Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Spiral Matrix
Easy
0/40
6 upvotes
Asked in companies



Problem statement
You are given a N x M matrix of integers, return the spiral path of the matrix
Example Of Spiral Path

Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases or queries to be run. Then the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains two single space separated integers N and M, denoting the number of rows and columns respectively.
The next 'N' lines, each contains 'M' single space-separated integers representing the elements in a row of the matrix.
For each test case/query, print the spiral path of the given matrix.
Output for every test case will be printed in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 5
1 <= N <= 10^2
1 <= M <= 10^2
-10^9 <= mat[i][j] <= 10^9
Time Limit: 1second
Sample Input 1 :
2
4 4
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
3 6
1 2 3 4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16 17 18
Sample Output 1 :
1 2 3 4 8 12 16 15 14 13 9 5 6 7 11 10
1 2 3 4 5 6 12 18 17 16 15 14 13 7 8 9 10 11
Explanation of the Sample Input 1 :
The spiral path for the test case 2 is as shown below:
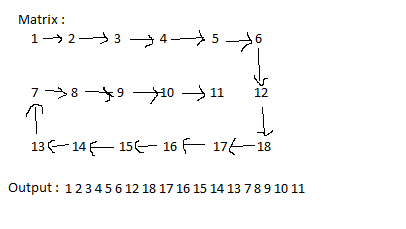
Sample Input 2 :
2
1 1
4
1 5
1 2 3 4 5
Sample Output 2 :
4
1 2 3 4 5
Explanation of the Sample Input 2 :
In the first test case there is only one element in the matrix, so the spiral path is only that element.
In the second test case there is only one row or 1-D matrix, so the spiral path is only the single traversal of the matrix.
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Try to traverse the matrix and keep track of the current row number and column number.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Spiral Matrix
Divide the matrix into loops. Print all the elements in the clockwise order from the first-outer layer, followed by the elements from the second outer layer, and so on. Use four loops to print all the elements. Every ‘for’ loop defines a single direction movement along with the matrix. The first loop represents the movement from left to right, the second loop represents the movement from top to bottom, the third represents the movement from the right to left, and the fourth represents the movement from bottom to up.
Algorithm:
- Run loop until all the squares of loops are printed.
- In each outer loop traversal push the elements of a square in a clockwise manner.
- Push the top row, i.e. Push the elements of a kth row and increase k..
- Push the right column, i.e. Push the last column and decrease the count of columns.
- Push the bottom row, and decrease the count of rows.
- Push the left column, and increase the count of the starting column index.
Time Complexity
O(N * M)., As you need to traverse the matrix element by element.
Where N is the number of rows and M is the number of columns of the matrix.
Space Complexity
O(1), as no extra space is required.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Spiral Matrix
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
