Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Subtree Count
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 25m
Problem statement
You are given an array ‘arr’ of the size ‘N’. The array is formed using a tree with the generator function. You have to obtain the tree which was used to generate the array and return the number of nodes in subtree of each node.
Below is the code given used to create the array - :
Function generate(node):
arr.Add(node.id)
visited[node.id] = True
for childNode in node.children:
if childNode is not visited:
generate(childNode)
arr.Add(node.id)
The function is called on the root node of the graph, which is 1.
For example:You are given N = 4, ‘arr’ = [1, 2, 2, 1].The resulting graph will be
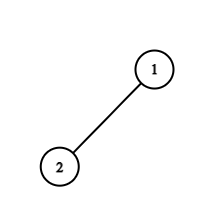
For node 1, the subtree count is 2, while for node 2 the subtree count is 1. Hence the answer is [2, 1].
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ representing the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer ‘N’ representing the size of the array.
The second line of input contains ‘N’ space-separated integers representing the given array.
For each test case, print space-separated integers, representing the number of nodes in each subtree.
Print a separate line for each test case.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
2 <= N <= 10^6
0 <= arr[i] <= 10^9
Time Limit: 1 sec
You do not need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the function.
Sample Input 1:
2
4
1 2 2 1
6
1 2 2 3 3 1
Sample Ouput 1
2 1
3 1 1
Explanation:
For the first test case, N = 4, ‘arr’ = [1, 2, 2, 1].The resulting graph will be

For node 1, the subtree count is 2, while for node 2 the subtree count is 1. Hence the answer is [2, 1].
For the second test case, N = 6, ‘arr’ = [1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 1]. The resulting graph will be

For node 1, the subtree count is 3, while for node 2 and node 3 the subtree count is 1. Hence the answer is [3, 1, 1].
Sample Input 2:
2
6
1 2 3 3 2 1
8
1 2 3 3 2 4 4 1
Sample Output 2:
3 2 1
4 2 1 1
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Try to build the tree from the array.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Build Tree
In this approach, we make a few observations,
- The array will always be of the size of 2*number of nodes
- Whenever a node id reoccurs in the array then there will not be any more children of that node in the array
We can build the tree by pushing the node id in a stack and adding the next node as the children of the top of the stack. Whenever the top of the stack is equal to the current node id in the array, then we will pop the node from the stack
After building the tree we can use DFS to find the nodes in each subtree of the tree
We will create a class TreeNode(id, children), where id is the id of the node and children is the array of child nodes of the current node.
We will create a function getSubTree(root, count), here root is the current node and count the array of subtree counts of the tree.
Algorithm:
- In the function getSubTree(root, count)
- Set count[root.val - 1] as 1
- Iterate child through root.children
- Call getSubTree(child, count)
- Add count[child.id - 1] to count[root.id - 1]
- Initialise an empty stack st
- Initialise TreeNode(0) as root
- Insert root into st
- Set currIndex as 1
- While st is not empty
- If arr[currIndex] is equal to top of st
- Pop the stack
- Otherwise,
- Initialise newNode as TreeNode(arr[currIndex])
- Insert newNode into st.top.children
- Insert newNode in st
- Increase currIndex by 1
- If arr[currIndex] is equal to top of st
- Initialise an empty array count of half the length of arr
- Call getSubTree(root, count)
- Return count
Time Complexity
O(N), Where N is the size of the array.
We are iterating through each element of the array to build a tree which will cost O(N) time. We are finding the number of nodes in subtrees of each node which takes O(N) time. Hence the final time complexity is O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), Where N is the size of the array.
We are maintaining a stack that will cost O(N) space. For performing DFS the recursion stack will also cost O(N) space. Hence the final space complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Subtree Count
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console


