Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Topological Sort
Easy
0/40
6 upvotes
Asked in companies



Problem statement
You are given a directed acyclic graph. Your task is to find any topological sorting of the graph.
A directed acyclic graph is a directed graph with no directed cycles.
Topological sorting for Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a linear ordering of vertices such that for every directed edge from u to v, vertex u comes before v in the ordering.
For example-
For the given DAG-
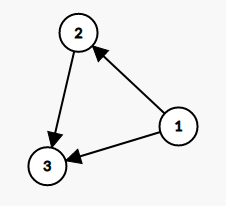
One of the possible topological sort will be-
1 2 3
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases to run. Then the test case follows.
The first line of each test case contains two single space-separated integers ‘N’, ‘M’, denoting the number of nodes and the number of edges respectively.
The next ‘M’ lines of each test case contain two single space-separated integers ‘U’, ‘V’ each denoting there is a directed edge from node ‘U’ to node ‘V’.
The only line of each test case will contain N single space-separated integers representing the topological sorting of the graph. You can print any valid sorting.
Print the output of each test case in a separate line.
Note:
You are not required to print the expected output, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 100
1 <= N <= 5000
0 <= M <= min(5000, (N*(N-1))/2)
1 <= U, V <= N and U != V
Time Limit: 1sec
Sample Input 1 :
2
3 1
1 2
4 5
1 2
1 3
2 4
3 4
1 4
Sample Output 1 :
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
Explanation for Sample 1:
The DAG corresponding to the first test case will be-
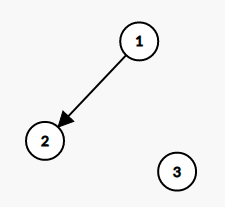
We can clearly see that one of the possible topological sorting will be 1 2 3.
The DAG corresponding to the second test case will be-

We can clearly see that one of the possible topological sorting will be 1 2 3 4.
Sample Input 2 :
1
5 0
Sample Output 2 :
5 4 3 2 1
Hint
Hint 1
Can we use DFS traversal to get the topological sort?
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
DFS traversal of DAG
In topological sort a vertex u must come before vertex v if there is a directed edge between u and v. We can modify DFS traversal of a graph to achieve this.
The algorithm will be-
- We can declare a stack ‘topSort’ which will store the nodes after the topological sort.
- We also maintain an array/list ‘visited’ of size N, denoting which node is visited in a dfs traversal. Initially, all elements of visited will be initialized to false.
- We will iterate through each node from 1 to N. Let the current node be ‘currNode’. In each iteration, we will-
- If currNode is not visited we will run a DFS from ‘currNode’. In each DFS call we will:
- Set visited[currNode] to true.
- Recurse over all directed neighbours of currNode which is not visited.
- Push ‘currNode’ to ‘topSort’.
- If currNode is not visited we will run a DFS from ‘currNode’. In each DFS call we will:
- We will finally print the elements of ‘topSort’ which will be our topological sort.
Time Complexity
O(N + M), where N denotes the number of nodes and M denotes the number of edges in the graph.
As every node and edge will be visited at most once, the time complexity will be O(N + M).
Space Complexity
O(N), where N denotes the number of nodes in the graph.
The space complexity due to recursion stack will be O(N). As the size of the ‘visited’ array/list is also N, overall space complexity will be O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Topological Sort
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console
