Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Water Supply In A Village
Hard
0/120
Average time to solve is 45m
Problem statement
There are ‘N’ houses in a village. Ninja wants to supply water for all the houses by building wells and laying pipes.
For each house ‘i’, we can either build a well inside it directly with cost ‘WELLS[i]’, or pipe in water from another well to it. The total cost to lay pipes between houses is given by the array ‘PIPES’, where ‘PIPES[i]’ = ‘[HOUSE1, HOUSE2, COST]’ and the ‘COST’ represent the total cost connect ‘HOUSE1’ and ‘HOUSE2’ together using a pipe.
Note: Given all the connections are bidirectional.
For Example:
For ‘N’ = 3, ‘WELLS[]’ = ‘[1,2,2]’, ‘PIPES[]’ = [ [1, 2, 1], [2 , 3, 1]]. The image shows the costs of connecting houses using pipes. The best strategy is to build a well in the first house with cost 1 and connect the other houses to it with cost 2 so the total cost is 3.
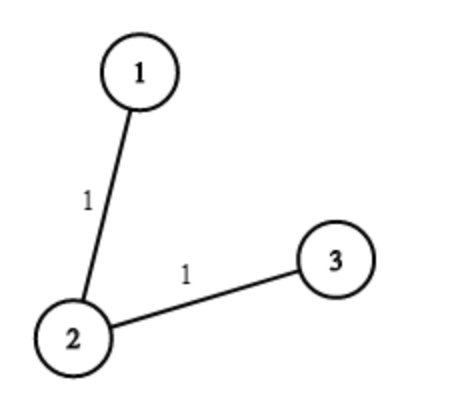
Ninja wants to find out the minimum total cost to supply water to all houses in the village. Can you help the Ninja to find out this minimum cost?
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format
The first line of input contains an integer 'T' representing the number of test cases. Then the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains two integers ‘N’ and ‘K’ representing the number of Houses in the village and the size of ‘PIPES’ respectively.
The next line contains ‘N’ single space-separated integers denoting ‘WELLS[i]’.
The next ‘K’ line contains 3 single space-separated integers denoting ‘PIPES[i][0]’, ‘PIPES[i][1]’ and ‘PIPES[i][2]’.
For each test case, print the minimum cost to supply water to all the houses in the village.
The output for each test case is printed in a separate line.
Constraints :
1 <= T <= 100
1 <= N <= 10 ^ 2
0 <= WELLS[i] <= 10^5
1 <= K <= 10000
1 <= PIPES[i][0], PIPES[i][1] <= N
0 <= PIPES[i][2] <= 10^5
PIPES[i][0] != PIPES[i][1]
Where ‘T’ is the number of test cases, ‘N’ is the number of houses in the village, WELL[i]’ denotes the cost of inserting a well at house ‘i’ and ‘PIPES[i][0]’, ‘PIPES[i][1]’ and ‘PIPES[2]’ represents the cost to connect house ‘PIPES[i][0]’ to ‘PIPES[i][1]’.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1 :
2
4 2
1 4 4 4
1 4 2
1 2 1
3 3
5 5 5
1 2 80
1 3 20
2 3 90
Sample Output 1:
8
15
Explanation for Sample Output 1:
For the first test case :
See the picture below for the output reference:
The efficient way to supply water to all houses is to connect 0 with 1 and 0 with 2 and build a well at house 0 and 3. So the total cost will be 1 (well at house 0) + 4 (well at house 3) + 2 (connect 0 and 1) + 1 (connect 0 and 2) which is 8.
For the second test case :
See the picture below for the output reference:
The efficient way to supply water to all houses is to make well at all the houses. So the total cost will be 5 (well at house 0) + 5 (well at house 1) + 5 (well at house 2) which is 15.
Sample Input 2 :
2
2 1
8 2
1 2 1
2 1
1 1
1 2 1
Sample Output 2 :
3
2
Explanation for Sample Output 2:
For the first test case:
The efficient way to supply water to all houses is to connect 1 with 2 and build a well at house 1. So the total cost will be 2 (well at house 1) + 1 (connect 1 and 2) Which is equal to 3.
For the second test case :
The efficient way to supply water to all houses is to connect 1 with 2 or build well at both of the houses. The answer will be the same for either case. Which is equal to 2.
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Can you think of a solution that uses a minimum cost algorithm?
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Minimum Spanning Tree
We can assume this problem as a Shortest path problem/Minimum spanning tree problem. In this problem, in a graph, consider cities as nodes, pipe connects two cities as edges with cost. Now wells cost, they are self-connected edges, we can add an extra node as root node 0, and connect all 0 and every node with costs ‘WELLS[i]’. So that we can have one graph/tree, and can get minimum spanning trees / shortest path in a graph.
Here is the complete algorithm:
- Create a helper function ‘edgeCost(house1, house2, cost)’, where ‘cost’ is the cost to connect ‘house1’ and ‘house2’.
- Assume ‘0’ as the root node, now build a graph with node 0 and all nodes (Houses).
- Connect all nodes with 0 while forming the graph.
- Turn houses into nodes well's costs and pipes' cost into edges value which connect into two cities.
- Sort all edges (from min to max).
- Scan all edges, check whether 2 nodes connected or not:(Union-Find method).
- If already connected, continue to check the next edge.
- If not yet connected, connect 2 nodes add cost to the final answer.
- If all nodes already connected, get minimum costs, return the result.
Time Complexity
O(N*log(N)), where ‘N’ is the number of houses in the village.
Because we are sorting all the edges in the graph and then the union-find algorithm does computation in O(log(N)) order. Hence the overall time complexity will be O(N*log(N)).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of houses in the village.
The size of the array/list storing all the edges will be of order ‘N’ because it considers new edges that are in between the 0th house and the ‘i-th’ house. Hence the overall space complexity will be O(N).
Video Solution
Unlock at level 3
(75% EXP penalty)
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Water Supply In A Village
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



