Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
The N - Queens Puzzle
Moderate
0/80
Problem statement
The N Queens puzzle is the problem of placing N chess queens on an N * N chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer ‘N’, print all distinct solutions to the ‘N’ queen puzzle.
Two queens on the same chessboard can attack each other if any of the below condition satisfies:
1. They share a row.
2. They share a column.
3. They share a diagonal.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases. Then the test cases follow.
The first and the only line of each test case contains an integer ‘N’ denoting the size of the chessboard.
Output Format
For each test case, print all the possible solutions, each in a new line.
Each line would be representing a single configuration.
Each configuration would contain N * N elements printed row-wise separated by spaces. The position where we can place the queen will have the value 1, rest will have the value 0.
The sequence of the configurations returned does not matter.
The output of each test case is printed in a separate line.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 10
Time Limit : 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
1
4
Sample Output 1:
0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
Explanation for Sample Input 1:
The 4 queens can be placed in two ways in a 4*4 chessboard. Both the configurations are shown in the below figure.
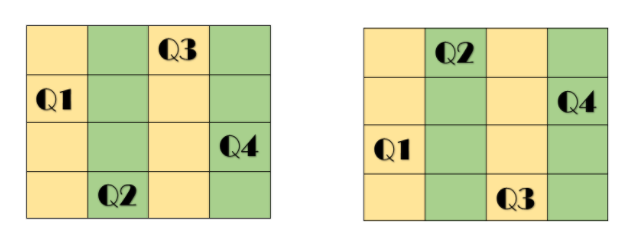
The chessboard matrix for the first configuration looks as follows:-
0 0 1 0
1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0
Queen contained cell is depicted by 1. As we can see, No queen is in the same row, column or diagonal of the other queens. Hence this is a valid configuration.
Similarly, the chessboard matrix for the second configuration looks as follows:-
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
Queen contained cell is depicted by 1. As we can see, No queen is in the same row, column or diagonal of the other queens. Hence this is also a valid configuration.
These are the only two valid configurations for 4-Queens.
Sample Input 2:
1
3
Sample Output 2:
Explanation of Sample Input 2:
Since no possible configuration exists for 3 Queen's, the output remains empty.
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Hint 3
Generate all configurations by placing N queens in N different rows/columns and check for the valid configurations.
Approaches (3)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Approach 3
Brute Force
A naive way to solve this problem is to generate all the possible combinations of given N queens on the N x N chessboard and check if the current combination satisfies the N Queen problem constraints or not. If it does, then add the configuration to the solution and move ahead to find other possible combinations.
Algorithm:
Create an output array that stores all the possible solutions of N - queen puzzle.
- Suppose we place the queens column-wise, and we start with the very first column.
- If all the queens are placed and the configuration is a valid one, then we have found a valid solution. Add it to the output array.
- Iterate over all the rows in the current column:
- Place the queen in this square(row, column) and recursively place the queens in the other columns
- If all rows have been tried and nothing worked, simply return from the function.
Checking if a configuration is valid:
- For checking if no queen is present in the current row:
- Iteratively check if there is a queen in any of the previous columns, i.e. (0, col - 1) for the current row ‘row’. If yes, this arrangement is not valid, return false.
- For checking if no queen is present along the diagonals:
- Iteratively check if there is a queen in the upper left diagonal and lower left diagonal. If yes, this arrangement is not valid, return false.
- For checking the diagonals, we can simply check if the difference between the coordinates of the queens is the same or not.
- If reached here, return true as placement is safe.
At last, we will return the output array containing all the configurations in which we can successfully place the N queens.
Time Complexity
O(N ^ N), where ‘N’ is the number of queens.
There are N possibilities to place the first queen, N possibilities to place the second queen, N possibilities to place the third queen, and so on. Thus, the final time complexity is O(N ^ N).
Space Complexity
O(N * N), where ‘N’ is the number of queens in the configuration.
We are using a linear array of size N to keep information about queens in a column. Thus, the effective space complexity is O(N). Also, we are using a 2-D array to store all the configurations in which we can successfully place the N queens. Thus, the final space complexity is O(N + (N * N)) = O(N * N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
The N - Queens Puzzle
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



