Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Water flow
Hard
0/120
Average time to solve is 10m
10 upvotes
Asked in companies



Problem statement
You are given a matrix 'A' having ‘N’ rows and ‘M’ columns. Each cell of the matrix represents the height of water placed in that cell. Water can flow only in four directions ( up, down, right, and left) but only to a cell having its height less than or equal to the height of the current cell.
The four boundaries of the matrix represent the oceans- the left and top boundary represent the Pacific ocean, and the right and bottom boundary represent the Atlantic ocean.
You need to find the list of coordinates from which water can flow to both the oceans. The list should be sorted in lexicographical order.

Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line of the input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two space-separated positive integers ‘N’ and ‘M’ denoting the number of the rows and columns in a matrix 'A' respectively.
In the next ‘N’ lines of each test case, the ith line contains ‘M’ space-separated integers denoting the height of water.
The first line of output of each test case should contain positive integer ‘K’ denoting the total number of coordinates.
The next ‘K’ lines contain one coordinate in each line.
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 50
1 <= N <= 10^4
1 <= M <= 10^4
1 <= N*M <= 10^4
1 <= A[i][j] <= 10^9
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
2
2 2
2 4
5 6
2 3
1 1 2
9 12 1
Sample Output 1:
3
0 1
1 0
1 1
3
0 2
1 0
1 1
Explanation for sample input 1:
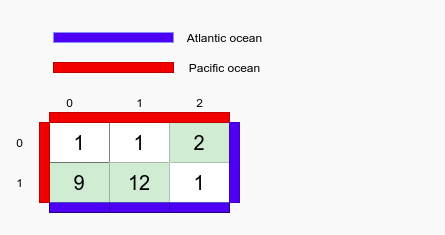
Test case 1:
The element present at [0,1] and [1,0] is adjacent to both the oceans. The element present at [1,1] (which is 6) can travel to [1,0] (which is 5) because 5 < 6. And from [1,0] you can reach both oceans hence it will also be included in our answer.

Test case 2:
The element present at [0,2] and [1,0] is adjacent to both the oceans. The element present at [1,1] (which is 12) can travel to [1,0] (which is 9) because 9 < 12. And from [1,0] you can reach both oceans hence it will also be included in our answer.
Sample Input 2:
2
3 3
4 7 30
1 2 12
20 40 50
1 2
3 6
Sample Output 2:
5
0 2
1 2
2 0
2 1
2 2
2
0 0
0 1
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Perform DFS from each cell
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Brute force, DFS
- We will run two nested loops to traverse each cell of the matrix.
- For each cell, we perform DFS in which we go to all adjacent neighbours having their height lower than the current cell.
- We take two boolean variables to mark the reachability of that cell to the ocean. If we somehow reach any of the ocean we mark the corresponding boolean variable to be true.
- In the end, if both of the boolean variables are true then it means this cell can reach both of the oceans hence we include this cell in our answer.
Time Complexity
O(N^2 * M^2), where ‘N’ is the number of rows and ‘M’ is the number of columns in the matrix.
We using two nested loops for traversing each element in a matrix that will take O(N*M) time.
For each cell, we perform a DFS which can traverse on all the elements in the worst case so it will take O(N*M) time.
Total time complexity O((N*M)^2)
Space Complexity
O(N*M), where ‘N’ is the number of rows and ‘M’ is the number of columns in the matrix.
In the worst case, the DFS recursive function stack can have ‘N*M’ entries.
Video Solution
Unlock at level 3
(75% EXP penalty)
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Water flow
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console
