#include<bits/stdc++.h>
pair<int,int> findCord(int num,int n)
{
int r = n-1 -(num-1)/n;
int c = (num-1)%n;
if(r%2 == n%2) c = n-1-c;
return {r,c};
}
int minDiceThrowToLastCell(int **board, int n)
{
vector<vector<int>> vis(n,vector<int>(n,0));
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
q.push({1,0}); // {intialStep , initailMove}
int target = n*n;
while(!q.empty())
{
int node = q.front().first;
int Throw = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if(node == target) return Throw;
for(int i=1;i<=6 ;i++)
{
if(node+i > target) continue;
auto cor = findCord(node+i,n);
int r = cor.first;
int c = cor.second;
if(vis[r][c]) continue;
vis[r][c]=1;
if(board[r][c]==-1) q.push({node+i,Throw+1});
else q.push({board[r][c],Throw+1});
}
}
return -1;
}Problem of the day
Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Snake and Ladder
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 30m
Problem statement
You have been given a Snake and Ladder Board with 'N' rows and 'N' columns with the numbers written from 1 to (N*N) starting from the bottom left of the board, and alternating direction each row.
For example
For a (6 x 6) board, the numbers are written as follows:
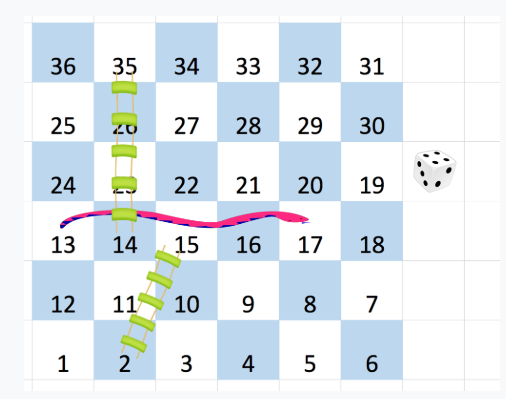
You start from square 1 of the board (which is always in the last row and first column). On each square say 'X', you can throw a dice which can have six outcomes and you have total control over the outcome of dice throw and you want to find out the minimum number of throws required to reach the last cell.
Some of the squares contain Snakes and Ladders, and these are possibilities of a throw at square 'X':
You choose a destination square 'S' with number 'X+1', 'X+2', 'X+3', 'X+4', 'X+5', or 'X+6', provided this number is <= N*N.
If 'S' has a snake or ladder, you move to the destination of that snake or ladder. Otherwise, you move to S.
A board square on row 'i' and column 'j' has a "Snake or Ladder" if board[i][j] != -1. The destination of that snake or ladder is board[i][j].
You can only take a snake or ladder at most once per move: if the destination to a snake or ladder is the start of another snake or ladder, you do not continue moving - you have to ignore the snake or ladder present on that square.
For example, if the board is:
-1 1 -1
-1 -1 9
-1 4 -1
Let's say on the first move your destination square is 2 [at row 2, column 1], then you finish your first move at 4 [at row 1, column 2] because you do not continue moving to 9 [at row 0, column 0] by taking the ladder from 4.
A square can also have a Snake or Ladder which will end at the same cell.
For example, if the board is:
-1 3 -1
-1 5 -1
-1 -1 9
Here we can see Snake/Ladder on square 5 [at row 1, column 1] will end on the same square 5.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
The first line of each test case or query contains a single integer value, 'N' representing the 'rows' and 'columns' for the two-dimensional square matrix.
The Second line onwards, the next 'N' lines or rows represent the ith row values.
Each of the i-th row constitutes 'N' column values separated by a single space.
'-1' denotes the square doesn't contain any Snake or Ladder.
The only line of output prints the minimum number of throws required to reach the last cell of the board. If it is impossible to reach the last cell of the board, then print -1.
Constraints :
1 <= N <= 10 ^ 2
1 <= board[i][j] <= N*N or board[i][j] = -1
Where (NxN) is the size of the board.
Sample Input 1 :
3
-1 1 -1
-1 -1 9
-1 4 -1
Sample Output 1 :
1
Explanation to Sample Input 1 :
In the beginning, you start at square 1 [at row 2, column 0]. The optimal path will be:
1. You decided to move to 4 [at row 1, column 2] and must take the ladder to square 9 [at row 0, column 0].
You finished at last cell of the board in 1 dice throw.
Sample Input 2 :
6
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 35 -1 -1 13 -1
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 15 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2 :
4
Explanation to Sample Input 2 :
In the beginning, you start at square 1 [at row 5, column 0]. The optimal path will be:
1. You decide to move to square 2 [at row 5, column 1] and must take the ladder to square 15 [at row 5, column 1].
2. You then decide to move to square 17 [at row 3, column 5] and must take the snake to square 13 [at row 3, column 0].
3. You then decide to move to square 14 [at row 5, column 1] and must take the ladder to square 35 [at row 0, column 1].
4. You then decide to move to square 36 [at row 5, column 1].
You finished at last cell of the board in 4 dice throw.
Hint
Hint 1
Try considering the given Snake and Ladder board as a directed graph with the number of vertices equal to the number of cells in the board. The problem reduces to finding the shortest path in a graph.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
BFS
We will use Breadth-First Search to find the shortest path from cellNumber 1 to cellNumber N*N.
- We will maintain a queue of cellNumber where the front of the queue will always contain a cell which can be reached by minimum dice throw from starting cell (cellNumber = 1).
- Create a minDiceThrow array of size N*N initialise it with the maximum value (INT_MAX)
- Start with pushing cellNumber 1 and updating minDiceThrow[1] = 0, as no. of throw required to reach cell no. 1 is 0.
- Iterate till we reach the destination or our queue is empty.
- In each iteration, we pop the front cellNumber having the minimum Dice Throw and try to update cells which are reachable from that cell at the cost of 1 dice throw.
- The cels which can be reached at 1 dice throw are:
- cellNumber + 1
- cellNumber + 2
- cellNumber + 3
- cellNumber + 4
- cellNumber + 5
- cellNumber + 6
- Now, if these cells contain any Snake or Ladder than change the nextCell to the end of the Snake or Ladder.
- If the updating minDiceThrow[] value of nextCell is more than prior minDiceThrow[] value then we update the minDiceThrow Array and push the nextCellNumber in our queue.
- Finally if minDiceThrow[N*N] = maximum value (INT_MAX) then we can’t reach last cell of the board so return -1 else return minDiceThrow[N*N].
- Also, take care of going out of bounds i.e. cellNumber more than N*N.
- The logic for getting row number and column no. from cellNumber is based on extracting the rowNumber by dividing cellNumber by N and for column no. taking mod of cellNumber by N. Also take care of alternating direction according to rowNumber.
Time Complexity
O(N ^ 2), where 'N' is the number of rows and number of columns in the board.
At max, we can push and pop each cell in our queue moreover each push or pop operation takes O(1) time. There are total N*N cells so, the overall complexity will be O(N ^ 2).
Space Complexity
O(N ^ 2), where 'N' is the number of rows and number of columns in the board.
We are using a minDiceThrow array of size N*N to store the minimum no. of dice throw required to reach each cell so, Overall Space Complexity is O(N ^ 2).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Snake and Ladder
Interview problems
C++ easy BFS solution
278 views
0 replies
2 upvotes
Interview problems
JAVA | fixed test cases after feedback
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Solution {
public static int[] findCoordinates(int cellNo,int n){
int row = n - (cellNo - 1)/n -1;
int col = (cellNo - 1)%n;
if(row%2 == n%2){
col = n - 1 - col ;
return new int[]{row,col};
}else{
return new int[]{row,col};
}
}
public static int minDiceThrowToLastCell(int[][] board) {
int n = board.length;
boolean vis[][] = new boolean[n][n];
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(1);
int steps = 0;
vis[n-1][0] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int size = q.size();
for(int i = 0;i<size;i++){
int currNode = q.poll();
// check for end
if(currNode == n*n) return steps;
for(int k = 1;k<=6;k++){
if(k+currNode>n*n) break;
int pos[] = findCoordinates(k+currNode,n);
int row = pos[0];
int col = pos[1];
if(vis[row][col] == true) continue;
vis[row][col] = true;
if(board[row][col] == -1){
q.add(k + currNode);
}else{
q.add(board[row][col]);
}
}
}
// check for all possible moves with dice.
steps++;
}
return -1;
}
} 138 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
python solution
def find_coordinates(curr, n):
r = n - (curr - 1) // n - 1
c = (curr - 1) % n
if r % 2 == n % 2:
return [r, n - 1 - c]
else:
return [r, c]
def minDiceThrowToLastCell(board, n):
steps = 0
q = [1]
visited = [[False for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]
visited[n - 1][0] = True
while q:
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
x = q.pop(0)
if x == n * n:
return steps
for k in range(1, 7):
if k + x > n * n:
break
pos = find_coordinates(k + x, n)
r, c = pos[0], pos[1]
if visited[r][c]:
continue
visited[r][c] = True
if board[r][c] == -1:
q.append(k + x)
else:
q.append(board[r][c])
steps += 1
return -1
111 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
C++ Solution
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
int minDiceThrowToLastCell(int **board, int n)
{
map<int, int> mp;
bool ltr = true;
int k = 1;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (ltr) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++, k++) {
if (board[i][j] != -1)
mp[k] = board[i][j];
}
} else {
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--, k++) {
if (board[i][j] != -1)
mp[k] = board[i][j];
}
}
ltr = !ltr;
}
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({1, 0});
vector<int> vis(n * n + 1);
vis[1] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
int sq = p.first, steps = p.second;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
int newSq = sq + i;
if (mp.count(newSq))
newSq = mp[newSq];
if(newSq > n *n)
break;
if (newSq == n * n)
return steps + 1;
if (!vis[newSq]) {
vis[newSq] = 1;
q.push({newSq, steps + 1});
}
}
}
return -1;
} 458 views
0 replies
1 upvote
Interview problems
C++ Easy solution
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int minDiceThrowToLastCell(int **board, int n)
{
// Write your code here
int val = n*n;
vector<pair<int,int>> cells(val+1);
int label =1;
vector<int> columns(n);
iota(columns.begin(), columns.end(),0);
for(int row=n-1; row>=0;row--){
for(int column: columns){
cells[label++] = {row,column};
}
reverse(columns.begin(),columns.end());
}
vector<int> dist(val+1,-1);
queue<int> q;
dist[1] =0;
q.push(1);
while(!q.empty()){
int curr = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int next=curr+1;next<=min(curr+6,val);next++){
int row = cells[next].first,column = cells[next].second;
int dest = board[row][column] != -1 ? board[row][column] : next;
if(dist[dest] == -1){
dist[dest] = dist[curr] +1;
q.push(dest);
}
}
}
return dist[val];
}
187 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Easy C++ Solution
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
vector<int> findCoordinates(int curr, int n){
int r = n-(curr-1)/n - 1;
int c = (curr - 1) % n;
if(r%2 == n%2){
return vector<int>{r,n-1-c};
}
else{
return vector<int>{r,c};
}
}
int minDiceThrowToLastCell(int **board, int n)
{
// Write your code here
// int n = board.size();
int steps = 0;
queue<int> q;
bool visited[n][n];
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
q.push(1);
visited[n-1][0] = true;
while(!q.empty()){
int size = q.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
if(x == n*n) return steps;
for(int k=1; k<=6; k++){
if(k+x > n*n) break;
vector<int> pos = findCoordinates(k+x,n);
int r = pos[0];
int c = pos[1];
if(visited[r][c] == true) continue;
visited[r][c] = true;
if(board[r][c] == -1){
q.push(k+x);
}
else{
q.push(board[r][c]);
}
}
}
steps++;
}
return -1;
} 295 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
Discussion thread on Interview Problem | Snake and Ladder
Hey everyone, creating this thread to discuss the interview problem - Snake and Ladder.
Practise this interview question on Coding Ninjas Studio (hyperlinked with the following link): Snake and Ladder
322 views
4 replies
0 upvotes
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console

