Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Single Source Shortest Path
Easy
0/40
Problem statement
You are given an undirected graph with 'N' nodes and 'M' edges. The weight of each edge in the graph is one unit.
Given a source vertex 'src', you must return an array 'answer' of length 'N', where 'answer[i]' is the shortest path length between the source vertex 'src' and 'i'th vertex.
All the nodes are zero-based.
Input:
N=5, M=5, edges=[(0, 1), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4)], src=1
Output: 1 0 2 2 1
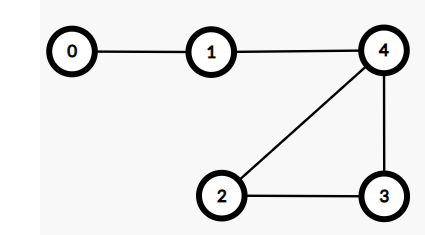
Explanation: The path from vertices are:-
(1->0) = 1 -> 0, path length is 1.
(1->1) = 1 -> 1, path length is 0.
(1->2) = 1 -> 4 -> 2, the path length is 2.
(1->3) = 1 -> 4 -> 3, path length is 2.
(1->4) = 1 -> 4, the path length is 1.
Hence we return [1, 0, 2, 2, 1]
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line of the input will contain integers 'N' and 'M', denoting the number of nodes and the number of edges.
The next 'M' lines contain two space-separated integers, denoting an undirected edge between 'a' and 'b'.
The next line contains an integer denoting 'src'.
The only line contains 'N' space-separated integers, i.e., the path length to each node.
You don't need to print anything. Just implement the given function.
Sample Input 1:
4 3
0 1
0 3
2 3
0
Sample Output 1:
0 1 2 1
Explanation Of Sample Input 1:
For test case one:
Input:
N=4, M=3, edges=[(0, 1), (0, 3), (2, 3)], src=0
Output: 0 1 2 1
Explanation: The path from vertices are:-
(0->0) = 0 -> 0, path length is 0.
(0->1) = 0 -> 1, path length is 1.
(0->2) = 0 -> 3 -> 2, path length is 2.
(0->3) = 0 -> 2, path length is 1.
Hence we return [0, 1, 2, 1]
Sample Input 2:
3 3
0 1
1 2
0 2
2
Sample Output 2:
1 1 0
Constraints:
1 <= N, M <= 10^2
0 <= src, edges[0], edges[0] <= N-1
Time Limit: 1 sec
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Hint 3
Perform DFS for each of the nodes.
Approaches (3)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Approach 3
DFS
Approach:
- The brute force algorithm for finding the shortest path in an undirected graph with unit distances exhaustively checks all possible paths between two given vertices and selects the shortest one.
- Here is the step-by-step algorithm for each node:
- Initialize a variable ‘minimumLength’ to store the shortest path found.
- For each pair of vertices (‘start_vertex’, ‘end_vertex’) in the graph, do the following:
- Initialize an empty list ‘currentLength’ to store the current path being explored.
- Use a depth-first search (DFS) algorithm to find all possible paths between ‘start_vertex’ and ‘end_vertex’. During the DFS, maintain a visited array to avoid cycles.
- For each path found during the DFS, compare its length to the value of ‘minimumLength’. If the ‘currentLength’ is shorter, update ‘minimumLength’ to the ‘currentLength’.
- Once all pairs of vertices have been processed, ‘minimumLength’ will contain the shortest path in the graph.
- Insert the value of ‘minimumLength’ in the ‘answer’ array.
- Return the ‘answer’ array.
Algorithm:
Function void DFS(int node, int dest, int[][] adjacencyList, int &minimumLength, int currentLength):
- If ‘node’ equals ‘dest’:
- Update ‘minimumLength’ with a minimum of ‘minimumLength’ and ‘currentLength’.
- Return
- Mark ‘visited[node]’ as true.
- For each ‘i’ in ‘adjacencyList[node]’:
- If ‘visited[i]’ is not visited:
- DFS(‘i’, ‘dest’, ‘adjacencyList’, ‘minimumLength’, ‘currentLength’+1)
- If ‘visited[i]’ is not visited:
- Mark ‘visited[node]’ as false.
Function int[] shortestPath(int n, int[] edges, int src):
- Initialize an ‘answer’ array of length ‘N’ with 0.
- Iterate over the edges and create the ‘adjacencyList’ for the graph.
- For ‘node’ from 0 to ‘N’-1:
- Initialize an integer variable ‘minimumLength’ with a verge large integer value and ‘currentLength’ with 0.
- Initialize an empty boolean array ‘visited’ with false.
- Call DFS(‘node’, ‘src’, ‘adjacencyList’ ‘minimumLength’, ‘currentLength’, 0)
- ‘answer[i]’=’minimumLength’
- Return ‘answer’
Time Complexity
O( N*(N+M) ), Where ‘N’ is the number of nodes and ‘M’ is the total edges in the graph.
For each vertex in the graph, we are doing a DFS, which takes O(N+M) time in the worst case. Hence the total time complexity is O(N*(N+M)).
Space Complexity
O( N ), Where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the graph.
We are taking O( N ) extra space. Hence, the overall space complexity will be O( N ).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Single Source Shortest Path
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console

