes. So after the rotation, list will become
7 <-> 8 <-> 4 <-> 3 <-> 9 <-> 1 <-> NULL
For the second test case:
The given linked list is
1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 4 <-> 5 <-> NULL
And K = 2 therefore we have to rotate the linked list by 2 nodes. So after the rotation, list will become
3 <-> 4 <-> 5 <-> 1 <-> 2 <-> NULL
Sample Input 2 :
2
6 2 4 2 1 4 -1
2
12 33 55 11 22 -1
3
Sample Output 2 :
4 2 1 4 6 2
11 22 12 33 55
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Can you use a new list to rotate?
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Using extra space
The idea is to use an extra list to first store the last N - K elements then store the starting K elements.
- Declare an integer variable 'count' and initialize it with 0.
- First, iterate through the list and keep a count for the nodes, that is, iterate it till the count becomes equal to K and store that pointer to the node.
- Now make a new linked list and start storing nodes from the pointer that is stored above till the last node of the original list.
- Again iterate through the initial list from starting till the count becomes equal to 0 and keep storing these nodes in the new list.
Keep decreasing count by 1. - Return the head of the new list.
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ denotes the number of nodes in the linked list.
Since we are iterating the linked list once for storing after the Kth node, therefore, it will be O(K) and for further N-K nodes will be O(N-K) and then again for putting first K nodes back in the new list so overall Time Complexity will be O(K) + O(N-K) + O(K) = O(2*K) + O(N-K) = O(N + K) which will effectively give = O(N) since K is less than equal to N.
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ denotes the number of nodes in the linked list.
We are creating a new list to store all the elements of the previous list that takes O(N) Space Complexity. Hence, the overall Space Complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Rotate DLL
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console


