Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Topological Sort
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 30m
Problem statement
A Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a directed graph that contains no cycles.
Topological Sorting of DAG is a linear ordering of vertices such that for every directed edge from vertex ‘u’ to vertex ‘v’, vertex ‘u’ comes before ‘v’ in the ordering. Topological Sorting for a graph is not possible if the graph is not a DAG.
Given a DAG consisting of ‘V’ vertices and ‘E’ edges, you need to find out any topological sorting of this DAG. Return an array of size ‘V’ representing the topological sort of the vertices of the given DAG.
For example, Consider the DAG shown in the picture.
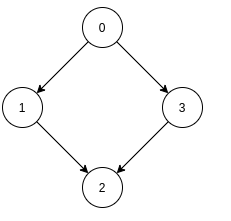
In this graph, there are directed edges from 0 to 1 and 0 to 3, so 0 should come before 1 and 3. Also, there are directed edges from 1 to 2 and 3 to 2 so 1 and 3 should come before 2.
So, The topological sorting of this DAG is {0 1 3 2}.
Note that there are multiple topological sortings possible for a DAG. For the graph given above one another topological sorting is: {0, 3, 1, 2}
Note:1. It is guaranteed that the given graph is DAG.
2. There will be no multiple edges and self-loops in the given DAG.
3. There can be multiple correct solutions, you can find any one of them.
4. Don’t print anything, just return an array representing the topological sort of the vertices of the given DAG.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases. The description of ‘T’ test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two space-separated integers ‘V’, ‘E’, representing the number vertices and edges in the graph respectively.
Then ‘E’ lines follow, each containing 2 space-separated integers ‘u’, ‘v’ representing that there is a directed edge from vertex ‘u’ to vertex ‘v’
For each test case, return an array representing the topological sort of the vertices of the given DAG.
Note :
You do not need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 50
1 <= V <= 10^4
0 <= E <= 10^4
0 <= u, v < V
Where ‘T’ is the total number of test cases, ‘V’ is the number of vertices, ‘E’ is the number of edges, and ‘u’ and ‘v’ both represent the vertex of a given graph.
Time limit: 2 sec
Sample Input 1:
2
2 1
1 0
3 2
0 1
0 2
Sample Output 1:
1 0
0 2 1
Explanation of Sample Input 1:
Test case 1:
The number of vertices ‘V’ = 2 and number of edges ‘E’ = 1.
The graph is shown in the picture:
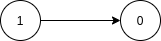
The topological sorting of this graph should be {1, 0} as there is a directed edge from vertex 1 to vertex 0, thus 1 should come before 0 according to the given definition of topological sorting.
Test case 2:
The number of vertices ‘V’ = 3 and number of edges ‘E’ = 2.
The graph is shown in the picture:
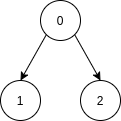
As there are two directed edges starting from 0, so 0 should come before 1 and 2 in topological sorting.
Thus the topological sorting of this graph should be {0, 2, 1} or {0, 1, 2}
Sample Input 2:
2
1 0
4 4
0 1
0 3
1 2
3 2
Sample Output 2:
0
0 1 3 2
Explanation of Sample Input 2:
Test case 1:
There is only a single vertex in the graph that is 0, so its topological sort will be {0}.
Test case 2:
See problem statement for its explanation
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Can you modify the Depth First Search Algorithm to find topological sorting of DAG?
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Modify Depth First Search
In the Depth First Search (DFS), we start from a vertex, we first print it and then recursively call DFS for its adjacent vertices. In topological sorting, we use a stack. We don’t print the vertex immediately, we first recursively call topological sorting for all its adjacent vertices, then push it to a stack. Finally, print contents of the stack. Note that a vertex is pushed to stack only when all of its adjacent vertices (and their adjacent vertices and so on) are already in the stack.
- This is a recursive approach.
- Make an adjacency list of the given graph.
- Make a boolean array ‘visited’ of size ‘V’ and initially fill it by ‘false’. This will keep track of the vertex that is already visited.
- Make a stack that will keep topological sorting of vertices in the top to bottom order.
- Run a loop where ‘i’ ranges from 0 to V-1. For each vertex ‘i’ which is not already visited, we will call a recursive function that will perform the following steps -:
- Mark the current vertex ‘i’ visited by setting ‘visited[i]’:= true.
- Iterate over all the adjacent vertices of ‘i’ that are not already visited and recursively call this function.
- Push vertex ‘i’ in the stack.
- Make a vector ‘result’ and push all the elements of the stack in it from top to bottom.
- Return the vector ‘result’, It will represent topological sorting of given DAG.
Time Complexity
O(V + E), where ‘V’ is the number of vertices and ‘E’ is the number of edges.
The above algorithm is simply DFS with an extra stack. So time complexity is the same as DFS.
Space Complexity
O(V), where ‘V’ is the number of vertices.
The size of the stack and ‘result’ array both will be of the order of ‘V’.
Video Solution
Unlock at level 3
(75% EXP penalty)
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Topological Sort
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console




