Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Sum Tree
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 29m
Problem statement
For a given binary tree, convert it to its sum tree. That is, replace every node data with sum of its immediate children, keeping leaf nodes 0. Finally, return its preorder.
For example:The input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
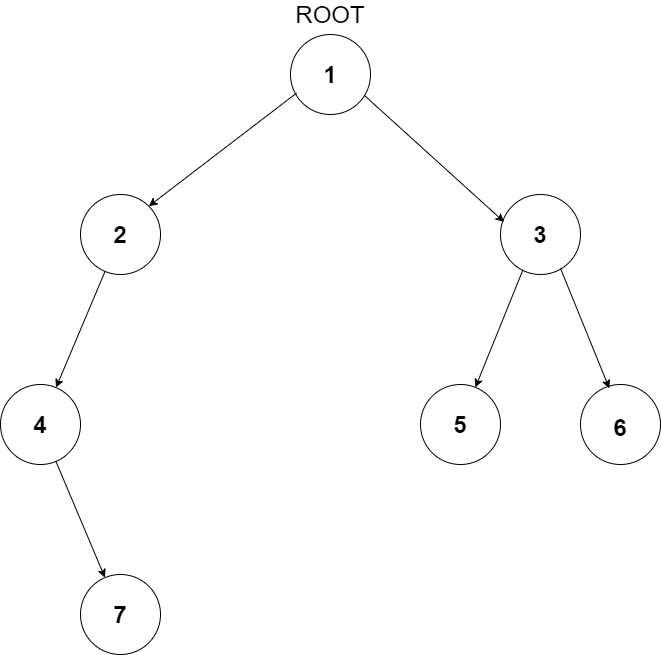
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
In the input, each value of the sequence will be present on a separate line.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
Elements are in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes, each value is present on a separate line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
Print the updated preorder form of the binary tree.
You are required to return the preorder form of the given tree and hence not required to print anything explicitly.
Constraints:
0 <= Number of nodes <= 10 ^ 7
0 <= Value of node <= 10 ^ 8
Sample Input 1:
3
1
2
-1
-1
-1
-1
Sample Output 2:
3
0
0
Explanation for Sample 1:

Sample Input 2:
1
2
3
4
-1
5
6
-1
-1
-1
-1
-1
-1
Sample Output 2:
5
4
0
11
0
0
Explanation for Sample 2:

Hint
Hint 1
Try to divide the tasks into two.
- Build the Sum Tree
- Build the preorder from the resultant tree
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
DFS Approach
The approach is very simple and can be achieved using the tree Depth First traversal approach.
Divide the tasks into two parts.
- Build the Sum Tree
- You need to update the root data with the sum of the left and right children’s data given that the root itself is not null.
- Well, you can do so by checking the left node and right node. If they are not null, take their sum and update the root data.
- Extend this idea further by making a recursive call on to the left and right subtrees.
- Now that you have built the sum tree, let's do a pre order traversal.
- To keep track of the node data in the preorder traversal manner, we take a dynamic array.
- If the root is not null, put the root data to the dynamic array and do the same for the left and the right subtrees by making recursive calls.
Time Complexity
O(N), Where N is the total number of nodes in the binary tree.
We make N operations to build the sum tree since we will visit every tree node once. We make another N operation to find the preorder. Hence, overall Time Complexity is O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), Where N is the total number of nodes in the binary tree.
The Space Complexity O(N) is required by the recursion stack. Hence, the overall Space Complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Sum Tree
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console




