Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Save Ninja Land
Hard
0/120
Problem statement
Unfortunately, Ninja Land is facing an epidemic. There are ‘N’ unique virus variants spread across Ninja Land. The Ninja Land is an infinite 2D grid. You are in charge of creating a vaccine to stop the spread of the epidemic. Your research team provides you with a 2D array ‘POINTS’, where POINTS[i] = [Xi, Yi] represent a virus originating at point (Xi, Yi) and an integer ‘K’.
Every day, each cell infected with a virus variant will spread the virus to all neighboring points in the four cardinal directions (i.e., up, down, left, and right). If a cell has multiple variants, all the variants will spread without interfering with each other.
To create the vaccine, you must find the minimum number of days for any point to contain at least k of the unique virus variants. Can you save the Ninja Land?
For example:You are given ‘POINTS’ = [[1, 1], [3, 1]] and ‘K’ = 2. The answer will be 1.
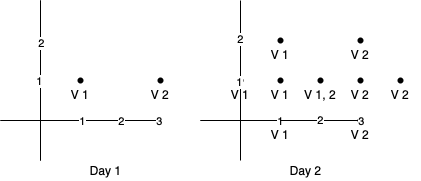
On day 2, the point (2, 1) will have K = 2 variants(V1, V2).
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two space-separated integers, ‘N’ and ‘K’, representing the number of unique viruses and integer ‘K’, respectively.
The next ‘N’ lines contain two-space separated integers ‘X’ and ‘Y’ representing the originating point of the i-th virus variant.
For each test case, print a single integer, denoting the minimum number of days for any point to contain at least k of the unique virus variants.
The output of each test case will be printed in a separate line.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
2 <= N <= 100
2 <= K <= N
POINTS[i].length == 2
1 <= POINTS[i][j] <= 10^7
Time limit: 2 sec
You do not need to input or print anything, as it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Sample Input 1:
2
2 2
1 3
3 3
3 2
1 1
2 3
4 5
Sample Output 1:
1
2
Explanation:
For the first test case, the answer is 1. It will take at least one day for any point to have two unique virus variants.
For the second test case, the answer is 2. It will take at least two days for any point to have two unique virus variants.
Sample Input 2:
2
2 2
1 2
3 3
3 3
2 1
2 3
3 5
Sample Output 2:
2
3
Hint
Hint 1
Try to find the intersection of areas affected by virus variants.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Sweep Line Algorithm
Level - Hard
Prerequisites - Binary Search, Vectors, Sweep Line Algorithm.
We will use binary search to optimally find our answer. Set the lower bound as 0 and upper bound as 10000000. Now, check if it is possible in the ‘mid' number of days for any point to have k unique variants. If yes, we will check for a lesser number of days because we want a minimum. If not, we will increase the number of days to let the virus spread to some points.
For any virus V originating at point (X, Y), on a given day, the spread of this virus V on the grid will be formed as diamond-shaped squares with center at (X, Y), and the distance of the center to each corner is the day.
Now, consider the above image below. We can see that if two of these squares intersect that means the intersection point will have 2 unique variants. So, we just need to find if at point k of these squares intersect or not.
If instead of a diamond-shaped square, if it would have been a normal square we can do a 2D sweep line on each square. So, to get a normal square we will rotate the axis of every diamond-shaped square by 45 degrees.
Sweep Line Algorithm: The idea behind this algorithm is to imagine that a line is swept or moved across the plane, stopping at some points. This algorithm can be used to find any two of the given n lines intersect or not.
This algorithm first sorts the end points of the given lines along the x-axis from left to right.
Then it passes a sweep line(a vertical line that is swept across the plane rightwards) and checks for intersections.
We will use this sweep line to count the overlapping virus at each point we track at a given day.
Algorithm:
- Initialize a variable low with a value of 0
- Initialize a variable high with a value 10 ^ 7
- Start Binary Search. Iterate while low < high
- Find mid.
- Check if in 'mid' number of days any point have k variants using a function containAtleastK()
- If yes, check for a lower number of days.
- Otherwise, increase the number of days.
- Finally, return low.
- Maintain a function containAtLeastK(int[][] points, int k, int days) :
- Initialize a map 'lines' to store sweep lines.
- Iterate point in points.
- Find current point. x = point[0] and y = point[1]
- Initialze a variable xLeft with value x and a variable yLeft with value y - days.
- Initialze a variable xBottom with value x - days and a variable yBottom with value y.
- Initialze a variable xRight with value x + days and a variable yRight with value y.
- Initialze a variable xTop with value x and a variable yTop with value y + days.
- Initialize a variable xLeftR with value xLeft + yLeft.
- Initialize a variable yLeftR with value yLeft - xLeft.
- Initialize a map, map1 to store left points of rotated square.
- map1 = lines.getOrDefault(xLeftR, new HashMap<Long, Integer>());
- map1.put(yLeftR, map1.getOrDefault(yLeftR, 0) + 1)
- lines.put(xLeftR, map1);
- Initialize three similar maps, map2, map3, and map4 to store the bottom, right and upper points of rotated squares.
- Initialize a map ranges.
- Initialize a TreeSet, set1 = (lines.keySet())
- Iterate key1 in set1
- Initialize a map to store values of key key1.
- Initialize a TreeSet set2 = (map.keySet());
- Iterate key2 in set2
- Set count as map.get(key2)
- ranges.put(key2, ranges.get(key2) + count);
- Set total as 0
- Initialize a TreeSet, rangeSet = ranges.keySet().
- Iterate num in rangeSet
- Get value for key 'num' in map ranges and store in a variable count.
- Add count to the total.
- If the total is greater than or equal to K, return true.
- Return, false.
Time Complexity
O((N ^ 2 + N Log(N)) * Log(N)), where N is the number of unique virus variants.
Time taken by binary search is Log(N) and for each search time complexity of sweep algorithm is N Log(N), and time taken by creating lines map is N ^ 2. Hence, total time complexity is O((N ^ 2 + N Log(N)) * Log(N)).
Space Complexity
O(N ^ 2), where N is the number of unique virus variants.
Space taken by lines map in the worst case is N ^ 2. Hence, the total space complexity is O(N ^ 2).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Save Ninja Land
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console


