Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Saving Money
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 20m
Problem statement
Ninja likes to travel a lot, but at the same time, he wants to save as much money as possible.
There are ‘N’ Stations connected by ‘M’ Trains. Each train that he boards starts from station ‘A’ and reaches destination station ‘B’ with a ticket price ‘P’.
Your task is to return the cheapest price from the given ‘source’ to ‘destination’ with up to ‘K’ stops. If there is no such route, return ‘-1’.
Input:
5 6
0 1 10
0 2 10
0 3 40
1 4 10
2 4 20
4 3 5
0 3 40

There are three ways to reach station ‘3’ from station ‘0’. The first path is 0->1->4->3, which will cost us 10+ 10+ 5= 25 and the second path 0->2->4->3 will cost us, 10+ 20+ 5 = 35, and the third path 0->3 will cost us 40.
We can’t take the first path since K = 1 and in this path, we are taking 2 stops, at station ‘1’ and station ‘4’.
Similarly, there are 2 stops in the second path. Hence we’ll finally choose the 3rd path i.e. 0->3, which is colored in blue.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line contains two space-separated integers, 'N' and 'M', the number of stations and the number of trains, respectively.
The next ‘M’ line has three space-separated integers, the source stations, the destination station, and the ticket price for traveling from this source to this destination.
The final line contains three space-separated integers, the source station, the destination station, and ‘K’, the maximum number of stations at which Ninja can stop.
The only line that contains the cheapest price from the given ‘source’ to ‘destination’ with up to ‘K’ stops or -1 if there is no such route.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Sample Input 1 :
4 4
0 1 5
0 2 10
1 3 50
2 3 10
0 3 2
Sample Output 1 :
20
Explanation of Sample Input 1 :
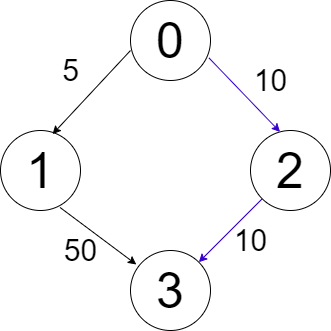
There are two ways to reach Station ‘3’ from Station ‘0’. One path is 0->1->3 which will cost us 5+50 = 55 and the other path is 0->2->3 which will cost us 10+10 = 20 and both these ways have 1 stop which is less than K (= 2).
That means we can take both of these paths but since path 2 is the cheapest, we’ll choose the latter i.e 0->2->3, which is colored in blue.
Sample Input 2 :
3 2
2 0 2
1 2 2
0 2 2
Sample Output 2 :
-1
Constraints :
1 <= 'N' <= 100
0 <= 'M' <= N*(N-1)/2
0 <= 'K' <= 'N' - 1
1 <= 'price' <= 10^4
Time limit : 1 sec
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Hint 3
Traverse all possible paths.
Approaches (3)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Approach 3
DFS Approach
Depth-First Search is a graph traversal algorithm where we start from the root node and visits as far as possible along each branch before backtracking. We can modify our Dfs algorithm to break cycles i.e to avoid preprocessing of already preprocessed nodes.
Algorithm
- Create an adjacency list ‘adjList’ to store the stations and the distance between them.
- Make a boolean array ‘visited’ to avoid preprocessing of already preprocessed nodes, and another integer variable ‘price’ initialized it to an infinite value(INT_MAX), which will store our ticket price.
- Make another 2 Dimensional array of ‘tickets’, which will store the price of the tickets.
- Now we’ll perform a Depth-first search from our source station using a helper function savingMoneyHelper() which will have the adjacency List(adjList), the boolean array(visited), the source, the destination, the 2-dimensional array(tickets), price of the ticket, the number of stops(K), and the cost of the current path(currentPrice) as its parameters.
- If K < -1, we’ll stop. Here we’re checking if K < -1 because we decrease K value each time by 1 only after making a call to the next node.
- If source = destination, i.e we have reached our destination, update price = min(price,currentPrice).
- If none of the above two conditions is met, update visited[source] = true, i.e marking this current node as visited.
- Now run a loop(loop variable i) to traverse all the adjacent nodes. You need to traverse only when visited[adj[source][i]] = false.
- Update visited[source] = false (backtrack).
- Finally check if price = infinite value(INT_MAX), if this condition is true, return ‘1’ else return ‘price’.
Time Complexity
O(N^K), where N is the number of stations and K is the number of stops.
The height of our recursion tree will be ‘K’ and since there are ‘N’ nodes, the complexity will be exponential i.e O(N^K). Hence total time complexity will be O(N^K).
Space Complexity
O(N), where N is the number of stations.
In the worst case, we’ll make N recursive calls, hence the recursion stack will take O(N) space and the visited array is of Size ‘N’. Hence total space complexity will be O(N+N) = O(N).
Video Solution
Unlock at level 3
(75% EXP penalty)
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Saving Money
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console




