Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Selection Sort
Easy
0/40
Problem statement
Sort the given unsorted array 'arr' of size 'N' in non-decreasing order using the selection sort algorithm.
Change in the input array/list itself.
Input:
N = 5
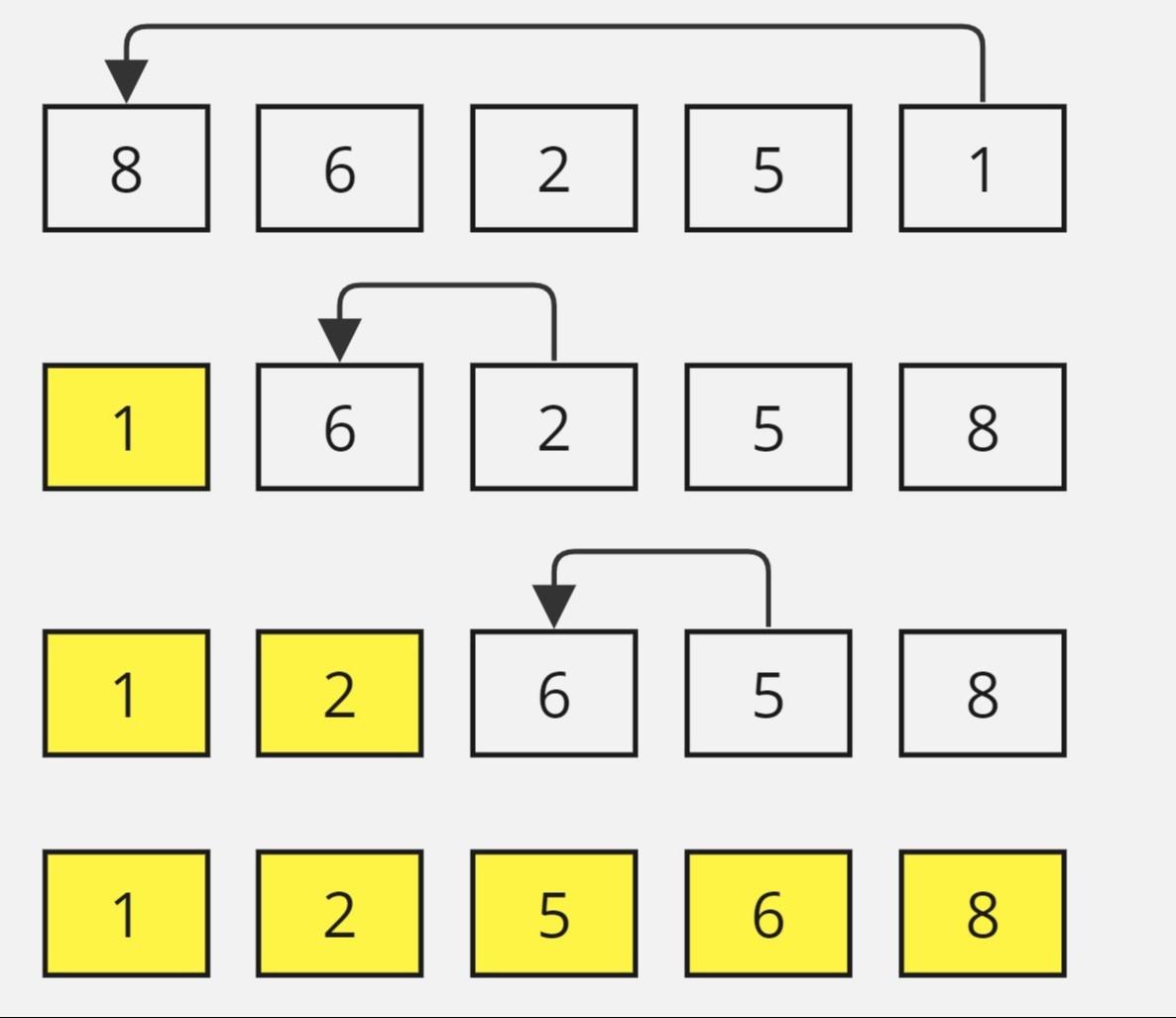
arr = {8, 6, 2, 5, 1}
Output:
1 2 5 6 8
Explanation:
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
First line contains an integer 'N' representing the size of the array/list.
Second line contains 'N' single space separated integers representing the elements in the array/list.
The output contains the integers of the sorted array, separated by a single space.
You don’t need to print anything. Just implement the given function.
Sample Input 1:
6
2 13 4 1 3 6
Sample Output 1:
1 2 3 4 6 13
Explanation Of Sample Input 1:
Select 1 and swap with element at index 0. arr= {1,13,4,2,3,6}
Select 2 and swap with element at index 1. arr= {1,2,4,13,3,6}
Select 3 and swap with element at index 2. arr= {1,2,3,13,4,6}
Select 4 and swap with element at index 3. arr= {1,2,3,4,13,6}
Select 6 and swap with element at index 4. arr= {1,2,3,4,6,13}
Sample Input 2:
5
9 3 6 2 0
Sample Output 2:
0 2 3 6 9
Constraints :
1 <= N <= 10^3
0 <= arr[i] <= 10^5
Time Limit: 1 sec
Hint
Hint 1
Repeatedly find the minimum element in the unsorted part of the array and swap it with the first element of the unsorted part.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Selection sort
Approach:
The selection sort algorithm works by repeatedly selecting the smallest element from the unsorted part of the array and moving it to the beginning of the unsorted part. This process is done iteratively until the entire array is sorted.
Here is the step-by-step approach for selection sort:
- Start with the entire array as the unsorted part.
- Find the minimum element in the unsorted part.
- Swap the found minimum element with the first element of the unsorted part.
- Move the boundary between the sorted and unsorted parts one element to the right. The element at the boundary is now considered part of the sorted subarray.
- Repeat steps 2 to 4 until the entire array is sorted.
Algorithm:
function selectionSort(arr):
- n = length(arr)
- for i from 0 to n-1:
- minIndex = i
- for j from i+1 to n:
- if arr[j] < arr[minIndex]:
- minIndex = j
- swap arr[i] with arr[minIndex]
Time Complexity
O(N^2), where ‘N’ is the number of length of array.
The algorithm consists of two nested loops. The outer loop runs n-1 times, as it iterates from the first element to the second-to-last element of the array. The inner loop runs from i+1 to n-1, which is also approximately n iterations on average.
Therefore, the total number of comparisons and updates performed by the algorithm is approximately (n-1) + (n-2) + ... + 1, which is equal to (n * (n-1)) / 2. This gives us the time complexity of O(n^2) for the selection sort algorithm.
Space Complexity
O(1)
No extra space is used.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Selection Sort
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
