Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Shortest Path in DAG
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 30m
Problem statement
You are given a directed acyclic graph of 'N' vertices(0 to 'N' - 1) and 'M' weighted edges.
Return an array that stores the distance(sum of weights) of the shortest path from vertex 0 to all vertices, and if it is impossible to reach any vertex, then assign -1 as distance.
'N' = 3, 'M' = 3, 'edges' = [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 3], [0, 2, 6]].

Distance (0 to 0) = 0.
Distance (0 to 1) = 2.
Distance (0 to 2) = 0->1 + 1->2 = 2+3 = 5.
So our answer is [0, 2, 5].
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format:
The first line contains two integers, 'N', and 'M'.
The next 'M' lines contain three integers each, 'u', 'v', and 'w', representing there is a directed edge from 'u' to 'v' of weight 'w'.
The only line contains an array that stores the distance(sum of weights) of the shortest path from vertex 0 to all vertices, and if it is impossible to reach any vertex, then assign -1 as distance.
You don’t need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just complete the given function.
Sample Input 1:
3 3
2 0 4
0 1 3
2 1 2
Sample Output 1:
0 3 -1
Explanation of sample output 1:
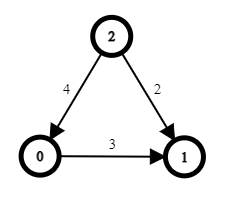
Distance (0 to 0) = 0.
Distance (0 to 1) = 3.
Distance (0 to 2) = We cannot reach vertex 2 from 0.
So our answer is [0, 3, -1].
Sample Input 2:
4 4
2 1 5
0 2 3
0 1 2
2 3 1
Sample Output 2:
0 2 3 4
Constraints:
1 <= 'N', 'M' <= 10^5
1 <= edge weight <= 10^5
Time Limit: 1 sec
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Think of using Dijkstra Algorithm to find the shortest distances.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Graph, Priority Queue
Approach:
- We can use the Dijkstra algorithm to find the shortest distances.
- In the Dijkstra algorithm, we start with 0 and traverse to all other vertex and update the shortest distance.
- After Calculating all the shortest distances, we can return the array 'dis'.
Algorithm:
- Create an adjacency list 'adj' using given edges, which stores {destination, weight}.
- Initialize a priority queue 'pq', which stores the distance of any vertex with 0 and that vertex.
- Initialize array 'dis' of size 'N' with 10^9.
- Assign dis[0] equals 0.
- Insert {dis[0],0} in 'pq'.
- While 'pq' is non-empty:
- 'd' and 'u' be the values from the top of the priority queue.
- Remove the top element from 'pq'.
- Traverse using [v,w] in adj[u]:
- if(dis[v]>d+w)
- Update dis[v] and insert {dis[v], v} in 'pq'.
- if(dis[v]>d+w)
- If 'dis[i]' is 10^9 for some vertex 'i', then assign -1 in 'dis[i]'.
- Return 'dis'.
Time Complexity
O(N+M*log(N)), where 'N' and 'M' are the number of vertices and the number of edges, respectively.
We are traversing through all edges and inserting elements in the priority queue, so the overall time complexity is O(N+M*log(N)).
Space Complexity
O(N+M), where 'N' and 'M' are the number of vertices and the number of edges, respectively.
We are creating 'pq' and 'dis'. Hence the space complexity is O(N+M).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Shortest Path in DAG
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console

